Magnetic Field Lines
... When many of these orbits are aligned, so are the micro-magnetic fields, creating a larger overall magnetic field around the entire substance. Some substances are temporary magnets because the electron structure of its atoms is not protected from disturbances and the orbits are eventually randomly o ...
... When many of these orbits are aligned, so are the micro-magnetic fields, creating a larger overall magnetic field around the entire substance. Some substances are temporary magnets because the electron structure of its atoms is not protected from disturbances and the orbits are eventually randomly o ...
Earth`s interio
... • P-wave shadow zone • S-wave shadow zone • Outer Core- liquid • Inner Core- solid • believed to be mostly iron – with some nickel – Overall Density of earth = 5.5 • Crust 2.7-3.0 • Upper Mantle 3.3 • Mantle is 85% of volume of earth • Fe at core boundary around 10.0 • at center is around 13.0 – Evi ...
... • P-wave shadow zone • S-wave shadow zone • Outer Core- liquid • Inner Core- solid • believed to be mostly iron – with some nickel – Overall Density of earth = 5.5 • Crust 2.7-3.0 • Upper Mantle 3.3 • Mantle is 85% of volume of earth • Fe at core boundary around 10.0 • at center is around 13.0 – Evi ...
Magnetic Fields
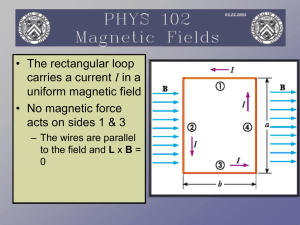
... • The torque has a maximum value when the field is perpendicular to the normal to the plane of the loop • The torque is zero when the field is parallel to the normal to the plane of the loop • τ = IA x B where A is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and has a magnitude equal to the area of the ...
... • The torque has a maximum value when the field is perpendicular to the normal to the plane of the loop • The torque is zero when the field is parallel to the normal to the plane of the loop • τ = IA x B where A is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and has a magnitude equal to the area of the ...
Magnets- a body having the property of attracting iron and
... Ørsted made a surprising observation. As he was setting up his materials, he noticed a compass needle deflected from magnetic north when the electric current from the battery he was using was switched on and off. This deflection convinced him that magnetic fields radiate from all sides off of a wire ...
... Ørsted made a surprising observation. As he was setting up his materials, he noticed a compass needle deflected from magnetic north when the electric current from the battery he was using was switched on and off. This deflection convinced him that magnetic fields radiate from all sides off of a wire ...
Toward Understanding the Sun`s Magnetic Field Topologies
... For the internetwork fields F = 1 1017 Mx, B = 50-200 gauss, R = 108 cm, and T =3600 seconds, which yields ED (internetwork) = 2-7.0 105 ergs/cm2/sec. For the granulation scale fields F = 5 1016 Mx, B = 1200 gauss, R = 5 107 cm, and T =300 seconds, which yields an energy dissipation rate of ED (gran ...
... For the internetwork fields F = 1 1017 Mx, B = 50-200 gauss, R = 108 cm, and T =3600 seconds, which yields ED (internetwork) = 2-7.0 105 ergs/cm2/sec. For the granulation scale fields F = 5 1016 Mx, B = 1200 gauss, R = 5 107 cm, and T =300 seconds, which yields an energy dissipation rate of ED (gran ...
Magnetic Fields and Oersted`s Principle
... The discovery of magnets is attributed in legend to Magnes, a shepherd who lived in the area of Magnesia, Greece, over 4000 years ago. He was surprised one day when he stepped on a rock and the iron nails in his sandals stuck to it. This type of rock came to be known as magnetite. Basic Properties o ...
... The discovery of magnets is attributed in legend to Magnes, a shepherd who lived in the area of Magnesia, Greece, over 4000 years ago. He was surprised one day when he stepped on a rock and the iron nails in his sandals stuck to it. This type of rock came to be known as magnetite. Basic Properties o ...
Magnetism - District 196
... Similar, yet DIFFERENT than electric charges. Similarities 1. Can attract and repel without touching 2. The amount of attracting or repelling depends on distance 3. Like poles repel, opposite poles attract. Difference Magnetic poles can NOT be separated. They always occur in pairs. ...
... Similar, yet DIFFERENT than electric charges. Similarities 1. Can attract and repel without touching 2. The amount of attracting or repelling depends on distance 3. Like poles repel, opposite poles attract. Difference Magnetic poles can NOT be separated. They always occur in pairs. ...
3-8 electricity1 - Worth County Schools
... near the geographic north pole is sometimes called the geomagnetic north pole. ...
... near the geographic north pole is sometimes called the geomagnetic north pole. ...
Teacher Notes PDF
... audio and video tapes, and credit cards. Storing magnets near compasses may result in permanent damage to the compasses. 7. Readings may fluctuate due to deviation, the influence of the immediate environment upon your sensor, caused by things such as electrical currents, computer monitors, or metal ...
... audio and video tapes, and credit cards. Storing magnets near compasses may result in permanent damage to the compasses. 7. Readings may fluctuate due to deviation, the influence of the immediate environment upon your sensor, caused by things such as electrical currents, computer monitors, or metal ...
Magnetic Domains
... note that the color red refers to North and white refers to South. Place the compass near the North end of the magnet and observe which way the “red tip” of the compass points. Move the compass to the South end and observe where the “red tip” of the compass points. a. What conclusions can you draw a ...
... note that the color red refers to North and white refers to South. Place the compass near the North end of the magnet and observe which way the “red tip” of the compass points. Move the compass to the South end and observe where the “red tip” of the compass points. a. What conclusions can you draw a ...
magnetic line of force
... 1. The magnetic lines of force start from the North Pole of a magnet and end at its South Pole. 2. The magnetic lines of force come closer near the poles of a magnet but they are widely separated at other places. 3. The magnetic lines of force do not cross one another. 4. When a magnetic compass is ...
... 1. The magnetic lines of force start from the North Pole of a magnet and end at its South Pole. 2. The magnetic lines of force come closer near the poles of a magnet but they are widely separated at other places. 3. The magnetic lines of force do not cross one another. 4. When a magnetic compass is ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.