magnetic - Timber Ridge Elementary
... Earth acts like a giant magnet and is surrounded by a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to point either North or South. ...
... Earth acts like a giant magnet and is surrounded by a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to point either North or South. ...
What creates an electric current
... A parallel circuit has two or more pathways for the electrical current to run through. ...
... A parallel circuit has two or more pathways for the electrical current to run through. ...
2016 Farada review sheet[1][1]
... how to calculate it for a solenoid <30,40> Be able to solve for current as a function of time for both “charging” and ...
... how to calculate it for a solenoid <30,40> Be able to solve for current as a function of time for both “charging” and ...
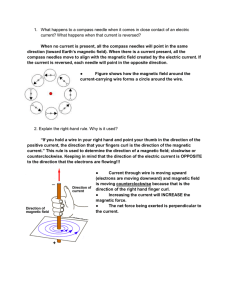
When no current is present, all the compass
... 3. Why is a solenoid used to create a stronger magnetic field? What does it resemble? To increase the magnetic force from the presence of a current, without increasing the current (because that is often dangerous), you can wrap a wire into a coil. This is called a solenoid and it is MUCH safer. By ...
... 3. Why is a solenoid used to create a stronger magnetic field? What does it resemble? To increase the magnetic force from the presence of a current, without increasing the current (because that is often dangerous), you can wrap a wire into a coil. This is called a solenoid and it is MUCH safer. By ...
41B Magnetic Fields of Force - Merrillville Community School
... Part B: Magnetic Fields 13. Place one magnet on the tabletop and place the magnetic field visualizer directly above, but not quite touching, the magnet. Gently shake the magnetic field visualizer so that the iron filings spread out evenly. Sketch the appearance of the filings. ...
... Part B: Magnetic Fields 13. Place one magnet on the tabletop and place the magnetic field visualizer directly above, but not quite touching, the magnet. Gently shake the magnetic field visualizer so that the iron filings spread out evenly. Sketch the appearance of the filings. ...
Magnets and Electromagnets
... Earth’s magnetic north pole is not the same as Earth’s axis north pole. It is about 1250 km (776 miles) away from the true north pole The angle between true north and magnetic north is the magnetic declination. ...
... Earth’s magnetic north pole is not the same as Earth’s axis north pole. It is about 1250 km (776 miles) away from the true north pole The angle between true north and magnetic north is the magnetic declination. ...
Magnetism Activity Write-up
... Describe the science: Magnetic poles that are alike repel each other and magnetic poles that are unlike attract each other. Magnetic field lines spread out from one pole, curve around a magnet and return to the other pole. In a magnetized material, all or most of the domains are arranged in the same ...
... Describe the science: Magnetic poles that are alike repel each other and magnetic poles that are unlike attract each other. Magnetic field lines spread out from one pole, curve around a magnet and return to the other pole. In a magnetized material, all or most of the domains are arranged in the same ...
Magnets - kdavis10
... • The North and South seeking poles of magnets have been helpful to people for hundreds of years. ...
... • The North and South seeking poles of magnets have been helpful to people for hundreds of years. ...
Evidence Sheet 2 Locations of past glaciers
... dipole, but the north and south magnetic directions are switched. The most recent magnetic reversal happened 780,000 years ago. In the ancient past, before humans existed, your compass could have pointed at the South pole! Geologists made a timeline of these reversals (normal-reverse-normal-reverse… ...
... dipole, but the north and south magnetic directions are switched. The most recent magnetic reversal happened 780,000 years ago. In the ancient past, before humans existed, your compass could have pointed at the South pole! Geologists made a timeline of these reversals (normal-reverse-normal-reverse… ...
THE HALF-FILLED LANDAU LEVEL: THE CASE FOR
... In a two-dimensional electron gas under a strong magnetic field, correlations generate emergent excitations fundamentally distinct from electrons. Halperin, Lee and Read predicted that composite fermions bound states of an electron with two magnetic flux quanta can experience zero net magnetic field ...
... In a two-dimensional electron gas under a strong magnetic field, correlations generate emergent excitations fundamentally distinct from electrons. Halperin, Lee and Read predicted that composite fermions bound states of an electron with two magnetic flux quanta can experience zero net magnetic field ...
magnetism ppt
... • Early magnets called lodestones, naturally occurring iron ore magnetite • Named magnets by Greeks since they were found in the region Magnesia • Important for early navigation • Coulomb showed magnetic force has similar relationship to electric and gravitational forces ...
... • Early magnets called lodestones, naturally occurring iron ore magnetite • Named magnets by Greeks since they were found in the region Magnesia • Important for early navigation • Coulomb showed magnetic force has similar relationship to electric and gravitational forces ...
Discussion 10
... energy from one circuit to another through magnetic coupling. A changing current in the first coil (the primary ) creates a changing magnetic field; in turn, this magnetic field induces a changing voltage in the second coil (the secondary). Discussion: - The secondary induced voltage V2 is scaled fr ...
... energy from one circuit to another through magnetic coupling. A changing current in the first coil (the primary ) creates a changing magnetic field; in turn, this magnetic field induces a changing voltage in the second coil (the secondary). Discussion: - The secondary induced voltage V2 is scaled fr ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
![2016 Farada review sheet[1][1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001271395_1-fc9c1a7e3076b57ba2cfadfbf9c2de3d-300x300.png)