Chapter 15 - Cloudfront.net
... Ordinarily – the charges are in equal balance and the atom is said to be “neutral.” If an atom loses an electron or gains an electron, it is “charged”.. Too many electrons? It is negatively charged. Too many protons? It is positively charged. ...
... Ordinarily – the charges are in equal balance and the atom is said to be “neutral.” If an atom loses an electron or gains an electron, it is “charged”.. Too many electrons? It is negatively charged. Too many protons? It is positively charged. ...
english guide
... and energy. Matter is easy to categorize. We use the properties of matter to organize it. We can use tools such as a balance scale to measure mass. We can also use a tool such as a graduated cylinder to measure volume. The volume of a solid object may be measured using a graduated cylinder and water ...
... and energy. Matter is easy to categorize. We use the properties of matter to organize it. We can use tools such as a balance scale to measure mass. We can also use a tool such as a graduated cylinder to measure volume. The volume of a solid object may be measured using a graduated cylinder and water ...
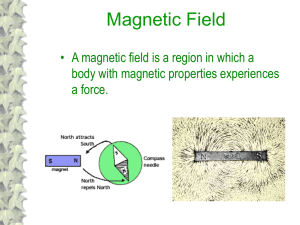
1 Magnetism 2 Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force
... National High Magnetic Field Laboratory Mathematica Demonstrations: A Simple Model of Magnetization Mathematica Demonstrations: Magnetic Field of a Bar Magnet Mathematica Demonstrations: Magnetic Field of a Current Loop Mathematica Demonstrations: The earth’s Magnetosphere ...
... National High Magnetic Field Laboratory Mathematica Demonstrations: A Simple Model of Magnetization Mathematica Demonstrations: Magnetic Field of a Bar Magnet Mathematica Demonstrations: Magnetic Field of a Current Loop Mathematica Demonstrations: The earth’s Magnetosphere ...
Lecture 23 ppt
... Also not completely understood. Maybe thermal energy from core giving convection currents. ...
... Also not completely understood. Maybe thermal energy from core giving convection currents. ...
Sources of Magnetic Field
... to come from a giant bar magnet, but with its south pole located up near the Earth's north pole. ...
... to come from a giant bar magnet, but with its south pole located up near the Earth's north pole. ...
18.3 - Faculty Perry, Oklahoma
... transform boundary occurs where tectonic plates scrape past each other rift valley a gap formed between two diverging plates magnetic reversal when Earth’s magnetic north and south poles switch places hot spot an area of volcanic activity that develops above a plume in the mantle ...
... transform boundary occurs where tectonic plates scrape past each other rift valley a gap formed between two diverging plates magnetic reversal when Earth’s magnetic north and south poles switch places hot spot an area of volcanic activity that develops above a plume in the mantle ...
Chapter_1_Section1
... Seismic Waves – the indirect evidence geologists use to study Earth's interior; created when earthquakes occur ...
... Seismic Waves – the indirect evidence geologists use to study Earth's interior; created when earthquakes occur ...
magnet
... attracts North." Of course, this is NOT true. The magnetic pole near the north geographic pole is ACTUALLY A SOUTH MAGNETIC POLE. Common usage has named this "the North Pole" - just remember that MAGNETICALLY it's a SOUTH pole. ...
... attracts North." Of course, this is NOT true. The magnetic pole near the north geographic pole is ACTUALLY A SOUTH MAGNETIC POLE. Common usage has named this "the North Pole" - just remember that MAGNETICALLY it's a SOUTH pole. ...
Magnetism
... magnets by bringing them close to a magnet; magnetism is induced by aligning areas called domains within a magnetic field Domains strong coupling between neighboring atoms of ferromagnetic materials to form large groups of atoms whose net spins are aligned Unmagnetized substance domains randomly ...
... magnets by bringing them close to a magnet; magnetism is induced by aligning areas called domains within a magnetic field Domains strong coupling between neighboring atoms of ferromagnetic materials to form large groups of atoms whose net spins are aligned Unmagnetized substance domains randomly ...
Magnetic Field and High-Voltage Power Lines
... I already checked the Hydro-Québec website about the health effects of the magnetic fields generated by their network, and there seems to be no danger, but I would like to hear the opinion of an disinterested party. I thought I would call on your expertise, as I understand that you are studying the ...
... I already checked the Hydro-Québec website about the health effects of the magnetic fields generated by their network, and there seems to be no danger, but I would like to hear the opinion of an disinterested party. I thought I would call on your expertise, as I understand that you are studying the ...
74. Leakage field of the transformer
... the integration path. (n is the number of windings, the indices refer to the primary and secondary windings, respectively.) Now, the magnetic field strength H inside the iron core is smaller than outside by the factor μ. Since typical values of μ are greater than 1000, the contribution of the path i ...
... the integration path. (n is the number of windings, the indices refer to the primary and secondary windings, respectively.) Now, the magnetic field strength H inside the iron core is smaller than outside by the factor μ. Since typical values of μ are greater than 1000, the contribution of the path i ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.