Unit 3earthmoon part 1
... Some high-energy particles leak through the magnetic field and produce a belt of high-energy particles around Earth: Van Allen belts ...
... Some high-energy particles leak through the magnetic field and produce a belt of high-energy particles around Earth: Van Allen belts ...
magnetism
... the case of steady currents) describe the origin and behavior of the fields that govern these forces. Therefore magnetism is seen whenever electrically charged particles are in motion---for example, from movement of electrons in an electric current, or in certain cases from the orbital motion of ele ...
... the case of steady currents) describe the origin and behavior of the fields that govern these forces. Therefore magnetism is seen whenever electrically charged particles are in motion---for example, from movement of electrons in an electric current, or in certain cases from the orbital motion of ele ...
Heat Capacity Studies of NdNi4Si Compound
... reveals a peak close to the magnetic ordering temperature. This is typical of ferromagnets because larger fields cause a strong magnetization already well above the zero field TC and the magnetization does not develop spontaneously below a critical temperature anymore. The maximum is shifting to hig ...
... reveals a peak close to the magnetic ordering temperature. This is typical of ferromagnets because larger fields cause a strong magnetization already well above the zero field TC and the magnetization does not develop spontaneously below a critical temperature anymore. The maximum is shifting to hig ...
Magnetic field Conductor
... Fleming's right hand rule Right hand rule: If the first finger of the right hand is pointed in the direction of the magnetic flux, and if the thumb is pointed in the direction of motion of the conductor relative to the magnetic field, then the second finger, held at right angles to both the thumb a ...
... Fleming's right hand rule Right hand rule: If the first finger of the right hand is pointed in the direction of the magnetic flux, and if the thumb is pointed in the direction of motion of the conductor relative to the magnetic field, then the second finger, held at right angles to both the thumb a ...
Theme 2: The story of Magnets
... magnetic poles repel each other whereas unlike poles attract each other. Remember the force when you held two magnets close and felt them either attract (pull toward one another) or repel (push away)? One of the most amazing things about magnets is the way they can attract other magnets (or other ma ...
... magnetic poles repel each other whereas unlike poles attract each other. Remember the force when you held two magnets close and felt them either attract (pull toward one another) or repel (push away)? One of the most amazing things about magnets is the way they can attract other magnets (or other ma ...
Magnetism Free Response HW 1. A student performs an experiment
... A student performs an experiment to measure the magnetic field along the axis of the long, 100 turn solenoid PQ shown above. She connects ends P and Q of the solenoid to a variable power supply and an ammeter as shown. End P of the solenoid is taped at the 0 cm mark of a meterstick. The solenoid can ...
... A student performs an experiment to measure the magnetic field along the axis of the long, 100 turn solenoid PQ shown above. She connects ends P and Q of the solenoid to a variable power supply and an ammeter as shown. End P of the solenoid is taped at the 0 cm mark of a meterstick. The solenoid can ...
Faraday`s Law
... loop, a current is induced in the direction shown. The magnetic field lines shown are those due to the bar magnet. (b) This induced current produces its own magnetic field directed to the left that counteracts the increasing external flux. The magnetic field lines shown are those due to the induced ...
... loop, a current is induced in the direction shown. The magnetic field lines shown are those due to the bar magnet. (b) This induced current produces its own magnetic field directed to the left that counteracts the increasing external flux. The magnetic field lines shown are those due to the induced ...
esga3092 - 4J Blog Server
... The Process of Sea-Floor Spreading 4. Circle the letter of the description of a subduction zone. a. where an oceanic plate is forced beneath a second plate b. where an oceanic plate grinds past a second plate c. where a continental plate grinds past a second plate d. where an oceanic plate moves awa ...
... The Process of Sea-Floor Spreading 4. Circle the letter of the description of a subduction zone. a. where an oceanic plate is forced beneath a second plate b. where an oceanic plate grinds past a second plate c. where a continental plate grinds past a second plate d. where an oceanic plate moves awa ...
Full Chapter
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
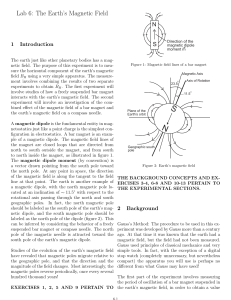
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.