Nome del paese - European Shared Treasure
... Vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid's evaporation rate. It relates to the tendency of molecules and atoms to escape from a liquid or a solid. A substance with a high vapor pressure at normal temperatures is often referred to as volatile. The higher the vapor pressure of a material at a given ...
... Vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid's evaporation rate. It relates to the tendency of molecules and atoms to escape from a liquid or a solid. A substance with a high vapor pressure at normal temperatures is often referred to as volatile. The higher the vapor pressure of a material at a given ...
Tyler Levy notes - Mark W. Williams, Ph.D
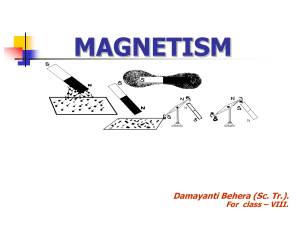
... o The magnetic field causes the northern lights Origin of the Magnetic Field o Magnetic fields are produced by the motion of electrical charges. For example, the magnetic field of a bar magnet results from the motion of negatively charged electrons in the magnet. o The origin of the Earth's magnetic ...
... o The magnetic field causes the northern lights Origin of the Magnetic Field o Magnetic fields are produced by the motion of electrical charges. For example, the magnetic field of a bar magnet results from the motion of negatively charged electrons in the magnet. o The origin of the Earth's magnetic ...
Measurement of magnetic moments of free BiNMnM clusters
... exclusively determined by the value of M in that case. In this context note that Bi/ Co is an immiscible system so that a BiNCoM cluster is probably segregated and hence the total magnetic moment is mainly due to the Co component. In contrast, Bi/ Mn forms an alloy, so that it is likely that in a Bi ...
... exclusively determined by the value of M in that case. In this context note that Bi/ Co is an immiscible system so that a BiNCoM cluster is probably segregated and hence the total magnetic moment is mainly due to the Co component. In contrast, Bi/ Mn forms an alloy, so that it is likely that in a Bi ...
7-2 Summary
... • New ocean crust forms along midocean ridges. • Mid-ocean ridges are large mountain ranges that extend throughout Earth’s oceans. ...
... • New ocean crust forms along midocean ridges. • Mid-ocean ridges are large mountain ranges that extend throughout Earth’s oceans. ...
Nuclear Magnetism and NMR Spectroscopy
... • The energy E of a spin is the product of the z-component of the magnetic moment µz and the magnetic field B. • µz = γ Iz = γ m ħ • E = - γ m ħ B. ...
... • The energy E of a spin is the product of the z-component of the magnetic moment µz and the magnetic field B. • µz = γ Iz = γ m ħ • E = - γ m ħ B. ...
Plate Tectonics Internet Scavenger Hunt - wikifuller
... 14. How long ago was Africa and South America positioned side by side? ...
... 14. How long ago was Africa and South America positioned side by side? ...
MRI Anaesthesia talk
... rapid and precise adjustments to their field strength and direction. Typical gradient systems are capable of producing gradients from 20 mT/m to 100 mT/m (i.e. in a 1.5 T magnet, when a maximal z-axis gradient is applied the field strength may be 1.45 T at one end of a 1m long bore, and 1.55 T at th ...
... rapid and precise adjustments to their field strength and direction. Typical gradient systems are capable of producing gradients from 20 mT/m to 100 mT/m (i.e. in a 1.5 T magnet, when a maximal z-axis gradient is applied the field strength may be 1.45 T at one end of a 1m long bore, and 1.55 T at th ...
CGG Vol. 32 No. 2
... properties, magnetic mineralogy and the reproducible self-reversal RM of the Neogene andesites from the Javorie and Poľana mountain range (Part III) Orlický O.: Field-reversal versus self-reversal hypothesis: Paleomagnetic properties, magnetic mineralogy and the reproducible self - reversal RM of th ...
... properties, magnetic mineralogy and the reproducible self-reversal RM of the Neogene andesites from the Javorie and Poľana mountain range (Part III) Orlický O.: Field-reversal versus self-reversal hypothesis: Paleomagnetic properties, magnetic mineralogy and the reproducible self - reversal RM of th ...
magnetic energy acumulation in the coronal current sheet
... flare appearance. In [10] it is noted that a big flare occurs over the photospheric field configuration resembling the fractal development. It is shown in [6-9] that a flare occurs over AR with a complicated distribution of the magnetic field, when a singular magnetic field line of type X appears in ...
... flare appearance. In [10] it is noted that a big flare occurs over the photospheric field configuration resembling the fractal development. It is shown in [6-9] that a flare occurs over AR with a complicated distribution of the magnetic field, when a singular magnetic field line of type X appears in ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.