Lesson 2 - Electromagnetism
... Straight line conductors When electricity flows through a wire (straight line conductor) an ...
... Straight line conductors When electricity flows through a wire (straight line conductor) an ...
docx: Geo Magnetic Journal
... 9. What analogy can you make between the magnet you created and the Earth’s magnetic field? In other words, draw connections between features of your magnet and the features of the Earth’s magnetic field. ...
... 9. What analogy can you make between the magnet you created and the Earth’s magnetic field? In other words, draw connections between features of your magnet and the features of the Earth’s magnetic field. ...
Plate Tectonics - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
Plate Tectonics - Chapter Review Part 1
... 6. The process of _________________________ continually adds new crust to the ocean floor along both sides of the mid-ocean ridge. ...
... 6. The process of _________________________ continually adds new crust to the ocean floor along both sides of the mid-ocean ridge. ...
Superconductivity is the capacity that certain materials attain, when
... Superconductivity is the capacity that certain materials attain, when they are sufficiently cooled, to allow electric current to pass through without resistance. One of its properties is magnetic levitation. The discovery of this phenomenon, in 1911, opened up a vast field of research into material ...
... Superconductivity is the capacity that certain materials attain, when they are sufficiently cooled, to allow electric current to pass through without resistance. One of its properties is magnetic levitation. The discovery of this phenomenon, in 1911, opened up a vast field of research into material ...
32.28. Model: A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charge
... 32.28. Model: A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charge. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex32.28. Solve: (a) The force on a charge moving in a magnetic field is r r r Fon q = qv × B = (qvBsinα, direction of right-hand rule) The direction of the force on a negative charge is opposite the d ...
... 32.28. Model: A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charge. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex32.28. Solve: (a) The force on a charge moving in a magnetic field is r r r Fon q = qv × B = (qvBsinα, direction of right-hand rule) The direction of the force on a negative charge is opposite the d ...
Magnetism Conceptual Questions
... 1. Much like the static Electric force, there is a magnetic force between 2 magnets. How are the magnetic and electric forces similar? How are they different. 2. electricity has positive and negative charges. What does a magnet have and how are they similar/different than electric charges? ...
... 1. Much like the static Electric force, there is a magnetic force between 2 magnets. How are the magnetic and electric forces similar? How are they different. 2. electricity has positive and negative charges. What does a magnet have and how are they similar/different than electric charges? ...
EARTH`S MAGNETIC FIELD
... Earth is largely protected from the solar wind, a stream of energetic charged particles emanating from the Sun, by its magnetic field, which deflects most of the charged particles. Some of the charged particles from the solar wind are trapped in the Van Allen radiation belt. A smaller number of par ...
... Earth is largely protected from the solar wind, a stream of energetic charged particles emanating from the Sun, by its magnetic field, which deflects most of the charged particles. Some of the charged particles from the solar wind are trapped in the Van Allen radiation belt. A smaller number of par ...
Vocabulary # 1
... Chromosphere- a layer of the sun that is ten times hotter than the photosphere Corona- a layer of a star that escapes the star’s gravity and extends millions of miles into space as solar wind Magnetic Field- a region around a magnetic material within which the force of magnetism acts Surface- the ou ...
... Chromosphere- a layer of the sun that is ten times hotter than the photosphere Corona- a layer of a star that escapes the star’s gravity and extends millions of miles into space as solar wind Magnetic Field- a region around a magnetic material within which the force of magnetism acts Surface- the ou ...
Effects of static magnetic field on solidification of alloys
... Effect of static magnetic field on solidification of alloys has been an interesting topic for a long time. Over recent two decades, the research in this field has achieved a lot progress. Here some important research works in this field are reviewed. Static magnetic field has been shown apparent inf ...
... Effect of static magnetic field on solidification of alloys has been an interesting topic for a long time. Over recent two decades, the research in this field has achieved a lot progress. Here some important research works in this field are reviewed. Static magnetic field has been shown apparent inf ...
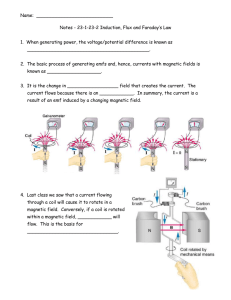
Name: Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday`s Law 1. When
... 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the change in __________________ field that creates the current. The current flows because there is an ____________. In summary, the current is a result of an emf induced by a ...
... 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the change in __________________ field that creates the current. The current flows because there is an ____________. In summary, the current is a result of an emf induced by a ...
Understand Ohm`s law in both microscopic
... Biot Savart Law: be able to use to calculate the magnetic field from simple current elements, e.g. the magnetic field at the center of a circle of radius R carrying current I. Magnetic dipole moment: what is it, how is it directed, what is its magnitude? Torque on a magnetic dipole τ m B . What ...
... Biot Savart Law: be able to use to calculate the magnetic field from simple current elements, e.g. the magnetic field at the center of a circle of radius R carrying current I. Magnetic dipole moment: what is it, how is it directed, what is its magnitude? Torque on a magnetic dipole τ m B . What ...
Week 2: Current and Intro to Circuits
... • Creates Aurora Borealis • Like to bar magnet • Why is North actually South? ...
... • Creates Aurora Borealis • Like to bar magnet • Why is North actually South? ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.