The total free energy of a magnetic substance
... For constant T and j, irreversible processes occur until is minimized. In equilibrium is a minimum with respect to changes in state occurring at constant T and j. ...
... For constant T and j, irreversible processes occur until is minimized. In equilibrium is a minimum with respect to changes in state occurring at constant T and j. ...
Chapter 1 Earth`s Magnetic Field
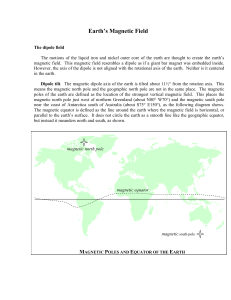
... Dipole offset. The magnetic dipole of the earth is not centered on the earth’s core, but instead is offset by about 700 kilometers towards the direction of southeastern Asia. This creates two features in the magnetic field at the earth’s surface. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The point on the e ...
... Dipole offset. The magnetic dipole of the earth is not centered on the earth’s core, but instead is offset by about 700 kilometers towards the direction of southeastern Asia. This creates two features in the magnetic field at the earth’s surface. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The point on the e ...
Circular Motion of a Charged Particle Moving in a Magnetic Field
... 5. A magnetic field is vertically upwards. Charge A moves vertically downwards in the region of this magnetic field. Charge B is stationary within this magnetic field. Which charge feels the greater force? Explain. 6. A charged particle enters a magnetic field directed out of the page, as shown belo ...
... 5. A magnetic field is vertically upwards. Charge A moves vertically downwards in the region of this magnetic field. Charge B is stationary within this magnetic field. Which charge feels the greater force? Explain. 6. A charged particle enters a magnetic field directed out of the page, as shown belo ...
Magnets and Electricity
... a North and South Pole? • If you answered The Earth you were right! • The Earth is one giant magnet. It has two magnetic poles and is surrounded by a magnetic field. • This magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to poin ...
... a North and South Pole? • If you answered The Earth you were right! • The Earth is one giant magnet. It has two magnetic poles and is surrounded by a magnetic field. • This magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to poin ...
Homework Set #3
... Partial credit may be given even if the final answer is incorrect so please show all work! Question 1 (1 point) What is Lenz’s Law, and to what conservation law is it related? Question 2 (3 points) A circular coil of wire with 350 turns and a radius of 7.5 cm is placed horizontally on a table. A uni ...
... Partial credit may be given even if the final answer is incorrect so please show all work! Question 1 (1 point) What is Lenz’s Law, and to what conservation law is it related? Question 2 (3 points) A circular coil of wire with 350 turns and a radius of 7.5 cm is placed horizontally on a table. A uni ...
Heat, Electricity, and Magnetism Vocabulary
... 10. Closed Circuit – A complete, unbroken circuit to allow electricity to flow through it. 11. Power Source – An object to power the electric current, such as a battery. 12. Energy Transfer – When energy flows from one object to another. 13. Conductor – Objects that transfer heat and electricity ver ...
... 10. Closed Circuit – A complete, unbroken circuit to allow electricity to flow through it. 11. Power Source – An object to power the electric current, such as a battery. 12. Energy Transfer – When energy flows from one object to another. 13. Conductor – Objects that transfer heat and electricity ver ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.