Magnetic Fields
... Magnetic Dipole Moment • The product IA is defined as the magnetic dipole moment, m, of the loop – Often called the magnetic moment ...
... Magnetic Dipole Moment • The product IA is defined as the magnetic dipole moment, m, of the loop – Often called the magnetic moment ...
Document
... stranded on the surface of Mars and must use a rocket, of mass 800 kg, to project himself into space in order to be rescued by a crew in orbiting Mars. Mars has a radius of 3.4 x 106 m and he must get to a height above the surface of 3.6 x 106 m in order to be rescued. ...
... stranded on the surface of Mars and must use a rocket, of mass 800 kg, to project himself into space in order to be rescued by a crew in orbiting Mars. Mars has a radius of 3.4 x 106 m and he must get to a height above the surface of 3.6 x 106 m in order to be rescued. ...
PHYSICS 571 – Master`s of Science Teaching “Electromagnetism
... by the rate of Bfield change within those loops amount of current produced by electromagnetic induction is dependent on ...
... by the rate of Bfield change within those loops amount of current produced by electromagnetic induction is dependent on ...
Applied Vibration Measurement, Analysis and Control Lab
... magnetic field around the coil. If an electrically conducting material is present within the range of this magnetic field, eddy currents will be generated within this surface and they will attenuate the oscillator circuit. This attenuation is converted into a gap proportional to the output signal by ...
... magnetic field around the coil. If an electrically conducting material is present within the range of this magnetic field, eddy currents will be generated within this surface and they will attenuate the oscillator circuit. This attenuation is converted into a gap proportional to the output signal by ...
magnetic line of force
... 2. The magnetic lines of force come closer near the poles of a magnet but they are widely separated at other places. 3. The magnetic lines of force do not cross one another. 4. When a magnetic compass is placed at different points on a magnetic line of force, it aligns itself along the tangent to th ...
... 2. The magnetic lines of force come closer near the poles of a magnet but they are widely separated at other places. 3. The magnetic lines of force do not cross one another. 4. When a magnetic compass is placed at different points on a magnetic line of force, it aligns itself along the tangent to th ...
Subject: Teacher Grade Level Length of Lesson
... electromagnets work without having (much) prior knowledge about either. In order for students to be successful in this activity as it is written, they will need to have a basic understanding of both electricity and magnetism. This lesson can be used to introduce electromagnetic force, and help stude ...
... electromagnets work without having (much) prior knowledge about either. In order for students to be successful in this activity as it is written, they will need to have a basic understanding of both electricity and magnetism. This lesson can be used to introduce electromagnetic force, and help stude ...
Chapter 7 Sec 1
... metallic, nonmetallic, and other recyclable materials. (Hint: Some of the materials are magnetic.) Accept all reasonable responses. Use a large magnet to remove all the magnetic materials, which are some of the metals. These can be separated further. Hand-sort or machine-sort the remaining materials ...
... metallic, nonmetallic, and other recyclable materials. (Hint: Some of the materials are magnetic.) Accept all reasonable responses. Use a large magnet to remove all the magnetic materials, which are some of the metals. These can be separated further. Hand-sort or machine-sort the remaining materials ...
magnetic field - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Magnetic North Pole is actually located in Northern Canada – about 1,250 kilometers (about 776 miles) from the geographic North Pole • Magnetic declination is the angle between the two lines – geographic north and magnetic north ...
... • Magnetic North Pole is actually located in Northern Canada – about 1,250 kilometers (about 776 miles) from the geographic North Pole • Magnetic declination is the angle between the two lines – geographic north and magnetic north ...
Layers of the Earth Unit 5 ES.7 The student will investigate and
... Continental crust makes up the land masses. This thicker, less dense material allows the continents to rise above sea ...
... Continental crust makes up the land masses. This thicker, less dense material allows the continents to rise above sea ...
Magnetism, electromagnetic induction, alternate - Biofizika
... Electric current creates a magnetic field (Ampere’s law) Every moving charge in general Every substance has its magnetic field Reverting the direction of the current the shift of the pointer is opposite ...
... Electric current creates a magnetic field (Ampere’s law) Every moving charge in general Every substance has its magnetic field Reverting the direction of the current the shift of the pointer is opposite ...
Estudio cristalogrfico de aleaciones nanomtricas de Fe-Cu-Ag
... nanostructures, fine ferromagnetic particles, granular giant magnetoresistance (GMR) materials, colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) manganates and frustrated pyrochlore oxides, and (ii) the nature of magnetic inhomogeneity basically decides the magnetic behaviour of a given system [1]. In this sense, w ...
... nanostructures, fine ferromagnetic particles, granular giant magnetoresistance (GMR) materials, colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) manganates and frustrated pyrochlore oxides, and (ii) the nature of magnetic inhomogeneity basically decides the magnetic behaviour of a given system [1]. In this sense, w ...
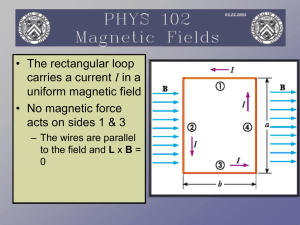
For a long straight wire B = ( ìo I )/ ( 2 ð r) ìo = 4 ð x 10-7
... Recall that we first used Coulomb’s Law to calculate the electric force. Then we used F = qE and found the value of E by using Gauss’ Law. As we saw in the last chapter with F = qvB, if the magnetic field is known then we can easily calculate the magnetic force. Ampere’s Law helps us to find the mag ...
... Recall that we first used Coulomb’s Law to calculate the electric force. Then we used F = qE and found the value of E by using Gauss’ Law. As we saw in the last chapter with F = qvB, if the magnetic field is known then we can easily calculate the magnetic force. Ampere’s Law helps us to find the mag ...
LAB: Magnetism
... 1. Tape the measuring tape or meter stick to the table, and tape the Magnetic Field Sensor to a convenient location. The sensor should be perpendicular to the stick, with the white spot inside the rod facing along the meter stick in the direction of increasing distance. Carefully measure the locatio ...
... 1. Tape the measuring tape or meter stick to the table, and tape the Magnetic Field Sensor to a convenient location. The sensor should be perpendicular to the stick, with the white spot inside the rod facing along the meter stick in the direction of increasing distance. Carefully measure the locatio ...
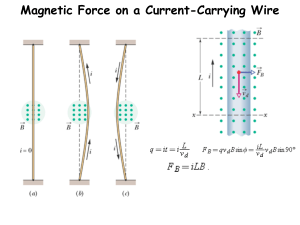
Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Wire - Easy Peasy All-in
... (a) If it is known that the external magnetic field is zero everywhere in this region, can you conclude that the external electric field is also zero? Explain. (b) If it is known that the external electric field is zero everywhere, can you conclude that the external magnetic field is also zero? Expl ...
... (a) If it is known that the external magnetic field is zero everywhere in this region, can you conclude that the external electric field is also zero? Explain. (b) If it is known that the external electric field is zero everywhere, can you conclude that the external magnetic field is also zero? Expl ...
ch29
... solenoid. The back portions of five turns are shown, as are the magnetic field lines due to a current through the solenoid. Each turn produces circular magnetic field lines near itself. Near the solenoid’s axis, the field lines combine into a net magnetic field that is directed along the axis. The c ...
... solenoid. The back portions of five turns are shown, as are the magnetic field lines due to a current through the solenoid. Each turn produces circular magnetic field lines near itself. Near the solenoid’s axis, the field lines combine into a net magnetic field that is directed along the axis. The c ...
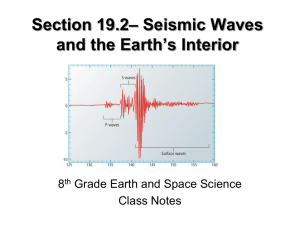
QR-6 Earthquakes and the Earth`s Interior Answer each of the
... 11. How much more energy does an earthquake measuring 7.0 on the Richter Scale release compared to an earthquake with a magnitude of 6.0. 12. Where does the greatest amount of seismic activity occur? 13. What type of plate boundary is associated with Earth’s largest earthquakes? 14. What is a tsunam ...
... 11. How much more energy does an earthquake measuring 7.0 on the Richter Scale release compared to an earthquake with a magnitude of 6.0. 12. Where does the greatest amount of seismic activity occur? 13. What type of plate boundary is associated with Earth’s largest earthquakes? 14. What is a tsunam ...
Document
... • Liquid OUTER CORE generates the magnetic field for the Earth • Earth’s magnetism is preserved in rocks • Iron minerals in the rocks line up and preserve the direction of the magnetic field ...
... • Liquid OUTER CORE generates the magnetic field for the Earth • Earth’s magnetism is preserved in rocks • Iron minerals in the rocks line up and preserve the direction of the magnetic field ...
Magnetotellurics

Magnetotellurics (MT) is an electromagnetic geophysical method for inferring the earth's subsurface electrical conductivity from measurements of natural geomagnetic and geoelectric field variation at the Earth's surface. Investigation depth ranges from 300m below ground by recording higher frequencies down to 10,000m or deeper with long-period soundings. Developed in the USSR and France during the 1950s, MT is now an international academic discipline and is used in exploration surveys around the world. Commercial uses include hydrocarbon (oil and gas) exploration, geothermal exploration, mining exploration, as well as hydrocarbon and groundwater monitoring. Research applications include experimentation to further develop the MT technique, long-period deep crustal exploration, and earthquake precursor prediction research.