Slide 1
... – A beam of - particles is scattered against gold sheet. – The intensity at different angles hints to structure of atoms. • WHY? – Investigate the internal structure of particles – To understand early methods of determining properties – Scattering (fixed target experiment) is a method to do particl ...
... – A beam of - particles is scattered against gold sheet. – The intensity at different angles hints to structure of atoms. • WHY? – Investigate the internal structure of particles – To understand early methods of determining properties – Scattering (fixed target experiment) is a method to do particl ...
Timeline of the development of the theory of plate tectonics
... 1968 The vessel Glomar Challenger set sail on an exploration of the mid-ocean ridge between South America and Africa. Core samples obtained from drilling revealed that rocks close to mid-ocean ridges are younger than rocks that are farther away from the ridges. 1968 Professor of Geophysics at the Un ...
... 1968 The vessel Glomar Challenger set sail on an exploration of the mid-ocean ridge between South America and Africa. Core samples obtained from drilling revealed that rocks close to mid-ocean ridges are younger than rocks that are farther away from the ridges. 1968 Professor of Geophysics at the Un ...
Electromagnets & magnetism
... A generator rotates a coil of wire through a magnetic field The changing magnetic field around the wire induces electric current in the wire The electric current produced by a generator changes direction each time the coil makes a ½ turn ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC) http://www.generatorguide.net/h ...
... A generator rotates a coil of wire through a magnetic field The changing magnetic field around the wire induces electric current in the wire The electric current produced by a generator changes direction each time the coil makes a ½ turn ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC) http://www.generatorguide.net/h ...
L 29 Electricity and Magnetism
... current. The current in B is only present when the current in A is changing. ...
... current. The current in B is only present when the current in A is changing. ...
Ass. prof. Ali_ H. Ibrahim - The Six International Conference of ESES
... physical factors such as magnetic fields on plants (TANVIR et al., 2012; BILALIS et al., 2013). The literature survey reveals that most studies have been concerned with the interactive effect of magnetic field and salinity stress on plants during the ...
... physical factors such as magnetic fields on plants (TANVIR et al., 2012; BILALIS et al., 2013). The literature survey reveals that most studies have been concerned with the interactive effect of magnetic field and salinity stress on plants during the ...
Where in the World was Lystrosaurus
... 6. Which diagram represents plate movement associated with transform faults such as those causing California earthquakes? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D ...
... 6. Which diagram represents plate movement associated with transform faults such as those causing California earthquakes? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D ...
Topic 6 - Blog.de
... Magnetism to Electricity • A magnet and a coil of wire can produce and electric current. – Watch demo- electric currentgenerating tube ...
... Magnetism to Electricity • A magnet and a coil of wire can produce and electric current. – Watch demo- electric currentgenerating tube ...
m L
... For atomic electrons, the relative orbital motion of the nucleus creates a magnetic field (for l 0). The electron spin can have ms = ±1/2 relative to the direction of the internal field, Bint. The state with ms aligned with Bint has a lower energy than ms anti-aligned (ms = spin magnetic dipole mo ...
... For atomic electrons, the relative orbital motion of the nucleus creates a magnetic field (for l 0). The electron spin can have ms = ±1/2 relative to the direction of the internal field, Bint. The state with ms aligned with Bint has a lower energy than ms anti-aligned (ms = spin magnetic dipole mo ...
STARS
... The presence of strong magnetic fields at the Sun’s surface can divert away hot blobs of gas convecting towards the surface This causes cool spots to form, 4,00 Kelvin as opposed to the normal temp of 6,000 Kelvin These cool regions appear as sunspots and are often wider than the Earth ...
... The presence of strong magnetic fields at the Sun’s surface can divert away hot blobs of gas convecting towards the surface This causes cool spots to form, 4,00 Kelvin as opposed to the normal temp of 6,000 Kelvin These cool regions appear as sunspots and are often wider than the Earth ...
The Dynamic Sun
... – mode mass increases toward low frequencies – mode compression decreases toward low frequencies ...
... – mode mass increases toward low frequencies – mode compression decreases toward low frequencies ...
PHYS 242 BLOCK 5 NOTES Sections 27.1 to 27.7, 27.9 Consider a
... υ is the object’s velocity (in s ) and B is the external magnetic field (in T = tesla, where 1 T = 1 A·m ). Cover up the solution and carefully work Example 27.1. Magnetic field lines: 1. They are used to visualize the magnetic field. ...
... υ is the object’s velocity (in s ) and B is the external magnetic field (in T = tesla, where 1 T = 1 A·m ). Cover up the solution and carefully work Example 27.1. Magnetic field lines: 1. They are used to visualize the magnetic field. ...
Interior Earth vocabulary.xlsx
... A hypothetical supercontinent that included all of the landmasses on Earth. It began breaking apart about 200 million years ago. A deep valley formed as tectonic plates move apart, such as along a mid-ocean ridge. ...
... A hypothetical supercontinent that included all of the landmasses on Earth. It began breaking apart about 200 million years ago. A deep valley formed as tectonic plates move apart, such as along a mid-ocean ridge. ...
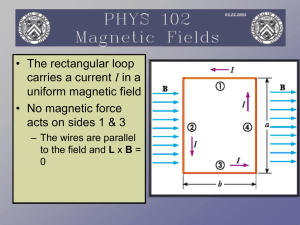
Magnetic Fields
... Magnetic Dipole Moment • The product IA is defined as the magnetic dipole moment, m, of the loop – Often called the magnetic moment ...
... Magnetic Dipole Moment • The product IA is defined as the magnetic dipole moment, m, of the loop – Often called the magnetic moment ...
Magnetotellurics

Magnetotellurics (MT) is an electromagnetic geophysical method for inferring the earth's subsurface electrical conductivity from measurements of natural geomagnetic and geoelectric field variation at the Earth's surface. Investigation depth ranges from 300m below ground by recording higher frequencies down to 10,000m or deeper with long-period soundings. Developed in the USSR and France during the 1950s, MT is now an international academic discipline and is used in exploration surveys around the world. Commercial uses include hydrocarbon (oil and gas) exploration, geothermal exploration, mining exploration, as well as hydrocarbon and groundwater monitoring. Research applications include experimentation to further develop the MT technique, long-period deep crustal exploration, and earthquake precursor prediction research.