36.1: The Nervous System
... • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle or gland. (effectors) • 3.Interneurons: connect sensory &motor neurons within the brain and spinal cord ...
... • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle or gland. (effectors) • 3.Interneurons: connect sensory &motor neurons within the brain and spinal cord ...
File - Perkins Science
... sheath of Schwann cells called the neurilemma. b. Schwann cells wrap also around the axon to form the myelin sheath. c. Gaps between Schwann cells, called nodes of Ranvier, are left open. d. Myelinated axons conduct impulses more rapidly. ...
... sheath of Schwann cells called the neurilemma. b. Schwann cells wrap also around the axon to form the myelin sheath. c. Gaps between Schwann cells, called nodes of Ranvier, are left open. d. Myelinated axons conduct impulses more rapidly. ...
Axon - Perkins Science
... Schwann cells called the neurilemma. b.Schwann cells wrap also around the axon to form the myelin sheath. c. Gaps between Schwann cells, called nodes of Ranvier, are left open. d.Myelinated axons conduct impulses more rapidly. ...
... Schwann cells called the neurilemma. b.Schwann cells wrap also around the axon to form the myelin sheath. c. Gaps between Schwann cells, called nodes of Ranvier, are left open. d.Myelinated axons conduct impulses more rapidly. ...
600 Kb PDF
... The goal of the Animat project is to create a neurallycontrolled artificial animal with which we can study learning in-vitro. This preliminary work has shown that it is possible to construct a system that can respond to and provide feedback in real-time to a living neural network. We do not yet know ...
... The goal of the Animat project is to create a neurallycontrolled artificial animal with which we can study learning in-vitro. This preliminary work has shown that it is possible to construct a system that can respond to and provide feedback in real-time to a living neural network. We do not yet know ...
1. 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter
... Roger Sperry received the Nobel Prize in physiology and medicine in 1981 for his experiments on split brain patients that provided strong evidence for lateralization of speech processing in the brain. Sperry's experiments showed, that the left hemisphere is responsible for the formation of speech wh ...
... Roger Sperry received the Nobel Prize in physiology and medicine in 1981 for his experiments on split brain patients that provided strong evidence for lateralization of speech processing in the brain. Sperry's experiments showed, that the left hemisphere is responsible for the formation of speech wh ...
The Review
... 6. What is the somatosensory cortex and primary motor cortex? 7. Who is Phineas Gage, what happen to him, what were the effects? 8. What parts make up the hindbrain? What is the function of each part? 9. What makes up the midbrain? What is the function? 10. What makes up the forebrain? What is the f ...
... 6. What is the somatosensory cortex and primary motor cortex? 7. Who is Phineas Gage, what happen to him, what were the effects? 8. What parts make up the hindbrain? What is the function of each part? 9. What makes up the midbrain? What is the function? 10. What makes up the forebrain? What is the f ...
Nervous Tissue
... – Sensory (afferent): message to CNS – Motor (efferent): message from CNS – Interneurons ...
... – Sensory (afferent): message to CNS – Motor (efferent): message from CNS – Interneurons ...
Recitation Worksheet 11
... 1. The gustatory system uses a labeled line model whereby each taste cell detects only one type of taste – for example, sweet is detected by taste cells that respond only to sweet, and each sweet taste cell is innervated only by neurons that carry sweet information. The olfactory system, however, us ...
... 1. The gustatory system uses a labeled line model whereby each taste cell detects only one type of taste – for example, sweet is detected by taste cells that respond only to sweet, and each sweet taste cell is innervated only by neurons that carry sweet information. The olfactory system, however, us ...
11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... neuron and an effector cell (p. 406; Fig. 11.16). B. Neurons conducting impulses toward the synapse are presynaptic cells, and neurons carrying impulses away from the synapse are postsynaptic cells (p. 406). C. Electrical synapses have neurons that are electrically coupled via protein channels and a ...
... neuron and an effector cell (p. 406; Fig. 11.16). B. Neurons conducting impulses toward the synapse are presynaptic cells, and neurons carrying impulses away from the synapse are postsynaptic cells (p. 406). C. Electrical synapses have neurons that are electrically coupled via protein channels and a ...
Ch 48: Nervous System – part 1
... transmit signals from one location to another made up of: many axons are enclosed by an insulating layer called the include: 2) GLIAL CELLS (“GLIA”) - SUPPORTING CELLS 10 to 50 times more numerous than neurons provide structure; protect, insulate, assist neurons example: ...
... transmit signals from one location to another made up of: many axons are enclosed by an insulating layer called the include: 2) GLIAL CELLS (“GLIA”) - SUPPORTING CELLS 10 to 50 times more numerous than neurons provide structure; protect, insulate, assist neurons example: ...
Parts of the Neuron 45
... The nervous system has three types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. These different types play specialized roles in the nervous system. Sensory neurons (also called afferent neurons) transmit information about the outside world to the spinal cord and brain. This informat ...
... The nervous system has three types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. These different types play specialized roles in the nervous system. Sensory neurons (also called afferent neurons) transmit information about the outside world to the spinal cord and brain. This informat ...
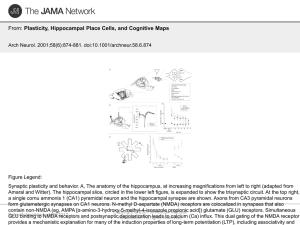
Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
... receptors and postsynapticAssociation. depolarization leads to calcium (Ca) influx. This dual gating of the NMDA receptor All rights reserved. provides a mechanistic explanation for many of the induction properties of long-term potentiation (LTP), including associativity and ...
... receptors and postsynapticAssociation. depolarization leads to calcium (Ca) influx. This dual gating of the NMDA receptor All rights reserved. provides a mechanistic explanation for many of the induction properties of long-term potentiation (LTP), including associativity and ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... Sympathetic v. Parasympathetic • Sympathetic = “Fight-orflight” response – Uses energy reserves to cope with stress or emergency – Adrenaline! ...
... Sympathetic v. Parasympathetic • Sympathetic = “Fight-orflight” response – Uses energy reserves to cope with stress or emergency – Adrenaline! ...
Blue Brain PPT
... • The simulation step involves synthesizing virtual cells using the algorithms that were found to describe real neurons. • Every single protein is simulated, and there are about a billion of these in one cell. First a network skeleton is built from all the different kinds of synthesized neurons. • T ...
... • The simulation step involves synthesizing virtual cells using the algorithms that were found to describe real neurons. • Every single protein is simulated, and there are about a billion of these in one cell. First a network skeleton is built from all the different kinds of synthesized neurons. • T ...
This Week in The Journal
... Michelle Brewer, Heather A. Cameron, and Leonardo Belluscio (see pages 13801–13810) Olfactory sensory neurons expressing the same odorant receptor converge onto two isofunctional columns in the olfactory bulb. Paired isofunctional columns are connected by tufted cell axons, which synapse on GABAergi ...
... Michelle Brewer, Heather A. Cameron, and Leonardo Belluscio (see pages 13801–13810) Olfactory sensory neurons expressing the same odorant receptor converge onto two isofunctional columns in the olfactory bulb. Paired isofunctional columns are connected by tufted cell axons, which synapse on GABAergi ...
neurons and the nervous system
... neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping ...
... neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an impulse is greatly increased by the message ‘jumping ...
Neuroanatomy
... down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
... down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
Slide 1
... down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
... down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
E.4.4 List three examples of excitatory and three examples of
... posterior lobe stores and releases hypothalamic hormones anterior lobe produces, stores, and secretes many hormones regulating many body functions ...
... posterior lobe stores and releases hypothalamic hormones anterior lobe produces, stores, and secretes many hormones regulating many body functions ...
L8_Nerve_tissue_and_organs
... • All neurons have a cell body (pericaryon) and processes, the axon and dendrites • Dendrites are neuronal processes that receive stimuli from other nerve cells or from the environment • Axons are neuronal processes that transmit stimuli to other neurons or to effector cells • There is only one axon ...
... • All neurons have a cell body (pericaryon) and processes, the axon and dendrites • Dendrites are neuronal processes that receive stimuli from other nerve cells or from the environment • Axons are neuronal processes that transmit stimuli to other neurons or to effector cells • There is only one axon ...
Organization of the Nervous System and the Neuron
... Nervous tissue is made up of two types of cellsSupporting and Neurons Supporting cells of the CNS are called Neuroglia or “nerve glue”. ...
... Nervous tissue is made up of two types of cellsSupporting and Neurons Supporting cells of the CNS are called Neuroglia or “nerve glue”. ...
Crossing the Synaptic Gap
... neurotransmitters, go from one neuron to the next. Point out that most neurons can receive messages from many other neurons. Some of these messages “stimulate” or cause firing, other messages “inhibit” or prevent firing. Neurons “decide” to fire or not depending on the kinds of messages they receive ...
... neurotransmitters, go from one neuron to the next. Point out that most neurons can receive messages from many other neurons. Some of these messages “stimulate” or cause firing, other messages “inhibit” or prevent firing. Neurons “decide” to fire or not depending on the kinds of messages they receive ...
Nervous System Poster
... 3. Schwann cells, which form the myelin sheath, are separated by gaps of unsheathed axon (nodes of Ranvier) over which the impulse travels as the signal propagates along the neuron. B. Action potentials propagate impulses along neurons. 1. Membranes of neurons are polarized by the establishment of e ...
... 3. Schwann cells, which form the myelin sheath, are separated by gaps of unsheathed axon (nodes of Ranvier) over which the impulse travels as the signal propagates along the neuron. B. Action potentials propagate impulses along neurons. 1. Membranes of neurons are polarized by the establishment of e ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.