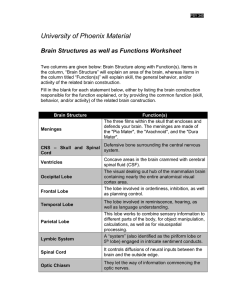
nervous system divisions cns, pns 1
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
Nervous System
... –Sensory – carry impulses from the sense organs (receptors) to the CNS –Motor – carry impulses from the CNS to the muscles or glands ...
... –Sensory – carry impulses from the sense organs (receptors) to the CNS –Motor – carry impulses from the CNS to the muscles or glands ...
chapter summary
... The spinal cord has two vital functions: 1. It serves as the neuronal link between the brain and the peripheral nervous system. All communication up and down the spinal cord is located in well-defined, independent ascending and descending tracts in the cord’s outer white matter. 2. It is the integra ...
... The spinal cord has two vital functions: 1. It serves as the neuronal link between the brain and the peripheral nervous system. All communication up and down the spinal cord is located in well-defined, independent ascending and descending tracts in the cord’s outer white matter. 2. It is the integra ...
CHAPTER NINE: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... and some brain regions f. Chemical synapses i. Specialized in the ___________ of neurotransmitters ii. Composed of two parts 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsyna ...
... and some brain regions f. Chemical synapses i. Specialized in the ___________ of neurotransmitters ii. Composed of two parts 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsyna ...
Document
... • Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP: • Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP ...
... • Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP: • Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP ...
Chapter Two
... “indulging at times in the grossest profanity (which was not previously his custom), manifesting but little deference for his fellows, impatient of restraint or advice when it conflicts with his desires “ ...
... “indulging at times in the grossest profanity (which was not previously his custom), manifesting but little deference for his fellows, impatient of restraint or advice when it conflicts with his desires “ ...
Chapter 2: Brain and Behavior
... Neurotransmitters called monoamines o Dopamine = A neurotransmitter that plays a role in learning, attention, and movement o Norepinephrine = A neurotransmitter affecting eating and sleep o Epinephrine = A neurotransmitter that affects the metabolism of glucose and energy stored in muscles to be rel ...
... Neurotransmitters called monoamines o Dopamine = A neurotransmitter that plays a role in learning, attention, and movement o Norepinephrine = A neurotransmitter affecting eating and sleep o Epinephrine = A neurotransmitter that affects the metabolism of glucose and energy stored in muscles to be rel ...
Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... about biological or psychological influences on behavior, but in reality, everything psychological is simultaneously biological. Franz Gall did not subject his beliefs about phrenology to scientific tests, but this early theory did help scientists to begin thinking about links among our biology, beh ...
... about biological or psychological influences on behavior, but in reality, everything psychological is simultaneously biological. Franz Gall did not subject his beliefs about phrenology to scientific tests, but this early theory did help scientists to begin thinking about links among our biology, beh ...
Brain PowerPoints - Raleigh Charter High School
... Includes Broca’s area (needed for forming words; located in left hemisphere only) Association areas in this region – judgment, ...
... Includes Broca’s area (needed for forming words; located in left hemisphere only) Association areas in this region – judgment, ...
File
... Round, centrally located structure Contains DNA Controls protein manufacturing Directs metabolism No role in neural signaling ...
... Round, centrally located structure Contains DNA Controls protein manufacturing Directs metabolism No role in neural signaling ...
Chapter 45 Central Nervous System BRain
... • Sensory Neurons (afferent) – Transmit information to the CNS ...
... • Sensory Neurons (afferent) – Transmit information to the CNS ...
From Vision to Movement
... Perhaps the most fundamental question in Visual-Motor Neuroscience is when, where, and how visual signals are transformed into motor signals. We will consider more complex aspects of this in the following sessions, but right now we just want to differentiate between visual and motor signals in the b ...
... Perhaps the most fundamental question in Visual-Motor Neuroscience is when, where, and how visual signals are transformed into motor signals. We will consider more complex aspects of this in the following sessions, but right now we just want to differentiate between visual and motor signals in the b ...
PSY 437 Sensation and Perception Knapp Study Guide 11 Primary
... Today we’ll trace the pathway from the retina to the primary visual cortex. We’ll also see how primary visual cortex is organized and some things it can do.. 1. What sources does each LGN receive information from and why would it be important to receive information from these sources? 2. What type o ...
... Today we’ll trace the pathway from the retina to the primary visual cortex. We’ll also see how primary visual cortex is organized and some things it can do.. 1. What sources does each LGN receive information from and why would it be important to receive information from these sources? 2. What type o ...
Maintaining the Inner Environment
... parasympathetic to keep blood pressure within normal limits. Hypertension occurs with deficient feedback. ...
... parasympathetic to keep blood pressure within normal limits. Hypertension occurs with deficient feedback. ...
Surface-uniform sampling, possibilities and limitations
... Surface-uniform sampling (SUGOS), possibilities and limitations H. J. G. Gundersen +45 8942 2954, [email protected] Stereological Research Laboratory, Aarhus University, Denmark ...
... Surface-uniform sampling (SUGOS), possibilities and limitations H. J. G. Gundersen +45 8942 2954, [email protected] Stereological Research Laboratory, Aarhus University, Denmark ...
Chapter 3: The Nervous System
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. ▫ Works as an off switch. ...
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. ▫ Works as an off switch. ...
669790507205MyersMod_LG_12
... 2. Discuss the different levels of visual information processing. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones is received and transmitted by the million or so ganglion cells whose fibers make ...
... 2. Discuss the different levels of visual information processing. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones is received and transmitted by the million or so ganglion cells whose fibers make ...
Vision
... that depend on the use of two eyes - Retinal disparity – a binocular cue for perceiving depth: by comparing images from the retinas in the two eyes, the brain computes distance – the greater the distance the greater the disparity between two ...
... that depend on the use of two eyes - Retinal disparity – a binocular cue for perceiving depth: by comparing images from the retinas in the two eyes, the brain computes distance – the greater the distance the greater the disparity between two ...
pharm chapter 8 [3-16
... In CNS, info not simply relayed from one area to another; receive signals from numerous sources and distribute axons widely (some neurons synapse with hundreds of thousands of other neurons) o Connections can be excitatory or inhibitory o 3 major motifs of CNS: long tract neuronal systems, local c ...
... In CNS, info not simply relayed from one area to another; receive signals from numerous sources and distribute axons widely (some neurons synapse with hundreds of thousands of other neurons) o Connections can be excitatory or inhibitory o 3 major motifs of CNS: long tract neuronal systems, local c ...
Nervous tissues (NS)
... CNS. 1-Ependymal cells: from a sheet that lines the ventricles of the brain (spaces that form and circulate cerebrospinal fluid) and the central canal of the spinal cord. 2- Astrocytes: star shaped cells with numerous processes. They are of two types: a- protoplasmic astrocytes: are found in the gra ...
... CNS. 1-Ependymal cells: from a sheet that lines the ventricles of the brain (spaces that form and circulate cerebrospinal fluid) and the central canal of the spinal cord. 2- Astrocytes: star shaped cells with numerous processes. They are of two types: a- protoplasmic astrocytes: are found in the gra ...
Slide 1
... just ahead to depolarize too. Speed of conduction depends on the size of the axon and the number of ion channels. Myelin permits the action potential to travel rapidly from node to node by blocking the membrane ...
... just ahead to depolarize too. Speed of conduction depends on the size of the axon and the number of ion channels. Myelin permits the action potential to travel rapidly from node to node by blocking the membrane ...
HP Authorized Customer
... Supplies the brain with nourishment (food) and oxygen. The main white substance area of dendrites as well as axons linking both hemispheres of the brain. It adds information from the two dissimilar halves of the cerebral cortex, main sensory as well as motor information. These 12 formations send and ...
... Supplies the brain with nourishment (food) and oxygen. The main white substance area of dendrites as well as axons linking both hemispheres of the brain. It adds information from the two dissimilar halves of the cerebral cortex, main sensory as well as motor information. These 12 formations send and ...
Slide ()
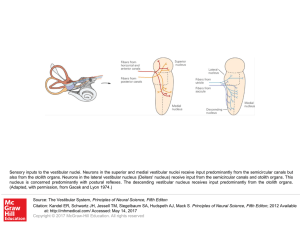
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
Neurons are the cells that carry messages between parts of the body
... The cell remains at resting potential until a stimulus reaches the cell, either from another neuron or the environment. Channels in the membrane open to allow Na+ ions to enter the cell. The inside of the cell temporarily becomes more positive. This is called the action potential. Refer to fig. 35-7 ...
... The cell remains at resting potential until a stimulus reaches the cell, either from another neuron or the environment. Channels in the membrane open to allow Na+ ions to enter the cell. The inside of the cell temporarily becomes more positive. This is called the action potential. Refer to fig. 35-7 ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.