Chapter 2 - Safford Unified School
... system conveys information between the CNS and sense organs and muscles. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls internal bodily processes such as heartbeat and respiration. The ANS contains two divisions, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic division speeds up mos ...
... system conveys information between the CNS and sense organs and muscles. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls internal bodily processes such as heartbeat and respiration. The ANS contains two divisions, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic division speeds up mos ...
The Challenge of Connecting the Dots in the B.R.A.I.N.
... The first category comprises tools that have already found neuroscience applications. Measurement modalities in this category include, for example, electrophysiological recordings using arrays of electrodes, multiphoton microscopy, photoacoustic and optical coherence tomography, voltage-sensitive dy ...
... The first category comprises tools that have already found neuroscience applications. Measurement modalities in this category include, for example, electrophysiological recordings using arrays of electrodes, multiphoton microscopy, photoacoustic and optical coherence tomography, voltage-sensitive dy ...
Introduction to Psychology
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
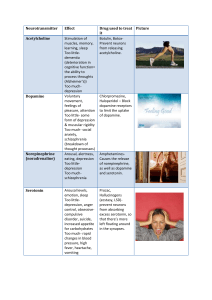
Ch 2 neurotrans and nervous sys
... – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizure ...
... – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizure ...
Grade 11 College Biology – Unit 3
... Task – Questions 1, 2, 4-6 – Pages 73-76 in Science Perspectives 10 ...
... Task – Questions 1, 2, 4-6 – Pages 73-76 in Science Perspectives 10 ...
Neural correlates of decision processes
... percent correct, then either the neurons are not really playing a critical role in guiding the choice, or the analysis is flawed. The fourth issue concerns the incompatibility of this scheme with earlier demonstrations that saccades are initiated when the absolute, not relative, firing rate of sacca ...
... percent correct, then either the neurons are not really playing a critical role in guiding the choice, or the analysis is flawed. The fourth issue concerns the incompatibility of this scheme with earlier demonstrations that saccades are initiated when the absolute, not relative, firing rate of sacca ...
Neural Basis of the Ventriloquist
... Neurons use electrical potentials to communicate Multiple, aligned, synchronously-firing neurons produce enough voltage change to be read by electrodes on the scalp. ...
... Neurons use electrical potentials to communicate Multiple, aligned, synchronously-firing neurons produce enough voltage change to be read by electrodes on the scalp. ...
Neurotransmitter - Pamoja Education Blogs
... & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
... & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... Similar in spirit to Fourier decomposition. Bumps = radial basis ...
... Similar in spirit to Fourier decomposition. Bumps = radial basis ...
No Slide Title - Reza Shadmehr
... neurons, killing them. Muscle fibers in the motor unit are paralyzed. Neighboring motor neurons grow sprouts to take over orphaned fibers, creating a giant motor unit. ...
... neurons, killing them. Muscle fibers in the motor unit are paralyzed. Neighboring motor neurons grow sprouts to take over orphaned fibers, creating a giant motor unit. ...
Diapositive 1
... 1) The first is that the two bipolar cells are of entirely different types—one responding by depolarizing in response to the glutamate neurotransmitter released by the rods and cones, and the other responding by hyperpolarizing. 2) The other possibility is that one of the bipolar cells receives dire ...
... 1) The first is that the two bipolar cells are of entirely different types—one responding by depolarizing in response to the glutamate neurotransmitter released by the rods and cones, and the other responding by hyperpolarizing. 2) The other possibility is that one of the bipolar cells receives dire ...
26_1986 Wasilewska
... body mass in both analysed animals. In the man, the total number of neurons in the St is 68.1 million (66), while in the GP/GPe ranges from 540,000 to 465,000 ...
... body mass in both analysed animals. In the man, the total number of neurons in the St is 68.1 million (66), while in the GP/GPe ranges from 540,000 to 465,000 ...
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I notes
... extensions (instead of being small round cells without extensions)? *Make a drawing of a synapse and label the important structures described above. *What ends the stimulation of the postsynaptic neuron? *Explain how a drug that blocks Ca++ channels could be a depressant and how a drug that makes me ...
... extensions (instead of being small round cells without extensions)? *Make a drawing of a synapse and label the important structures described above. *What ends the stimulation of the postsynaptic neuron? *Explain how a drug that blocks Ca++ channels could be a depressant and how a drug that makes me ...
Document
... Parts of the brain, and even neurons, can be stimulated electrically, chemically, or magnetically. This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, a ...
... Parts of the brain, and even neurons, can be stimulated electrically, chemically, or magnetically. This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, a ...
2
... Parts of the brain, and even neurons, can be stimulated electrically, chemically, or magnetically. This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, a ...
... Parts of the brain, and even neurons, can be stimulated electrically, chemically, or magnetically. This can result in behaviors such as giggling, head turning, or simulated vivid recall. Researchers can see which neurons or neural networks fire in conjunction with certain mental experiences, a ...
outline28002
... c. Photoreceptors-Subretinal Space d. Ganglion Cells-Epiretinal Space C. Three Physiologic Principles a. Electric currents can substitute light photons in producing visual sensations (phosphene). b. Most etiologies of blindness leave upstream structure intact. c. Retinotopic organization of target n ...
... c. Photoreceptors-Subretinal Space d. Ganglion Cells-Epiretinal Space C. Three Physiologic Principles a. Electric currents can substitute light photons in producing visual sensations (phosphene). b. Most etiologies of blindness leave upstream structure intact. c. Retinotopic organization of target n ...
chapter_12 - The Anatomy Academy
... detect changes in body and external environment information transmitted into brain or spinal cord lie between sensory and motor pathways in CNS 90% of our neurons are interneurons process, store and retrieve information ...
... detect changes in body and external environment information transmitted into brain or spinal cord lie between sensory and motor pathways in CNS 90% of our neurons are interneurons process, store and retrieve information ...
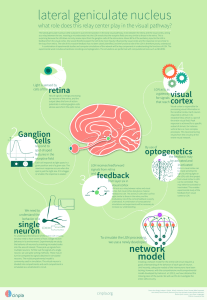
lgn - cinpla
... The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is placed in a prominent position in the early visual pathway. It sits between the retina and the visual cortex, acting as a relay between the two. Inserting a microelectrode into the LGN reveals that the receptive fields are very similar to those in the retina. ...
... The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is placed in a prominent position in the early visual pathway. It sits between the retina and the visual cortex, acting as a relay between the two. Inserting a microelectrode into the LGN reveals that the receptive fields are very similar to those in the retina. ...
Blockade of NMDA receptors in the developing cortex and
... autophagy (3-MA, rapamycin) did not interfere with the anti-excitotoxic effect of MK801 observed in deep layers V and VI. In vivo, 3-MA blocked the rapid increase in caspase-3 cleavage induced by NMDA antagonists and prevented death of Gad67-GFP neurons in layers II-IV. Together, these data suggest ...
... autophagy (3-MA, rapamycin) did not interfere with the anti-excitotoxic effect of MK801 observed in deep layers V and VI. In vivo, 3-MA blocked the rapid increase in caspase-3 cleavage induced by NMDA antagonists and prevented death of Gad67-GFP neurons in layers II-IV. Together, these data suggest ...
Nervous System Organization and Components
... Outside the myelin, surrounding the axon is a sheath of cells, the neurilemma or Schwann sheath. The neurilemma and myelin are not continuous but are interrupted at intervals along the length of the axon. The point of interruption is the neurofibril node (node of Ranvier). Axons of the PNS Surroundi ...
... Outside the myelin, surrounding the axon is a sheath of cells, the neurilemma or Schwann sheath. The neurilemma and myelin are not continuous but are interrupted at intervals along the length of the axon. The point of interruption is the neurofibril node (node of Ranvier). Axons of the PNS Surroundi ...
Nervous System
... The two major ions are sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+). Sodium diffuses out of the neuron, and Potassium diffuses into the neuron.The two ions cross the membrane through channel proteins (3). Some channel proteins never shut, so the ions diffuse through them all the time. Other channel proteins act ...
... The two major ions are sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+). Sodium diffuses out of the neuron, and Potassium diffuses into the neuron.The two ions cross the membrane through channel proteins (3). Some channel proteins never shut, so the ions diffuse through them all the time. Other channel proteins act ...
Nervous system Lab - Sonoma Valley High School
... twice as many neurons as you have now. The die-off of neurons occurs early in life, and with more room, the remaining neurons make many connections with other existing neurons. The degree of interconnectedness apparently determines our intelligence and memory. It is estimated that the human brain co ...
... twice as many neurons as you have now. The die-off of neurons occurs early in life, and with more room, the remaining neurons make many connections with other existing neurons. The degree of interconnectedness apparently determines our intelligence and memory. It is estimated that the human brain co ...
Nervous system - Effingham County Schools
... • Vital centers - cardiac, dilates blood vessels (drops and increases blood pressure), respiratory ...
... • Vital centers - cardiac, dilates blood vessels (drops and increases blood pressure), respiratory ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.