APES Fall Semester Peer Review
... Use the following to answer questions 57-58: A species can withstand a narrow range of temperature. Above 100°F there are no species present. In the range from 97°F–100°F and 90°F–94°F there are a few species present. Below 90°F there are no species present. 57. What would you label the range of tem ...
... Use the following to answer questions 57-58: A species can withstand a narrow range of temperature. Above 100°F there are no species present. In the range from 97°F–100°F and 90°F–94°F there are a few species present. Below 90°F there are no species present. 57. What would you label the range of tem ...
Fig. 3 - ePrints Soton - University of Southampton
... experimentally assess how the rearrangement of species dominance structure within specific levels of evenness, rather than changes in species richness and composition, affect invertebrate particle reworking and burrow ventilation behaviour - important moderators of microbial-mediated remineralisatio ...
... experimentally assess how the rearrangement of species dominance structure within specific levels of evenness, rather than changes in species richness and composition, affect invertebrate particle reworking and burrow ventilation behaviour - important moderators of microbial-mediated remineralisatio ...
Bison are a keystone species for ecosystem restoration
... Prairie dogs also provide food for foxes, hawks and eagles and their colonies are home to other small mammals and reptiles. Nutrient cycling Bison also affect the nutrient cycling in prairie ecosystems. Nitrogen is an essential element for plant productivity that is found in both plant material and ...
... Prairie dogs also provide food for foxes, hawks and eagles and their colonies are home to other small mammals and reptiles. Nutrient cycling Bison also affect the nutrient cycling in prairie ecosystems. Nitrogen is an essential element for plant productivity that is found in both plant material and ...
Ecology is - El Paso High School
... • Global Climate Change • Changes in Earth’s climate can profoundly affect the biosphere • One way to predict the effects of future global climate change is to study previous change • As glaciers retreated 16,000 years ago, tree distribution patterns changed • As climate changes, species that have d ...
... • Global Climate Change • Changes in Earth’s climate can profoundly affect the biosphere • One way to predict the effects of future global climate change is to study previous change • As glaciers retreated 16,000 years ago, tree distribution patterns changed • As climate changes, species that have d ...
Vaughn.BioScience.2010
... date suggests that tropical amphibian declines, primarily through the catastrophic loss of primary consumers (grazing tadpole biomass), will have large-scale and lasting ecosystemlevel effects, including changes in algal community structure and primary production; altered organic-matter dynamics; ch ...
... date suggests that tropical amphibian declines, primarily through the catastrophic loss of primary consumers (grazing tadpole biomass), will have large-scale and lasting ecosystemlevel effects, including changes in algal community structure and primary production; altered organic-matter dynamics; ch ...
Biodiversity
... Video: Rediscovering Biology DVD, Disk #4 Molecular and Global Perspectives #12 Biodiversity biodiversity, species diversity, genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, species, proton, neutron, electron, atom, element, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, commu ...
... Video: Rediscovering Biology DVD, Disk #4 Molecular and Global Perspectives #12 Biodiversity biodiversity, species diversity, genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, species, proton, neutron, electron, atom, element, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, commu ...
Villy Cristensen: Using ecosystem modeling for fisheries
... • Habitat and environmental changes (including those caused by fishing) and intensive fishery removals are creating novel situations, which we can only handle with difficulty: – We do not to understand the ‘mechanics’ of ecological response well enough to be able to predict all important responses t ...
... • Habitat and environmental changes (including those caused by fishing) and intensive fishery removals are creating novel situations, which we can only handle with difficulty: – We do not to understand the ‘mechanics’ of ecological response well enough to be able to predict all important responses t ...
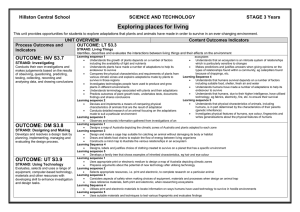
Exploring places for living
... Plant and animal systems share common features, however some functions are carried out by specific plant and animal systems The particular set or community of living things, together with its habitat, make up ecosystems: ecosystems differ from place to place because of different sets of conditions L ...
... Plant and animal systems share common features, however some functions are carried out by specific plant and animal systems The particular set or community of living things, together with its habitat, make up ecosystems: ecosystems differ from place to place because of different sets of conditions L ...
Chapter 10 Biological Productivity in the Ocean
... environment encompassing all chemical, physical, geological and biological parts. • Ecosystems function by the exchange of matter and energy. • Material is constantly recycled in the ecosystem, but energy gradually dissipates as heat and is lost. – Energy flows downhill, materials cycle! ...
... environment encompassing all chemical, physical, geological and biological parts. • Ecosystems function by the exchange of matter and energy. • Material is constantly recycled in the ecosystem, but energy gradually dissipates as heat and is lost. – Energy flows downhill, materials cycle! ...
ASPB – BSA Working Group on Core Concepts in Plant Biology
... nonliving physical environment. Ecosystems are defined by many hierarchical systems of networks consisting of interactions among individuals and populations of organisms, as well as interactions between organisms and their environment. All organisms in an ecosystem are linked through energy flow and ...
... nonliving physical environment. Ecosystems are defined by many hierarchical systems of networks consisting of interactions among individuals and populations of organisms, as well as interactions between organisms and their environment. All organisms in an ecosystem are linked through energy flow and ...
Discussion
... The reduction of live root surface area causes a decrease in active root length for interaction with symbiotic rhizosphere organisms and causes a decrease in absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. Reduction of active root biomass and diminishment of grass plant health vigor result in a los ...
... The reduction of live root surface area causes a decrease in active root length for interaction with symbiotic rhizosphere organisms and causes a decrease in absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. Reduction of active root biomass and diminishment of grass plant health vigor result in a los ...
A framework for community and ecosystem
... in which the phenotype of one organism is part of the environment of another 36. This hypothesis is supported by studies of multi-level selection33–35,48,49 in which the fitness consequences of IGEs among individuals of the same species are important in group and social evolution50. An analogous mec ...
... in which the phenotype of one organism is part of the environment of another 36. This hypothesis is supported by studies of multi-level selection33–35,48,49 in which the fitness consequences of IGEs among individuals of the same species are important in group and social evolution50. An analogous mec ...
Environmental impact of pesticides
... 3. Effects on organisms Soil organisms and processes Soil microorganisms . They are essential for mineralization of organic matter and making nutrients available for plants. Soil microorganisms are also able to metabolise and degrade a lot of pollutants and pesticides . On the other hand, microbial ...
... 3. Effects on organisms Soil organisms and processes Soil microorganisms . They are essential for mineralization of organic matter and making nutrients available for plants. Soil microorganisms are also able to metabolise and degrade a lot of pollutants and pesticides . On the other hand, microbial ...
Siberian Tiger By: Irvinder Sohi
... Firstly, what is biodiversity? Biodiversity is specific areas around the world where different species of all shapes and sizes live together, and basically depend on each other to keep everything in that ecosystem stable and sustainable for life. Examples of different ecosystems include; rain forest ...
... Firstly, what is biodiversity? Biodiversity is specific areas around the world where different species of all shapes and sizes live together, and basically depend on each other to keep everything in that ecosystem stable and sustainable for life. Examples of different ecosystems include; rain forest ...
13.4 Food Chains And Food Webs
... – The carbon cycle moves carbon from the atmosphere, through the food web, and returns to the atmosphere. – Carbon is emitted by the burning of fossil fuels. – Some carbon is stored for long periods of time in areas called carbon sinks. carbon dioxide in air combustion ...
... – The carbon cycle moves carbon from the atmosphere, through the food web, and returns to the atmosphere. – Carbon is emitted by the burning of fossil fuels. – Some carbon is stored for long periods of time in areas called carbon sinks. carbon dioxide in air combustion ...
Beyond Yield: Plant Disease in the Context of
... herbicides are used to kill plants that might act as hosts to maintain pathogen and vector populations. When tillage practices leave little residue in agricultural fields, there is greater potential for soil erosion by wind and water, resulting in reduced top soil and removal of nutrients, air pollu ...
... herbicides are used to kill plants that might act as hosts to maintain pathogen and vector populations. When tillage practices leave little residue in agricultural fields, there is greater potential for soil erosion by wind and water, resulting in reduced top soil and removal of nutrients, air pollu ...
Chapter 4 Part 2 - Learn District 196
... means of natural selection – competition within a population of its own kind chooses those that are most fit to the environment. In this case, that means being faster ...
... means of natural selection – competition within a population of its own kind chooses those that are most fit to the environment. In this case, that means being faster ...
7 - ICFCST
... need a special consideration. 7.3. Hereditary selection This type of natural selection begins to operate at shortage of the vital resources (nutrients and moisture in the soil, light). The plants need to compete with each other to keep balance between growing stock of them and available supply of th ...
... need a special consideration. 7.3. Hereditary selection This type of natural selection begins to operate at shortage of the vital resources (nutrients and moisture in the soil, light). The plants need to compete with each other to keep balance between growing stock of them and available supply of th ...
Mixotrophy everywhere on land and in water
... Comments on other more restrictive definitions. In the past, this diversity of mechanisms has somewhat blurred the uniting feature, namely the combination of autotrophy and heterotrophy within a single organism. Several authors use more restrictive definitions. First, some aquatic ecologists only co ...
... Comments on other more restrictive definitions. In the past, this diversity of mechanisms has somewhat blurred the uniting feature, namely the combination of autotrophy and heterotrophy within a single organism. Several authors use more restrictive definitions. First, some aquatic ecologists only co ...
Ecosystem-based Management
... forms of ecosystem-based management, they are not guaranteed unless adequate time and effort is devoted to achieving this end. In order for any approach to find its proverbial niche and experience an objective success, researchers and other interested parties must take special note. As Imperial (199 ...
... forms of ecosystem-based management, they are not guaranteed unless adequate time and effort is devoted to achieving this end. In order for any approach to find its proverbial niche and experience an objective success, researchers and other interested parties must take special note. As Imperial (199 ...
Qi Peng
... the ecosystem as “composed of physical-chemical-biological processes active within a space time unit of any magnitude” (Lindeman) , in other words, the biotic communities plus their abiotic environment. Within this system, Lindeman further groups organisms into several trophic levels such as produce ...
... the ecosystem as “composed of physical-chemical-biological processes active within a space time unit of any magnitude” (Lindeman) , in other words, the biotic communities plus their abiotic environment. Within this system, Lindeman further groups organisms into several trophic levels such as produce ...
Root Distribution of Trees in Relation to Soil Profile
... One of the pronounced trends in American forestry during the past decade has been the development of a widespread interest in soils. As a consequence to the soil as a part of the environmental complex has been attributed much In fact, the individual greater importance than formerly in forest product ...
... One of the pronounced trends in American forestry during the past decade has been the development of a widespread interest in soils. As a consequence to the soil as a part of the environmental complex has been attributed much In fact, the individual greater importance than formerly in forest product ...
Intro to Ecology
... Biomes • Life on Earth is distributed into Biomes • Biomes are determined by particular combinations of biotic and abiotic factors • Broken into two categories • Terrestrial vs Aquatic ...
... Biomes • Life on Earth is distributed into Biomes • Biomes are determined by particular combinations of biotic and abiotic factors • Broken into two categories • Terrestrial vs Aquatic ...
File - Pedersen Science
... 10. Is the evolution of Batesian mimicry an example of coevolution, support your answer? 11. Provide an example that correctly uses the terms species diversity, species richness and relative abundance correctly. 12. What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Which provides a more “f ...
... 10. Is the evolution of Batesian mimicry an example of coevolution, support your answer? 11. Provide an example that correctly uses the terms species diversity, species richness and relative abundance correctly. 12. What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Which provides a more “f ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.