Regional Limiting Factors Affecting Salmon Strongholds and
... strongholds vary greatly across the range of Pacific salmon. However common categories of limiting factors affect many salmon strongholds. Limiting factors are the physical, biological, or chemical conditions, and associated ecological processes and interactions (e.g., population size, habitat conne ...
... strongholds vary greatly across the range of Pacific salmon. However common categories of limiting factors affect many salmon strongholds. Limiting factors are the physical, biological, or chemical conditions, and associated ecological processes and interactions (e.g., population size, habitat conne ...
Biodiversity and ecosystem stability: a synthesis of underlying
... Therefore, we first focus on the special case of symmetrical communities in this section, as in several previous studies (Ives et al. 1999; Loreau & de Mazancourt 2008; Loreau 2010) – that is, we assume that all species have identical parameter values, and accordingly we drop the subscripts for all ...
... Therefore, we first focus on the special case of symmetrical communities in this section, as in several previous studies (Ives et al. 1999; Loreau & de Mazancourt 2008; Loreau 2010) – that is, we assume that all species have identical parameter values, and accordingly we drop the subscripts for all ...
Are planthopper problems caused by a breakdown in ecosystem
... was restored and planthopper outbreaks became negligible. Since planthoppers are r-strategists, which have high migratory ability, high reproductive capacity, and a short life span, their populations would be more effectively managed at the regional scale. Ecological engineering techniques can be us ...
... was restored and planthopper outbreaks became negligible. Since planthoppers are r-strategists, which have high migratory ability, high reproductive capacity, and a short life span, their populations would be more effectively managed at the regional scale. Ecological engineering techniques can be us ...
Ragnar Arnason*
... This paper considers the optimal utilization and management of ecosystem fisheries. It is divided into two main sections. In the first section, a general aggregative ecosystem fishery model is developed and its properties analysed. A major result of this part of the paper is that ecosystem fisheries ...
... This paper considers the optimal utilization and management of ecosystem fisheries. It is divided into two main sections. In the first section, a general aggregative ecosystem fishery model is developed and its properties analysed. A major result of this part of the paper is that ecosystem fisheries ...
Seagrass and Seagrass Beds
... habitat. The meadows provide canopy cover that shelters small organisms such as invertebrates and juvenile fish, including commercial fish species. Many species of algae, bacteria and plankton grow directly on the living and dead leaves. Some of these bacteria can extract nutrients (e.g. nitrogen) f ...
... habitat. The meadows provide canopy cover that shelters small organisms such as invertebrates and juvenile fish, including commercial fish species. Many species of algae, bacteria and plankton grow directly on the living and dead leaves. Some of these bacteria can extract nutrients (e.g. nitrogen) f ...
Biology B Ecology
... Ecology, focuses on concepts related to the ecological levels of organization in the biosphere and the interactions and relationships in an ecosystem. Students investigate and use data to build explanations of ecological interdependencies and cause-and-effect relationships within the biosphere and a ...
... Ecology, focuses on concepts related to the ecological levels of organization in the biosphere and the interactions and relationships in an ecosystem. Students investigate and use data to build explanations of ecological interdependencies and cause-and-effect relationships within the biosphere and a ...
Toward a Better Integration of Ecological
... explicit links to variation in biological community structure or biodiversity are still not made in these studies. Here, we argue that the variability of biological variables should also be considered in ecogeoscience research in order to better describe the relationships between biological and phys ...
... explicit links to variation in biological community structure or biodiversity are still not made in these studies. Here, we argue that the variability of biological variables should also be considered in ecogeoscience research in order to better describe the relationships between biological and phys ...
Land Use, Biodiversity, and Ecosystem Integrity
... results from ecological processes such as maintenance of soil fertility, water quality, the composition of the atmosphere, and numerous other global household repairs. Diverse assemblages of species carry out these functions. Thus a variety of species maintains habitat, from the local and regional t ...
... results from ecological processes such as maintenance of soil fertility, water quality, the composition of the atmosphere, and numerous other global household repairs. Diverse assemblages of species carry out these functions. Thus a variety of species maintains habitat, from the local and regional t ...
Critical Review - University of South Florida
... [30], the presence of other stressors [31], and functional redundancy [26] determine recovery rates in aquatic communities. In addition to identifying local and regional factors that influence recovery, appropriate experimental designs are essential for demonstrating cause-and-effect relationships b ...
... [30], the presence of other stressors [31], and functional redundancy [26] determine recovery rates in aquatic communities. In addition to identifying local and regional factors that influence recovery, appropriate experimental designs are essential for demonstrating cause-and-effect relationships b ...
Does eutrophication-driven evolution change aquatic ecosystems?
... phenotypic homogenization among lakes and among niches within lakes. We argue that the associated loss in functional diversity and niche differentiation may lead to decreased carrying capacity and lower resource-use efficiency by consumers. We show that in central European whitefish species radiatio ...
... phenotypic homogenization among lakes and among niches within lakes. We argue that the associated loss in functional diversity and niche differentiation may lead to decreased carrying capacity and lower resource-use efficiency by consumers. We show that in central European whitefish species radiatio ...
Net Primary Productivity - Sonoma Valley High School
... Is survivorship type related to number of offspring produced? ...
... Is survivorship type related to number of offspring produced? ...
Fundamentals of Ecology - University of West Florida
... Approximately 16.4 to 20.4 million hectares of tropical forest are being destroyed each year. Only 50% of the mature tropical forests remain! Course Overview Ecology is a broad subject dealing with the distribution of living organisms in time and space, and the interaction of organisms with other li ...
... Approximately 16.4 to 20.4 million hectares of tropical forest are being destroyed each year. Only 50% of the mature tropical forests remain! Course Overview Ecology is a broad subject dealing with the distribution of living organisms in time and space, and the interaction of organisms with other li ...
The Effect of Recycling on Plant Competitive Hierarchies
... conditions required for such positive feedback to exist has never been presented. Here we present a model of N cycling and plant competition and investigate the conditions that can lead to such feedback effects. In terrestrial ecosystems, the majority of the N in the soil is in a complex organic for ...
... conditions required for such positive feedback to exist has never been presented. Here we present a model of N cycling and plant competition and investigate the conditions that can lead to such feedback effects. In terrestrial ecosystems, the majority of the N in the soil is in a complex organic for ...
Ecology
... Why are the cycles important? How do organisms interact with each other? How can we show trends in populations over time? ...
... Why are the cycles important? How do organisms interact with each other? How can we show trends in populations over time? ...
Preface: Soil processes in cold-climate environments
... (Zubrzycki et al., 2014). Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane trapped in frozen soils may be released to the atmosphere as a consequence of increasing temperatures in permafrost environments and amplify warming, especially in the Arctic (Tarnocai et al., 2009; Natali et al., 2014). A ...
... (Zubrzycki et al., 2014). Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane trapped in frozen soils may be released to the atmosphere as a consequence of increasing temperatures in permafrost environments and amplify warming, especially in the Arctic (Tarnocai et al., 2009; Natali et al., 2014). A ...
Chapter 6: Dimension 3: Disciplinary Core Ideas—Life Sciences
... move from place to place, and seek, find, and take in food, water and air. Plants also have different parts (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits) that help them survive, grow, and produce more plants. By the end of grade 5. Plants and animals have both internal and external structures that serve v ...
... move from place to place, and seek, find, and take in food, water and air. Plants also have different parts (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits) that help them survive, grow, and produce more plants. By the end of grade 5. Plants and animals have both internal and external structures that serve v ...
Long-term ecological dynamics: reciprocal
... Gradient studies such as these are valuable not necessarily because they represent typical ecosystems, but rather because there are few confounding factors that influence ecosystem processes, thus making it easier to infer causal relationships. (c) Disturbance gradients Natural gradients can also be ...
... Gradient studies such as these are valuable not necessarily because they represent typical ecosystems, but rather because there are few confounding factors that influence ecosystem processes, thus making it easier to infer causal relationships. (c) Disturbance gradients Natural gradients can also be ...
Ecology Review - Science
... • Succession - natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • Primary succession – takes where no soil exists • Secondary succession – takes place where soil is already present ...
... • Succession - natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • Primary succession – takes where no soil exists • Secondary succession – takes place where soil is already present ...
New Zealand as ecosystems - Department of Conservation
... and restoration of natural processes—the margin of insufficiency will only increase in the near future. Driving this concern is a sea change in ecological theory and science, revitalising the ancient view that holds the life of the world as a myriad of interacting systems, alive and effortlessly sel ...
... and restoration of natural processes—the margin of insufficiency will only increase in the near future. Driving this concern is a sea change in ecological theory and science, revitalising the ancient view that holds the life of the world as a myriad of interacting systems, alive and effortlessly sel ...
Ecology Review
... • Succession - natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • Primary succession – takes where no soil exists • Secondary succession – takes place where soil is already present ...
... • Succession - natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • Primary succession – takes where no soil exists • Secondary succession – takes place where soil is already present ...
Three selected ecological observations interpreted in
... output, and cycling of mass and energy constitute the basis of ecological processes without exception. In this paper, we try to show that it is possible to explain different empirical biological and ecological observations in terms of a comprehensive thermodynamic hypothesis, instead of interpreting ...
... output, and cycling of mass and energy constitute the basis of ecological processes without exception. In this paper, we try to show that it is possible to explain different empirical biological and ecological observations in terms of a comprehensive thermodynamic hypothesis, instead of interpreting ...
Fundamentals of Ecology - University of West Florida
... Approximately 16.4 to 20.4 million hectares of tropical forest are being destroyed each year. Only 50% of the mature tropical forests remain! Course Overview Ecology is a broad subject dealing with the distribution of living organisms in time and space, and the interaction of organisms with other li ...
... Approximately 16.4 to 20.4 million hectares of tropical forest are being destroyed each year. Only 50% of the mature tropical forests remain! Course Overview Ecology is a broad subject dealing with the distribution of living organisms in time and space, and the interaction of organisms with other li ...
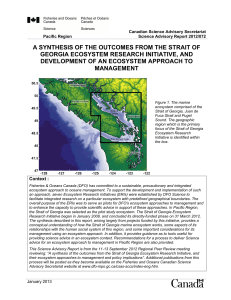
A synthesis of the outcomes from the Strait of Georgia Ecosystem
... Fisheries & Oceans Canada (DFO) has committed to a sustainable, precautionary and integrated ecosystem approach to oceans management. To support the development and implementation of such an approach, seven Ecosystem Research Initiatives (ERIs) were established by DFO Science to facilitate integrate ...
... Fisheries & Oceans Canada (DFO) has committed to a sustainable, precautionary and integrated ecosystem approach to oceans management. To support the development and implementation of such an approach, seven Ecosystem Research Initiatives (ERIs) were established by DFO Science to facilitate integrate ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.