Ecology
... 7. Given a specific geographic area (state, country), name several biomes that should be native to that locale. ...
... 7. Given a specific geographic area (state, country), name several biomes that should be native to that locale. ...
ECOLOGY TEST STUDY GUIDE
... The nitrogen cycle includes decomposers that break down wastes and put nutrients into the soil ...
... The nitrogen cycle includes decomposers that break down wastes and put nutrients into the soil ...
Year 12 Biology
... • Damschanges distribution of populations in ecosystems – can get animals accumulating around dams over grazing near the water source; loss of original ecosystem in flooded area • Presence of bores lowers water table; increases number of animals around bore over grazing near the water source ...
... • Damschanges distribution of populations in ecosystems – can get animals accumulating around dams over grazing near the water source; loss of original ecosystem in flooded area • Presence of bores lowers water table; increases number of animals around bore over grazing near the water source ...
Ecosystems - Mr Goldbaum`s Biology CLass Page
... particular species living in the same area at the same time. DIVERSITY – the richness or number of different species present. – the relative distribution (evenness) of abundance of species. ...
... particular species living in the same area at the same time. DIVERSITY – the richness or number of different species present. – the relative distribution (evenness) of abundance of species. ...
IMCC Yr12 Integrated Science Course Outline
... changes in ecosystems affect the survival of organisms within the ecosystem; individual variation assists survival, which over time results in changes in characteristics of the species ...
... changes in ecosystems affect the survival of organisms within the ecosystem; individual variation assists survival, which over time results in changes in characteristics of the species ...
Carrying Capacity and Limiting Factors
... living at one of the extreme ends of that range, many will experience stress and the population will decrease; if the species is living in conditions that are optimal then the population will be higher. ...
... living at one of the extreme ends of that range, many will experience stress and the population will decrease; if the species is living in conditions that are optimal then the population will be higher. ...
Nitrogen cycle review - West Perry School District
... 1st idea: Living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) factors make up an ecosystem. 1. Which of the following is NOT a basic need for a living organism in any habitat? Food (nutrients) ...
... 1st idea: Living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) factors make up an ecosystem. 1. Which of the following is NOT a basic need for a living organism in any habitat? Food (nutrients) ...
APES Review Worksheet #1
... b. Label each layer of the Earth’s atmosphere and identify where the greenhouse effect occurs and the ozone layer is situated. The chemicals that deplete the ozone layer are __________. In the box below, describe how a CFC interacts with ozone, naming the Altitude important atom responsible on the C ...
... b. Label each layer of the Earth’s atmosphere and identify where the greenhouse effect occurs and the ozone layer is situated. The chemicals that deplete the ozone layer are __________. In the box below, describe how a CFC interacts with ozone, naming the Altitude important atom responsible on the C ...
11.17-Community-Interactions-and-Succession
... Niche = an organism’s role in an ecosystem Ex: mushrooms are decomposers living on tree stumps Analogy: baseball players can be pitchers, catchers, shortstops, etc. ...
... Niche = an organism’s role in an ecosystem Ex: mushrooms are decomposers living on tree stumps Analogy: baseball players can be pitchers, catchers, shortstops, etc. ...
File - Biology and Other Sciences for KICS
... Competition – these two species need the same thing in the environment, and there may not be enough of that thing for both species – rhinoceros and zebra both need to eat the grass in one place Predation – one species kills and eats the other species – lions and zebras ...
... Competition – these two species need the same thing in the environment, and there may not be enough of that thing for both species – rhinoceros and zebra both need to eat the grass in one place Predation – one species kills and eats the other species – lions and zebras ...
Unit 6 Ecology Study Guide Behavioral ecology: study of interaction
... Parasitism: one organism benefits at another’s expense (ticks and humans) Commensalism: one organism benefits while the other is unaffected (clownfish and anemones) Mutualism: both organisms benefit from the interaction (acacia trees and ants) Competition: both species are harmed by the interaction ...
... Parasitism: one organism benefits at another’s expense (ticks and humans) Commensalism: one organism benefits while the other is unaffected (clownfish and anemones) Mutualism: both organisms benefit from the interaction (acacia trees and ants) Competition: both species are harmed by the interaction ...
Slide 1
... • Complex of terrestrial communities that covers a large area and is characterized by certain soil and climate conditions and particular assemblages of plants and animals • Not all kinds of organisms can live in every biome. – Adaptation: inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s ability ...
... • Complex of terrestrial communities that covers a large area and is characterized by certain soil and climate conditions and particular assemblages of plants and animals • Not all kinds of organisms can live in every biome. – Adaptation: inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s ability ...
The lonely wolves of the microscopic world Rare microbes have a
... as well. This is the conclusion of a team of researchers who have reviewed studies that investigate the role of low-abundance microbes in different ecosystems. This research field is still in its infancy, but rapidly emerging, as study leader Gera Hol (University of Wageningen, NL) explains. "We are ...
... as well. This is the conclusion of a team of researchers who have reviewed studies that investigate the role of low-abundance microbes in different ecosystems. This research field is still in its infancy, but rapidly emerging, as study leader Gera Hol (University of Wageningen, NL) explains. "We are ...
Ch 3-4 study guide ANSWERS
... 18. Complete the energy pyramid by writing the source of the energy for the food web and how much energy is available to first-, second-, and thirdlevel consumers. ...
... 18. Complete the energy pyramid by writing the source of the energy for the food web and how much energy is available to first-, second-, and thirdlevel consumers. ...
Interactions of Living Things
... Base of an energy pyramid is represented by producers. Looks like a pyramid. ...
... Base of an energy pyramid is represented by producers. Looks like a pyramid. ...
File
... b. What type of organisms are nitrogen fixers? And what do they do? Bacteria! They take nitrogen from the atmosphere is converted into ammonia in the soil, where it may be more readily used by plants. c. How do legumes fit into the nitrogen cycle? Legumes have a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen ...
... b. What type of organisms are nitrogen fixers? And what do they do? Bacteria! They take nitrogen from the atmosphere is converted into ammonia in the soil, where it may be more readily used by plants. c. How do legumes fit into the nitrogen cycle? Legumes have a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen ...
Science 8 - Lesson 14 Guided Notes, Part One, Answer Key
... To understand relationships within the biosphere, ecologists ask questions about events and organisms that range in complexity from a single individual to the entire biosphere. -The many levels of organization that ecologists study are as follows: ...
... To understand relationships within the biosphere, ecologists ask questions about events and organisms that range in complexity from a single individual to the entire biosphere. -The many levels of organization that ecologists study are as follows: ...
4.620Mb Microsoft PowerPoint
... been shown to enhance critical ecosystem processes such as decomposition, productivity, and nutrient recycling. However, functional diversity, that is, the number of different traits expressed by the species that make up a community, may be a more important factor in determining the functional capac ...
... been shown to enhance critical ecosystem processes such as decomposition, productivity, and nutrient recycling. However, functional diversity, that is, the number of different traits expressed by the species that make up a community, may be a more important factor in determining the functional capac ...
Chapter 18
... Food chains vs. food webs • Food chains – show a single pathway of energy flow • Single food chains are rare in nature ...
... Food chains vs. food webs • Food chains – show a single pathway of energy flow • Single food chains are rare in nature ...
Community Interactions and Populations
... • First species to populate this area – “pioneer species” – For example, pioneer species on volcanic rock are lichens (LY-kunz) • Lichens made up of fungus and algae that can grow on bare rock • When lichens die, they for organic material that becomes soil…now plants can grow ...
... • First species to populate this area – “pioneer species” – For example, pioneer species on volcanic rock are lichens (LY-kunz) • Lichens made up of fungus and algae that can grow on bare rock • When lichens die, they for organic material that becomes soil…now plants can grow ...
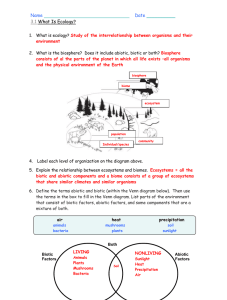
Name
... functioning together as an independent and relatively stable system 4. biosphere: that portion of the earth where life exists a. The biosphere is composed of numerous complex ecosystems. 5. An ecosystem involves interactions between abiotic (physical) and biotic (living) factors. The members of the ...
... functioning together as an independent and relatively stable system 4. biosphere: that portion of the earth where life exists a. The biosphere is composed of numerous complex ecosystems. 5. An ecosystem involves interactions between abiotic (physical) and biotic (living) factors. The members of the ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.