Succession Review - LACOE Moodle Sites
... Complex Community Example for a Northern Hemisphere lithosere: a succession on bare rock ...
... Complex Community Example for a Northern Hemisphere lithosere: a succession on bare rock ...
Worksheet - 1 - SunsetRidgeMSBiology
... 2. Primary consumers are animals that eat primary producers; they are also called herbivores (plant-eaters). 3. Secondary consumers eat primary consumers. They are carnivores (meat-eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants). 4. Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. 5. Qua ...
... 2. Primary consumers are animals that eat primary producers; they are also called herbivores (plant-eaters). 3. Secondary consumers eat primary consumers. They are carnivores (meat-eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants). 4. Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. 5. Qua ...
Forest Site Preparation
... • Destroy pests and harmful organisms and the habitats that sustain them • Increase water yields by altering the kind and size of vegetation and reducing transpiration • Induce sprouting of surviving vegetation to improve cover, browse or forage production ...
... • Destroy pests and harmful organisms and the habitats that sustain them • Increase water yields by altering the kind and size of vegetation and reducing transpiration • Induce sprouting of surviving vegetation to improve cover, browse or forage production ...
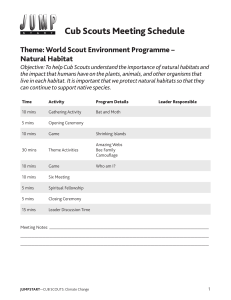
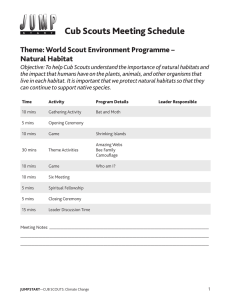
Natural Habitat - Scouts Canada Wiki
... and small invertebrates that break down the remains of dead organisms into smaller molecules that are then available to plants and other organisms as nutrients. For example, fungi digest wood fibers into simple sugars as a food source. Nutrients and elements such as carbon and nitrogen recycled by d ...
... and small invertebrates that break down the remains of dead organisms into smaller molecules that are then available to plants and other organisms as nutrients. For example, fungi digest wood fibers into simple sugars as a food source. Nutrients and elements such as carbon and nitrogen recycled by d ...
Cub Scouts Jumpstarts
... and small invertebrates that break down the remains of dead organisms into smaller molecules that are then available to plants and other organisms as nutrients. For example, fungi digest wood fibers into simple sugars as a food source. Nutrients and elements such as carbon and nitrogen recycled by d ...
... and small invertebrates that break down the remains of dead organisms into smaller molecules that are then available to plants and other organisms as nutrients. For example, fungi digest wood fibers into simple sugars as a food source. Nutrients and elements such as carbon and nitrogen recycled by d ...
Biodiversity and the Functioning of Selected Terrestrial Ecosystems
... The most obvious and direct element of planned agrobiodiversity is the crop plant. Breeding and selection for desirable agronomic traits has been at the centre of improving crop varieties since farming began. However, it is over the last 20 to 30 years that plant breeders have made greatest progress ...
... The most obvious and direct element of planned agrobiodiversity is the crop plant. Breeding and selection for desirable agronomic traits has been at the centre of improving crop varieties since farming began. However, it is over the last 20 to 30 years that plant breeders have made greatest progress ...
Squirrels feed mainly on acorns in an oak forest ecosystem
... Squirrels feed mainly on acorns in an oak forest ecosystem. However, many species of oak trees do not produce acorns every year if conditions are unfavorable. Which statement predicts the most likely effect this uneven production of acorns will have on a squirrel population? ...
... Squirrels feed mainly on acorns in an oak forest ecosystem. However, many species of oak trees do not produce acorns every year if conditions are unfavorable. Which statement predicts the most likely effect this uneven production of acorns will have on a squirrel population? ...
Biological soil crust and vascular ... sand savanna of northwestern Ohio1
... ria, eukaryotic algae, and heterotrophic bacteria. They have been found on all seven continents and in all climatic regions (Belnap and Lange 2001). They persist in environments that do not support higher organisms and often are the first colonizers of new or disturbed habitats. For example, algae a ...
... ria, eukaryotic algae, and heterotrophic bacteria. They have been found on all seven continents and in all climatic regions (Belnap and Lange 2001). They persist in environments that do not support higher organisms and often are the first colonizers of new or disturbed habitats. For example, algae a ...
plant adaptation
... Plants need water and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, but they also need many other nutrients to maintain healthy cells and to grow. These nutrients are not equally available in the world; so plants have made adaptations to acquire nutrients. One nutrient that is often in short supply in acidic h ...
... Plants need water and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, but they also need many other nutrients to maintain healthy cells and to grow. These nutrients are not equally available in the world; so plants have made adaptations to acquire nutrients. One nutrient that is often in short supply in acidic h ...
Notes - Being an Environmental Scientist
... • Parasitism where host dies is devastating to both the parasite and the host populations. • Important host survives and thrives long enough for the parasite to reproduce and spread. ...
... • Parasitism where host dies is devastating to both the parasite and the host populations. • Important host survives and thrives long enough for the parasite to reproduce and spread. ...
The Living Soil - Colorado State University Extension
... First, as soil organisms decompose organic matter, they transform nutrients into mineral forms that plants can use; thus this process is called mineralization. Without soil microorganisms, insects, and worms feeding on organic matter, the nutrients in organic matter would remain bound in complex org ...
... First, as soil organisms decompose organic matter, they transform nutrients into mineral forms that plants can use; thus this process is called mineralization. Without soil microorganisms, insects, and worms feeding on organic matter, the nutrients in organic matter would remain bound in complex org ...
Abbreviations
... Impacts can be characterised according to whether they are direct (primary) impacts arising from activities associated with the Project, or indirect (secondary and higher order) impacts that follow on as a consequence of direct impacts. An example of a direct impact would be the adverse impact on hu ...
... Impacts can be characterised according to whether they are direct (primary) impacts arising from activities associated with the Project, or indirect (secondary and higher order) impacts that follow on as a consequence of direct impacts. An example of a direct impact would be the adverse impact on hu ...
PowerPoint slides
... • Logical arguments & data to support the hypothesis But • Logical arguments & data contrary to hypothesis • Thus, biodiversity alone does not account for invasibility • Diversity patterns at different scales may explain paradox in part • Assumes competition is dominant driver structuring communitie ...
... • Logical arguments & data to support the hypothesis But • Logical arguments & data contrary to hypothesis • Thus, biodiversity alone does not account for invasibility • Diversity patterns at different scales may explain paradox in part • Assumes competition is dominant driver structuring communitie ...
North American Lakes and Pond Ecosystems Introductions to the
... Scientists, from all different backgrounds all have different perspectives have different beliefs on the whole idea of global warming and what the effects will be. Some believe that it’s a sign that we are just ending the Ice Age, or that the problem is global cooling not warming, or that we humans ...
... Scientists, from all different backgrounds all have different perspectives have different beliefs on the whole idea of global warming and what the effects will be. Some believe that it’s a sign that we are just ending the Ice Age, or that the problem is global cooling not warming, or that we humans ...
Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems
... Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems (textbook section 2.7) ...
... Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems (textbook section 2.7) ...
primary consumer - FreshmanBiology
... 37.11 Keystone species have a disproportionate impact on diversity A keystone species – is a species whose impact on its community is larger than its biomass or abundance indicates and – occupies a niche that holds the rest of its community in ...
... 37.11 Keystone species have a disproportionate impact on diversity A keystone species – is a species whose impact on its community is larger than its biomass or abundance indicates and – occupies a niche that holds the rest of its community in ...
The effect of grazing on plant species richness on the Qinghai
... 4.2) was marginally higher than that of SH (22.2 ± 3.9), but the difference in species richness ...
... 4.2) was marginally higher than that of SH (22.2 ± 3.9), but the difference in species richness ...
LS2.A- Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems
... If Doug was placed in the pond ecosystem things would be different,. He would interact with abiotic factors by drinking water, creating a shelter and contribute to the nitrogen and carbon cycle, by producing waste products, and breathing. Biotic interactions would occur, if he ate the plants, and an ...
... If Doug was placed in the pond ecosystem things would be different,. He would interact with abiotic factors by drinking water, creating a shelter and contribute to the nitrogen and carbon cycle, by producing waste products, and breathing. Biotic interactions would occur, if he ate the plants, and an ...
Biology Unit 2 Study Guide
... 1. The ____________________ consists of evaporation, precipitation, transpiration, runoff, and respiration. 2. Omnivores, carnivores, herbivores, scavengers, and decomposers are all ____________________. 3. Ecosystems, biotic factors, and abiotic factors make up the ____________________. 4. Organism ...
... 1. The ____________________ consists of evaporation, precipitation, transpiration, runoff, and respiration. 2. Omnivores, carnivores, herbivores, scavengers, and decomposers are all ____________________. 3. Ecosystems, biotic factors, and abiotic factors make up the ____________________. 4. Organism ...
Planting
... Soil and site • soil must be well drained, granular and well supplied with plant food nutrients • full sun and partial shade sites Planting • The size of bulb, type of soil, and manner of root growth are all factors in planting • in mid-October • A general rule is to set bulbs three times their own ...
... Soil and site • soil must be well drained, granular and well supplied with plant food nutrients • full sun and partial shade sites Planting • The size of bulb, type of soil, and manner of root growth are all factors in planting • in mid-October • A general rule is to set bulbs three times their own ...
Impacts of wood ants (Formica aquilonia Yarr.) on the invertebrate
... (Rosengren & Sundström 1991), and a positive association with earthworms (Laakso & Setälä 1997, Laakso 1999), which have a potential to indirectly control the rate of various soil processes (e.g. Swift et al. 1979). However, as the available data on the ant-induced effects on soil food webs are main ...
... (Rosengren & Sundström 1991), and a positive association with earthworms (Laakso & Setälä 1997, Laakso 1999), which have a potential to indirectly control the rate of various soil processes (e.g. Swift et al. 1979). However, as the available data on the ant-induced effects on soil food webs are main ...
THE NITROGEN CYCLE Terms List
... (sunlight) is converted by producers into chemical energy (food). This chemical energy is ultimately converted into thermal energy (heat). In time, thermal energy is radiated back to into outer space. For the most part, matter (atoms) stays (cycles) within the biosphere, being part of different mole ...
... (sunlight) is converted by producers into chemical energy (food). This chemical energy is ultimately converted into thermal energy (heat). In time, thermal energy is radiated back to into outer space. For the most part, matter (atoms) stays (cycles) within the biosphere, being part of different mole ...
THE NITROGEN CYCLE Terms List
... 2. How does the way that matter flows through an ecosystem differ from the way that energy flows through an ecosystem? Most energy that drives life comes from the sun, which is outside the biosphere. This energy is converted from one form to another as organisms utilize it. For example, electromagne ...
... 2. How does the way that matter flows through an ecosystem differ from the way that energy flows through an ecosystem? Most energy that drives life comes from the sun, which is outside the biosphere. This energy is converted from one form to another as organisms utilize it. For example, electromagne ...