What is population ecology? - Mrs. Cindy Williams Biology website
... • What affect population ecology? • density • age • distribution • growth • competition • predation ...
... • What affect population ecology? • density • age • distribution • growth • competition • predation ...
Chapter 3
... • Living organisms are temporary storage units for useful energy. • One organism can be used by another as a source of energy. • Energy cannot recycle; so there is a continuous requirement for new energy. • Plants - Photosynthesis ...
... • Living organisms are temporary storage units for useful energy. • One organism can be used by another as a source of energy. • Energy cannot recycle; so there is a continuous requirement for new energy. • Plants - Photosynthesis ...
Ecosystems and Nutrient Cycles
... How much energy is available if we are: carnivores? vegetarians? ...
... How much energy is available if we are: carnivores? vegetarians? ...
Notes for Ecology unit - Liberty Union High School District
... What are the two process that are responsible; for cycling Carbon in the environment? What things add carbon? Which things take it away? Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis : take it away Cellular Respiration, Fossil Fuels and ...
... What are the two process that are responsible; for cycling Carbon in the environment? What things add carbon? Which things take it away? Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis : take it away Cellular Respiration, Fossil Fuels and ...
Energy and Nutrients
... • A sedimentary cycle that moves phosphorus from its main reservoir (Earth’s crust) through soils and sediments, aquatic habitats, and bodies of living ...
... • A sedimentary cycle that moves phosphorus from its main reservoir (Earth’s crust) through soils and sediments, aquatic habitats, and bodies of living ...
Ecology Biomes - Peterson Science
... a group of ecosystems with similar climates and organisms the process by which nitrogen (a nutrient essential for plant growth) is changed from one form to another; removed from the air and fixed into the soil for biological use active at night active during the day a type of biome where the tree gr ...
... a group of ecosystems with similar climates and organisms the process by which nitrogen (a nutrient essential for plant growth) is changed from one form to another; removed from the air and fixed into the soil for biological use active at night active during the day a type of biome where the tree gr ...
Ecology - Warren County Schools
... of individuals that can occupy one area at a particular time. Limiting factors that ...
... of individuals that can occupy one area at a particular time. Limiting factors that ...
Ecology `15 Notes
... Carbon Does Not Stay Still – It Is On the Move! 1. In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to some oxygen in a gas called ______________ ______________________. 2. Plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make their own food and grow. The carbon becomes part of the plant. 3. Animals consume plants. T ...
... Carbon Does Not Stay Still – It Is On the Move! 1. In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to some oxygen in a gas called ______________ ______________________. 2. Plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make their own food and grow. The carbon becomes part of the plant. 3. Animals consume plants. T ...
MARINE ECOLOGY
... Synecology = Study of interacting groups (communities, ecosystems) Population = Group of individuals of same species Community = Interacting populations which are interdependent Ecosystem = Community + physical (abiotic) environment Biosphere (ecosphere) = Includes all parts of the earth where ecosy ...
... Synecology = Study of interacting groups (communities, ecosystems) Population = Group of individuals of same species Community = Interacting populations which are interdependent Ecosystem = Community + physical (abiotic) environment Biosphere (ecosphere) = Includes all parts of the earth where ecosy ...
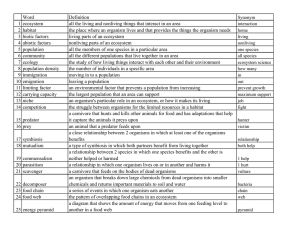
Unit 6 Vocabulary Flashcards
... Symbiotic relationship where organisms of different species work together and both are helped; ex: coral and algae, clownfish and sea anemone, sponge and brittle star ...
... Symbiotic relationship where organisms of different species work together and both are helped; ex: coral and algae, clownfish and sea anemone, sponge and brittle star ...
Interactions and Ecosystems Review JEOPARDY
... different species that live and interact in the same place form ….. ...
... different species that live and interact in the same place form ….. ...
Chapter 5 – Populations
... they become part of Humans use ________ as much energy and transport ________ as many materials as _________________________ all other multicellular species Some important activities combined that affect the biosphere are hunting and gathering, __________, industry and agriculture urban development ...
... they become part of Humans use ________ as much energy and transport ________ as many materials as _________________________ all other multicellular species Some important activities combined that affect the biosphere are hunting and gathering, __________, industry and agriculture urban development ...
Energy in an Ecosystem ppt
... trophic level • Only 10% of the energy in one trophic level is passed to the next level up. • The rest of the energy is either used by the organisms to do life processes (like growth, reproduction, respiration, How much of the energy available to etc.), or released as heat the producers is available ...
... trophic level • Only 10% of the energy in one trophic level is passed to the next level up. • The rest of the energy is either used by the organisms to do life processes (like growth, reproduction, respiration, How much of the energy available to etc.), or released as heat the producers is available ...
Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
... • Occur when predators limit the density (#/area) and/or behavior of their prey and thereby enhance survival of the next lower trophic level. • Effects of the presence/absence of the keystone species “cascades” down the food chain ...
... • Occur when predators limit the density (#/area) and/or behavior of their prey and thereby enhance survival of the next lower trophic level. • Effects of the presence/absence of the keystone species “cascades” down the food chain ...
Niche & Community Interactions PPT
... how organisms live. Tolerance Is the ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental conditions. All organisms have an upper and lower limit of tolerance for every environmental factor. ...
... how organisms live. Tolerance Is the ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental conditions. All organisms have an upper and lower limit of tolerance for every environmental factor. ...
(Ecology) Study Guide KEY
... What are the benefits of each of the 3 types of dispersion? Clumped = organisms help each other to stay alive if they’re prey, help each other to hunt if they’re predators, and for social companionship Uniform = territorial organisms that fight to preserve their own space, food, water, etc. Random = ...
... What are the benefits of each of the 3 types of dispersion? Clumped = organisms help each other to stay alive if they’re prey, help each other to hunt if they’re predators, and for social companionship Uniform = territorial organisms that fight to preserve their own space, food, water, etc. Random = ...
Section: 2.4 Name: Section Title: Ecology
... Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: I. ...
... Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: I. ...
Chapter 1 Review - science9atsouthcarletonhs
... 10. The diagram below shows the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in a plant leaf. Why do you think cellular respiration is the dominant process at night, whereas photosynthesis is the dominant process during the day? ...
... 10. The diagram below shows the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in a plant leaf. Why do you think cellular respiration is the dominant process at night, whereas photosynthesis is the dominant process during the day? ...
Flip Folder 8 KEY - Madison County Schools
... selected, autotroph, small). As they live/die, decomposers (bacteria) would eventually create soil out of their remains. This would provide a suitable living environment for any plants that may be dropped there by animals, wind, or water. They then grow and die which creates even better soil for big ...
... selected, autotroph, small). As they live/die, decomposers (bacteria) would eventually create soil out of their remains. This would provide a suitable living environment for any plants that may be dropped there by animals, wind, or water. They then grow and die which creates even better soil for big ...
Ecology - Cloudfront.net
... Nitrogen cycleAtmospheric nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly 78%-80% of air. Organisms can not use it in that form. Lightning and bacteria convert nitrogen into usable forms. ...
... Nitrogen cycleAtmospheric nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly 78%-80% of air. Organisms can not use it in that form. Lightning and bacteria convert nitrogen into usable forms. ...