Aposematic (Warning) Coloration in Plants
... if herbivores avoided such plants altogether, rather than testing leaves for palatability, and so causing some damage. A distinct leaf color pattern linked with chemical defense might function in this way. Polymorphism for leaf color should then coincide with polymorphisms for chemical defense. Müll ...
... if herbivores avoided such plants altogether, rather than testing leaves for palatability, and so causing some damage. A distinct leaf color pattern linked with chemical defense might function in this way. Polymorphism for leaf color should then coincide with polymorphisms for chemical defense. Müll ...
Boneseed (Chyrsantemoides monilifera subsp. monilifera, best
... vegetation in a controlled manner in many situations where natural fire is not possible, thereby assisting in the depletion of soil-stored seeds. Burning with gas can be undertaken when fuel moisture levels are high thus preventing uncontrolled burning of vegetation. Although time consuming and rest ...
... vegetation in a controlled manner in many situations where natural fire is not possible, thereby assisting in the depletion of soil-stored seeds. Burning with gas can be undertaken when fuel moisture levels are high thus preventing uncontrolled burning of vegetation. Although time consuming and rest ...
Energy flow and the nutrient cycling in an ecosystem
... : in general, the food chains in an ecos ystem are not isolated, but are interconnected with one another, i.e. an herbivore may feed on several species of plants, and/ or be consumed by many consumers and so on, such a number of interconnected food chains is known as food web Trophic level : organis ...
... : in general, the food chains in an ecos ystem are not isolated, but are interconnected with one another, i.e. an herbivore may feed on several species of plants, and/ or be consumed by many consumers and so on, such a number of interconnected food chains is known as food web Trophic level : organis ...
Vascular Seedless Plants
... grow and expand. Ferns grow in a variety of habitats, ranging in size from tiny aquatic species to giant tropical plants. ...
... grow and expand. Ferns grow in a variety of habitats, ranging in size from tiny aquatic species to giant tropical plants. ...
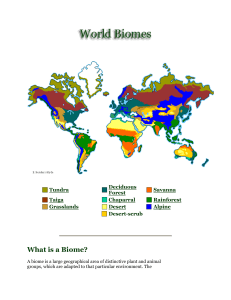
Biomes of the World information
... of Greenland. Another type of tundra is the alpine tundra, which is a biome that exists at the tops of high mountains. Special features: This is the earth's coldest biome. Since the sun does not rise for nearly six months of the year, it is not unusual for the temperature to be below -30°F in winter ...
... of Greenland. Another type of tundra is the alpine tundra, which is a biome that exists at the tops of high mountains. Special features: This is the earth's coldest biome. Since the sun does not rise for nearly six months of the year, it is not unusual for the temperature to be below -30°F in winter ...
Top-down and bottom-up control of large herbivore populations: a
... may vary spatially and temporally [5, 6]. Moreover, human activities can potentially affect both topdown and bottom-up processes in terrestrial ecosystems. Humans are a keystone species that alters terrestrial ecosystem structure and composition through actions such as setting fires and livestock gr ...
... may vary spatially and temporally [5, 6]. Moreover, human activities can potentially affect both topdown and bottom-up processes in terrestrial ecosystems. Humans are a keystone species that alters terrestrial ecosystem structure and composition through actions such as setting fires and livestock gr ...
TAKS Objective III
... Birds and reptiles are similar in that they are vertebrates and lay eggs. They differ in that reptiles have teeth and birds have beaks. Some birds do possess teeth. However, these teeth are present only in the embryonic stage. Which conclusion is best supported by the presence of teeth in ...
... Birds and reptiles are similar in that they are vertebrates and lay eggs. They differ in that reptiles have teeth and birds have beaks. Some birds do possess teeth. However, these teeth are present only in the embryonic stage. Which conclusion is best supported by the presence of teeth in ...
Worksheet - 1 - SunsetRidgeMSBiology
... 2. Primary consumers are animals that eat primary producers; they are also called herbivores (plant-eaters). 3. Secondary consumers eat primary consumers. They are carnivores (meat-eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants). 4. Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. 5. Qua ...
... 2. Primary consumers are animals that eat primary producers; they are also called herbivores (plant-eaters). 3. Secondary consumers eat primary consumers. They are carnivores (meat-eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants). 4. Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. 5. Qua ...
BioDasar2015 week19-ecology and Ecosystem
... Interspecific interactions are fundamental to community structure ! Interspecific competition occurs when populations of two different species compete for the same limited resource. – In mutualism, both populations benefit. – In predation, one species (the predator) kills and eats another (the p ...
... Interspecific interactions are fundamental to community structure ! Interspecific competition occurs when populations of two different species compete for the same limited resource. – In mutualism, both populations benefit. – In predation, one species (the predator) kills and eats another (the p ...
community context of an obligate mutualism
... mutualistic partner has a direct and major effect on the other’s fitness (Cook and Rasplus 2003, Kato et al. 2003, Pellmyr 2003), and identifying the cost–benefit ratio is much less complicated than in mutualisms in which plants and pollinators interact with a guild of mutualists. Species engaged in ...
... mutualistic partner has a direct and major effect on the other’s fitness (Cook and Rasplus 2003, Kato et al. 2003, Pellmyr 2003), and identifying the cost–benefit ratio is much less complicated than in mutualisms in which plants and pollinators interact with a guild of mutualists. Species engaged in ...
Predator-prey interactions: lecture content
... (often difficult to document in nature) Coevolution well documented in a few cases ...
... (often difficult to document in nature) Coevolution well documented in a few cases ...
Ecology of Ecosystems
... percent of all photosynthesis on the planet (i.e., produce 40% of the oxygen and 40% of the CO2 xation). Although not as diverse as the other two, deep ocean ecosystems contain a wide variety of marine organisms. Such ecosystems exist even at the bottom of the ocean where light is unable to penetra ...
... percent of all photosynthesis on the planet (i.e., produce 40% of the oxygen and 40% of the CO2 xation). Although not as diverse as the other two, deep ocean ecosystems contain a wide variety of marine organisms. Such ecosystems exist even at the bottom of the ocean where light is unable to penetra ...
Ecosystems
... Within each ecosystem there are habitats of various sizes. A habitat is a place with a population (a group of living organisms of the same kind). All the populations living in the same place at the same time interact, forming a community. Such community also interacts with the non-living world aroun ...
... Within each ecosystem there are habitats of various sizes. A habitat is a place with a population (a group of living organisms of the same kind). All the populations living in the same place at the same time interact, forming a community. Such community also interacts with the non-living world aroun ...
Science 5th primary 1st term unite 3 lesson 1 Symbiosis It is a
... 2 – the food relationship in which a living organism benefits from the other, while the other neither gets benefit nor is harmed known as ………………………….. 3 – in the ……………………………….. relationship between bees and flowers of plants , bees feed on …………………….. of flowers, while bees help the plant in transfer ...
... 2 – the food relationship in which a living organism benefits from the other, while the other neither gets benefit nor is harmed known as ………………………….. 3 – in the ……………………………….. relationship between bees and flowers of plants , bees feed on …………………….. of flowers, while bees help the plant in transfer ...
Grasslands and Tundra
... significant in determining whether they will return if stresses are removed. Some have suggested that they may have “multiple stable states.” ...
... significant in determining whether they will return if stresses are removed. Some have suggested that they may have “multiple stable states.” ...
Herbivore
_grazing_-_20050809.jpg?width=300)
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material.