Grounded cognition Mirror neurons Mirror neurons Mirror neurons in
... Cortical motor system in primates = a set of fronto-parietal circuits encoding different types of motor behavior (hand grasping, mouth and head movements, arm reaching and various types of eye movements) ...
... Cortical motor system in primates = a set of fronto-parietal circuits encoding different types of motor behavior (hand grasping, mouth and head movements, arm reaching and various types of eye movements) ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... Neurons are the nerve cells that transmit impulses. Supporting cells are neuroglia. The three components of a neuron are a cell body or soma, one or more afferent processes called dendrites, and a single efferent process called an axon. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cor ...
... Neurons are the nerve cells that transmit impulses. Supporting cells are neuroglia. The three components of a neuron are a cell body or soma, one or more afferent processes called dendrites, and a single efferent process called an axon. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cor ...
Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]
... • One person holds the yard stick up • Second person is being tested at how fast they can respond to the yard stick falling • The first person will release the yard stick and the second person will catch it. They will record where their hand grabs the yard stick. • Using this formula: t = √2y/g , y ...
... • One person holds the yard stick up • Second person is being tested at how fast they can respond to the yard stick falling • The first person will release the yard stick and the second person will catch it. They will record where their hand grabs the yard stick. • Using this formula: t = √2y/g , y ...
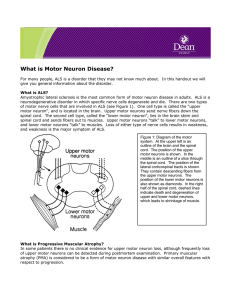
What is Motor Neuron
... Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) refers to rare patients who have no clinical evidence for lower motor neuron involvement. However, most patients who initially have only upper motor neuron signs eventually develop lower motor neuron signs and go to have ALS. Thus, to be certain that a patient has PLS ...
... Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) refers to rare patients who have no clinical evidence for lower motor neuron involvement. However, most patients who initially have only upper motor neuron signs eventually develop lower motor neuron signs and go to have ALS. Thus, to be certain that a patient has PLS ...
The nervous system - Science for Yr9@E
... 7. What is the main purpose of the spinal cord? Is it to; a. Produce chemical hormones b. Transmit information between the brain and the rest of the body c. Help communicate between the two halves of the brain d. Transmit information around the brain 8. The cerebellum controls our; a. Voluntary acti ...
... 7. What is the main purpose of the spinal cord? Is it to; a. Produce chemical hormones b. Transmit information between the brain and the rest of the body c. Help communicate between the two halves of the brain d. Transmit information around the brain 8. The cerebellum controls our; a. Voluntary acti ...
Part IV- Single neuron computation
... Active dendrite cause Many types of back propagations (as for “forward” propagation) Hausser M 2001 ...
... Active dendrite cause Many types of back propagations (as for “forward” propagation) Hausser M 2001 ...
65 Commentary - The Ideal DBS System The proliferation of DBS
... The proliferation of DBS systems allows for customization to meet the unique needs of the individual patient. However, the multiplicity of different systems, both current and anticipated, increases the complexity of deciding which to use. This monograph will not make any direct comparisons or recomm ...
... The proliferation of DBS systems allows for customization to meet the unique needs of the individual patient. However, the multiplicity of different systems, both current and anticipated, increases the complexity of deciding which to use. This monograph will not make any direct comparisons or recomm ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... The nervous system is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gathering information and for transmit ...
... The nervous system is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gathering information and for transmit ...
Lab 9 Nervous histology post lab answer key 2010
... bundles of intermediate filaments that, along with microtubules, help to maintain the shape of a neuron ...
... bundles of intermediate filaments that, along with microtubules, help to maintain the shape of a neuron ...
A1982NC82200001
... signals specifically related to sensorimotor processes from the random activity that predominates in the scalp-recorded electroencephalogram. Although cortical potentials elicited by external stimulation had begun to bewidely studied. no brain activity related to the initiation of voluntary movement ...
... signals specifically related to sensorimotor processes from the random activity that predominates in the scalp-recorded electroencephalogram. Although cortical potentials elicited by external stimulation had begun to bewidely studied. no brain activity related to the initiation of voluntary movement ...
LABORATORY 9
... bundles of intermediate filaments that, along with microtubules, help to maintain the shape of a neuron ...
... bundles of intermediate filaments that, along with microtubules, help to maintain the shape of a neuron ...
An Introduction to the Nervous System
... • The sodium–potassium exchange pump ejects 3 Na+ ions for every 2 K+ ions that it brings into the cell • It serves to stabilize the resting potential when the ratio of Na+ entry to ...
... • The sodium–potassium exchange pump ejects 3 Na+ ions for every 2 K+ ions that it brings into the cell • It serves to stabilize the resting potential when the ratio of Na+ entry to ...
Results: Mitochondrial transport in dendrites and axons Maximum
... The observed differences in mitochondrial transport at varying stages of axonal and dendritic maturity are consistent with previous suggestions that mitochondrial movement is dependent on both the stage of growth and position within a neurite [29,58,59,60]. The specific pattern, though, appears to ...
... The observed differences in mitochondrial transport at varying stages of axonal and dendritic maturity are consistent with previous suggestions that mitochondrial movement is dependent on both the stage of growth and position within a neurite [29,58,59,60]. The specific pattern, though, appears to ...
Supp-BDS 302
... d) An operative grading for carcinoma of breast A thiersch graft is a: a) Pinch skin graft b) Pedicle graft c) Small full thickness skin graft d) Partial thickness skin graft Blood for transfusion should be stored at: a) – 20 degree Celsius b) + 4 degree Celsius to +14 degree Celsius c) +2 degree Ce ...
... d) An operative grading for carcinoma of breast A thiersch graft is a: a) Pinch skin graft b) Pedicle graft c) Small full thickness skin graft d) Partial thickness skin graft Blood for transfusion should be stored at: a) – 20 degree Celsius b) + 4 degree Celsius to +14 degree Celsius c) +2 degree Ce ...
Long-term depression
... Cerebellum: & Motor Learning Long-term depression (LTD) requires concurrent activity climbing & parallel fibers active together in activity of specific Purkinje cells Climbing fibers may carry error signals corrections ---> parallel fiber influence input specificity only affects a ...
... Cerebellum: & Motor Learning Long-term depression (LTD) requires concurrent activity climbing & parallel fibers active together in activity of specific Purkinje cells Climbing fibers may carry error signals corrections ---> parallel fiber influence input specificity only affects a ...
New Title
... A resting neuron is one that is not carrying an impulse. When a neuron is resting, the inside of the cell has a net negative charge. The outside of the cell has a net positive charge. This charge difference across the cell membrane is called the resting potential of the neuron. When a resting neuron ...
... A resting neuron is one that is not carrying an impulse. When a neuron is resting, the inside of the cell has a net negative charge. The outside of the cell has a net positive charge. This charge difference across the cell membrane is called the resting potential of the neuron. When a resting neuron ...
What is Nervous System?
... Sensory receptor (neurons) send this message (receive from sensory organ) as a form of energy to the brain. Through the process of transduction (change from one form of energy to another), a memory is created. Memory in the sensory register is very short less than ½ second for vision and about 3 ...
... Sensory receptor (neurons) send this message (receive from sensory organ) as a form of energy to the brain. Through the process of transduction (change from one form of energy to another), a memory is created. Memory in the sensory register is very short less than ½ second for vision and about 3 ...
Neuroanatomy PP - Rincon History Department
... The electrical impulse • Positive ions will flow into the neuron if not stopped or pumped out by the membrane. This is called the electrical potential, which is measured in millivolts. • The resting potential is the neuron’s usual charge, which is – 70 millivolts. • When the resting potential has c ...
... The electrical impulse • Positive ions will flow into the neuron if not stopped or pumped out by the membrane. This is called the electrical potential, which is measured in millivolts. • The resting potential is the neuron’s usual charge, which is – 70 millivolts. • When the resting potential has c ...
last lecture neurophysiology - Evans Laboratory: Environmental
... • once the action potential reaches the AXON TERMINAL, the neuron must transmit the signal across the SYNPASE to the target cell • the cell that transmits the signal is called the PRE-SYNAPTIC CELL and the cell that receives the signal is referred to as the POST-SYNAPTIC CELL • the space between the ...
... • once the action potential reaches the AXON TERMINAL, the neuron must transmit the signal across the SYNPASE to the target cell • the cell that transmits the signal is called the PRE-SYNAPTIC CELL and the cell that receives the signal is referred to as the POST-SYNAPTIC CELL • the space between the ...
Physiology Study Guide 12
... ____10. The number 1 reason people take medication is for the treatment of pain. ____11. Rod photoreceptors are specifically associated with color vision. ____12. Rod photoreceptors permit us to see in dim light. ____13. Noxiceptors are normally stimulated by chemicals released from injured tissue c ...
... ____10. The number 1 reason people take medication is for the treatment of pain. ____11. Rod photoreceptors are specifically associated with color vision. ____12. Rod photoreceptors permit us to see in dim light. ____13. Noxiceptors are normally stimulated by chemicals released from injured tissue c ...
muscle stretch reflex
... opposition, to produce movement. When the quadriceps contracts, the hamstring must relax and vice verse. Therefore, as the quadriceps muscle is stretched by the doctor’s reflex hammer and the sensory afferent ...
... opposition, to produce movement. When the quadriceps contracts, the hamstring must relax and vice verse. Therefore, as the quadriceps muscle is stretched by the doctor’s reflex hammer and the sensory afferent ...
Chapter 14
... blood flow despite changes in perfusion pressure, independent of any neural or humoral influences ...
... blood flow despite changes in perfusion pressure, independent of any neural or humoral influences ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.

![Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008568661_1-062fb6959798aae5bb439e7880889016-300x300.png)