Discoveries From the Deepest Sleep
... Deepest Sleep Unusual changes take place inside the brains of hibernating animals. Understanding them may shed light on the mysteries of Alzheimer’s disease. By Jay Ingram ...
... Deepest Sleep Unusual changes take place inside the brains of hibernating animals. Understanding them may shed light on the mysteries of Alzheimer’s disease. By Jay Ingram ...
ALTERATIONS IN NEUROLOGIC FUNCTIONING
... system, 2nd most common CNS problem in US Most cases are idiopathic, onset usually 60+, no known cure Characterized by loss of dopamine production and neurons in basal ganglia and substantia nigra Diagnosed by response to L-dopa ...
... system, 2nd most common CNS problem in US Most cases are idiopathic, onset usually 60+, no known cure Characterized by loss of dopamine production and neurons in basal ganglia and substantia nigra Diagnosed by response to L-dopa ...
An Investigation into the Role of Cortical Synaptic Depression in
... the duration of the masker and masking increases with masker duration (Kidd and Feth, 1982). This was also found to be the case by (Brosch and Schreiner, 1997) in their recordings in AI. However, the sensitivity to duration was observed even when the AI cell responded only at the onset of the masker ...
... the duration of the masker and masking increases with masker duration (Kidd and Feth, 1982). This was also found to be the case by (Brosch and Schreiner, 1997) in their recordings in AI. However, the sensitivity to duration was observed even when the AI cell responded only at the onset of the masker ...
Bibliography
... A similar type of research has been undertaken by Keiichi Torimitsu at the NTT’s Biosciences Research Group in Atsugi, Japan. (Niwa and Torimitsu, 1998 His group is trying to develop an effective interface between computers and the brain. To test this possibility, his laboratory sent electronic sign ...
... A similar type of research has been undertaken by Keiichi Torimitsu at the NTT’s Biosciences Research Group in Atsugi, Japan. (Niwa and Torimitsu, 1998 His group is trying to develop an effective interface between computers and the brain. To test this possibility, his laboratory sent electronic sign ...
A zebrafish model exemplifies the long preclinical period of motor
... the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Thus, in the mutant sod1 zebrafish model, gradual and incremental changes occur within the neural circuit to finally impact on motor neurons and their accompanying neuromuscular connectivity. hpf, hours postfertilisation. neuron axons, we found that NMJ denervation oc ...
... the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Thus, in the mutant sod1 zebrafish model, gradual and incremental changes occur within the neural circuit to finally impact on motor neurons and their accompanying neuromuscular connectivity. hpf, hours postfertilisation. neuron axons, we found that NMJ denervation oc ...
Interactions between attention, context and learning in primary
... plexus of long range horizontal connections that link cells with widely separated receptive fields. This is a network of connectivity formed by the axons of cortical pyramidal cells. Pyramidal and spiny stellate cells represent 80% of the neurons in the cortex, each cell can form lateral connections ...
... plexus of long range horizontal connections that link cells with widely separated receptive fields. This is a network of connectivity formed by the axons of cortical pyramidal cells. Pyramidal and spiny stellate cells represent 80% of the neurons in the cortex, each cell can form lateral connections ...
11Cranial nerve 8 (Vestibulo-cochlear)
... postcentral gyrus (head area). • Responsible for conscious awareness of vestibular sensation. ...
... postcentral gyrus (head area). • Responsible for conscious awareness of vestibular sensation. ...
ppt - University of Rochester
... Takes a series of pictures over time, e.g. one every three seconds The “f” in fMRI means functional, i.e. you get a movie of brain function, not a still image of brain structure ...
... Takes a series of pictures over time, e.g. one every three seconds The “f” in fMRI means functional, i.e. you get a movie of brain function, not a still image of brain structure ...
Slides - UCSD Cognitive Science
... The University policy is linked off the course web page. You will all have to sign a form in section For this class: • Labs are done in small groups but writeups must be in your own words • There is no collaboration on midterms and final exam ...
... The University policy is linked off the course web page. You will all have to sign a form in section For this class: • Labs are done in small groups but writeups must be in your own words • There is no collaboration on midterms and final exam ...
New Autism Research
... 1990s, the neurons - also known as "monkey-see, monkey-do cells" - fire both when a monkey performs an action itself and when it observes another living creature perform that same action. Though it has been impossible to directly study the analogue of these neurons in people (since human subjects ca ...
... 1990s, the neurons - also known as "monkey-see, monkey-do cells" - fire both when a monkey performs an action itself and when it observes another living creature perform that same action. Though it has been impossible to directly study the analogue of these neurons in people (since human subjects ca ...
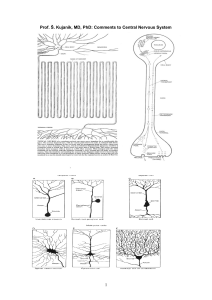
Study materials CNS
... reproduction, etc.) (3) Emotions and motivations Emotions – pleasure, anger, rage, fear (centre the limbic system) Motivations – reasons controlling our behaviour (motivation to learn, to have som hobby, to win in sport) (4) Instincts – set of motoric activities & behaviour, typical for one species. ...
... reproduction, etc.) (3) Emotions and motivations Emotions – pleasure, anger, rage, fear (centre the limbic system) Motivations – reasons controlling our behaviour (motivation to learn, to have som hobby, to win in sport) (4) Instincts – set of motoric activities & behaviour, typical for one species. ...
Unit 10 Chapter 36 The Nervous System
... to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor ...
... to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor ...
Forebrain Diseases of the Horse: Relevant Examination Techniques
... Test menace responses while standing in front of the horse. To do this, use the palm of the hand to make a threatening gesture toward the eye. Test from both temporal and nasal directions on each side. Stimulate the horse just before each menace gesture by tapping the skin below the eye. For safety ...
... Test menace responses while standing in front of the horse. To do this, use the palm of the hand to make a threatening gesture toward the eye. Test from both temporal and nasal directions on each side. Stimulate the horse just before each menace gesture by tapping the skin below the eye. For safety ...
Where Am I? Where Am I Going?
... in its environment. Yet even these processes do not tell the whole story of how mammals navigate. Our initial work focused on the medial (inner) entorhinal Robert U. Muller, both at SUNY Downstate Medical Center, cortex. Place cells may also receive signals from the lateral en- showed in the 1980s t ...
... in its environment. Yet even these processes do not tell the whole story of how mammals navigate. Our initial work focused on the medial (inner) entorhinal Robert U. Muller, both at SUNY Downstate Medical Center, cortex. Place cells may also receive signals from the lateral en- showed in the 1980s t ...
Star-cross`d neurons: astroglial effects on neural
... Kinouchi et al.’s experiments provide a useful paradigm by which to probe for both inhibitory and permissive factors associated with astroglia. There is an intimate interplay between the recipient environment and the donor cells themselves, and indeed one can imagine that this complex interplay occu ...
... Kinouchi et al.’s experiments provide a useful paradigm by which to probe for both inhibitory and permissive factors associated with astroglia. There is an intimate interplay between the recipient environment and the donor cells themselves, and indeed one can imagine that this complex interplay occu ...
2320lecture22
... Neural Correlates of Selection • Results: Neurons in visual system respond vigorously to certain stimuli but are then sharply suppressed if a different stimulus is selected by attention • Interpretation: this selection might be a neural correlate of the perceptual suppression of unattended informat ...
... Neural Correlates of Selection • Results: Neurons in visual system respond vigorously to certain stimuli but are then sharply suppressed if a different stimulus is selected by attention • Interpretation: this selection might be a neural correlate of the perceptual suppression of unattended informat ...
Limitations of Neural Map Topography for Decoding Spatial
... Topographic maps are common throughout the nervous system, yet their functional role is still unclear. In particular, whether they are necessary for decoding sensory stimuli is unknown. Here we examined this question by recording population activity at the cellular level from the larval zebrafish te ...
... Topographic maps are common throughout the nervous system, yet their functional role is still unclear. In particular, whether they are necessary for decoding sensory stimuli is unknown. Here we examined this question by recording population activity at the cellular level from the larval zebrafish te ...
The neuronal structure of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in the
... the dendrites of relay cells in the cat GLN. It is generally considered that interneurons (Golgi type II nerve cells) play an important role in inhibitory processes [1,17,21,26]. The lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary thalamic relay, through which retinal signals pass to the cortex. Retinal a ...
... the dendrites of relay cells in the cat GLN. It is generally considered that interneurons (Golgi type II nerve cells) play an important role in inhibitory processes [1,17,21,26]. The lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary thalamic relay, through which retinal signals pass to the cortex. Retinal a ...
6 CHAPTER Sensation and Perception Chapter Preview Sensation
... Sensation is the process by which we detect stimulus energy from our environment and transmit it to our brain. Perception is the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Clear evidence that perception is influenced by our exp ...
... Sensation is the process by which we detect stimulus energy from our environment and transmit it to our brain. Perception is the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. Clear evidence that perception is influenced by our exp ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... - because of weight symmetry, anti-patterns (binary reverse) are stored as well as the original patterns (also spurious local minima are created when many patterns are stored) - if one tries to store more than about 0.14*(number of neurons) patterns, the network exhibits unstable behavior - works we ...
... - because of weight symmetry, anti-patterns (binary reverse) are stored as well as the original patterns (also spurious local minima are created when many patterns are stored) - if one tries to store more than about 0.14*(number of neurons) patterns, the network exhibits unstable behavior - works we ...
Nervous System Notes
... 3. Chemical ~ response to chemicals in the body such as hormones (adrenaline) and outside stimuli (out of the body) odors, pheromones -Sensory organ: nose and mouth a. Response to chemicals in the body Ex. Hormones – adrenalin (fight or flight, super strength) b. Response to chemicals out of the bo ...
... 3. Chemical ~ response to chemicals in the body such as hormones (adrenaline) and outside stimuli (out of the body) odors, pheromones -Sensory organ: nose and mouth a. Response to chemicals in the body Ex. Hormones – adrenalin (fight or flight, super strength) b. Response to chemicals out of the bo ...
Neuroscientists identify brain circuit necessary for memory formation
... when artificially activated by light, but they did not They can also artificially reactivate memories by fire during natural memory recall. using optogenetics, a technique that allows them to turn target cells on or off using light. "Already the prefrontal cortex contained the specific memory inform ...
... when artificially activated by light, but they did not They can also artificially reactivate memories by fire during natural memory recall. using optogenetics, a technique that allows them to turn target cells on or off using light. "Already the prefrontal cortex contained the specific memory inform ...
TEACHER`S GUIDE
... After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: 1. The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. 2. Neurons send information to each other usi ...
... After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: 1. The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. 2. Neurons send information to each other usi ...