Connections of the Hypothalamus
... Model of the basic plan of the hypothalamus. It is convenient to start with the activation of a particular node (black) in the behavior control column. Note two classes of output. One consists of ‘descending’ projections to brainstem, and in some cases spinal, regions associated with the somatic and ...
... Model of the basic plan of the hypothalamus. It is convenient to start with the activation of a particular node (black) in the behavior control column. Note two classes of output. One consists of ‘descending’ projections to brainstem, and in some cases spinal, regions associated with the somatic and ...
Age-related changes in the hippocampal subdivisions of the rat
... This and similar descriptive studies demonstrate that throughout adulthood and senescence dendritic extent is regulated locally and that changes affect specific populations of neurons and restricted regions within the dendritic arbors. Recognition of which neurons are subject to dendritic regression ...
... This and similar descriptive studies demonstrate that throughout adulthood and senescence dendritic extent is regulated locally and that changes affect specific populations of neurons and restricted regions within the dendritic arbors. Recognition of which neurons are subject to dendritic regression ...
Brain and Nervous System
... Oligodendrocytes are cells that coat axons in the central nervous system (CNS) with their cell membrane forming a specialized membrane differenciation called myelin, producing the so-called myelin sheath. The myelin sheath provides insulation to the axon that allows electrical signals to propagate m ...
... Oligodendrocytes are cells that coat axons in the central nervous system (CNS) with their cell membrane forming a specialized membrane differenciation called myelin, producing the so-called myelin sheath. The myelin sheath provides insulation to the axon that allows electrical signals to propagate m ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM1.ppt [Recovered]
... The two TEMs below of insect tissue show an important difference between two types of chemical messengers. Can you see any differences between the two photos? The one on the left has electron-lucent vesicles, that are indicative of a neurotransmitter while the one on the right has electron-dense ma ...
... The two TEMs below of insect tissue show an important difference between two types of chemical messengers. Can you see any differences between the two photos? The one on the left has electron-lucent vesicles, that are indicative of a neurotransmitter while the one on the right has electron-dense ma ...
The effect of learning on the face selective responses of neurons in
... each one of which one of the stimuli from the set was shown. The order of presentation of the stimuli was re-randomized for each iteration. Then the standard set of images was replaced with a set of 4-9 novel face images. (None of these face images had ever been seen before. Most were of monkeys whi ...
... each one of which one of the stimuli from the set was shown. The order of presentation of the stimuli was re-randomized for each iteration. Then the standard set of images was replaced with a set of 4-9 novel face images. (None of these face images had ever been seen before. Most were of monkeys whi ...
Regulation of Astrocyte Plasticity
... Kleim et al. (papers and absts) have described synaptogenesis and changes in synapse morphology in association with the same AC motor learning procedure in the somatosensory-somatomotor forelimb cortex of rats. The first morphological change to occur is, on average, an increase in the size of PSDs, ...
... Kleim et al. (papers and absts) have described synaptogenesis and changes in synapse morphology in association with the same AC motor learning procedure in the somatosensory-somatomotor forelimb cortex of rats. The first morphological change to occur is, on average, an increase in the size of PSDs, ...
MS Word Version
... e. The main nutritional and metabolic region of the neuron. f. The transmitting or conductive region of the neuron. 7. (Page 6.) What are outgoing signals on neurons called? 8. (Page 6.) On what part of the neuron are action potentials conducted? In which direction do they go? 9. (Page 6.) How are a ...
... e. The main nutritional and metabolic region of the neuron. f. The transmitting or conductive region of the neuron. 7. (Page 6.) What are outgoing signals on neurons called? 8. (Page 6.) On what part of the neuron are action potentials conducted? In which direction do they go? 9. (Page 6.) How are a ...
Brain Development and Behavior
... • The limbic system is a complex set of structures that lies on both sides of the thalamus, just under the cerebrum. It includes the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and several other nearby areas. ...
... • The limbic system is a complex set of structures that lies on both sides of the thalamus, just under the cerebrum. It includes the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and several other nearby areas. ...
The nervous system
... • Many of the body’s control systems belong to the general category of stimulusresponse sequences known as reflexes. ...
... • Many of the body’s control systems belong to the general category of stimulusresponse sequences known as reflexes. ...
Full Material(s)-Please Click here
... Some glial cells function primarily as the physical support for neurons. Others regulate the internal environment of the brain, especially the fluid surrounding neurons and their synapses, and nutrify neurons. During early embryogeny, glial cells direct the migration of neurons and produce molecules ...
... Some glial cells function primarily as the physical support for neurons. Others regulate the internal environment of the brain, especially the fluid surrounding neurons and their synapses, and nutrify neurons. During early embryogeny, glial cells direct the migration of neurons and produce molecules ...
Sensory neuropathy
... relays of neurons: modulation can occur at higher levels of communication between second order neurons or feed down through descending inhibitory pathways to affect local circuits in made by the primary neurons. Descending system alters responses of reflex circuits. ...
... relays of neurons: modulation can occur at higher levels of communication between second order neurons or feed down through descending inhibitory pathways to affect local circuits in made by the primary neurons. Descending system alters responses of reflex circuits. ...
Chapter 14:
... Figure 14.3 The pathway from receptors in the skin to the somatosensory receiving area of the cortex. The fiber carrying signals from a receptor in the finger enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root and then travels up the spinal cord in two pathways: the medial lemniscus and the spinothalam ...
... Figure 14.3 The pathway from receptors in the skin to the somatosensory receiving area of the cortex. The fiber carrying signals from a receptor in the finger enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root and then travels up the spinal cord in two pathways: the medial lemniscus and the spinothalam ...
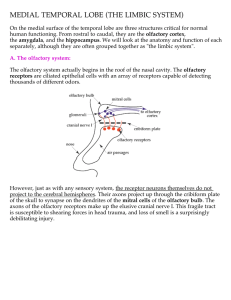
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... long-term or declarative memory, and is composed of all the facts, figures, and names you have ever learned. All of your experiences and conscious memory fall into this category. It is analogous to the hard drive of a computer. Although no one knows exactly where this enormous database is stored, it ...
... long-term or declarative memory, and is composed of all the facts, figures, and names you have ever learned. All of your experiences and conscious memory fall into this category. It is analogous to the hard drive of a computer. Although no one knows exactly where this enormous database is stored, it ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... • Interneurons work together to perform a common function (can be excitatory or inhibitory) • Each pool receives input from other neurons • Each pool generated output to other neurons ...
... • Interneurons work together to perform a common function (can be excitatory or inhibitory) • Each pool receives input from other neurons • Each pool generated output to other neurons ...
Psychology
... NB: Question is asking about pain threshold and therefore B is correct as there has been a distortion in Gerard’s perception of pain. QUESTION 7 ...
... NB: Question is asking about pain threshold and therefore B is correct as there has been a distortion in Gerard’s perception of pain. QUESTION 7 ...
Slide 1
... Responses in excitatory and inhibitory networks of firing-rate neurons. A. Response of a purely excitatory recurrent network to a square step of input (hE). The blue curve is the response without excitatory feedback. Adding recurrent excitation increases the response but makes it rise and fall more ...
... Responses in excitatory and inhibitory networks of firing-rate neurons. A. Response of a purely excitatory recurrent network to a square step of input (hE). The blue curve is the response without excitatory feedback. Adding recurrent excitation increases the response but makes it rise and fall more ...
Morphogenesis of the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus: How Singularities
... tion was triggered by the gaps. The transition surface, which passed through the gaps and was oriented roughly perpendicularly to the x axis, cut completely across the nucleus (Figure 4). Several factors were critical for the general behavior of the system. As in two dimensions, the size of the gap~ ...
... tion was triggered by the gaps. The transition surface, which passed through the gaps and was oriented roughly perpendicularly to the x axis, cut completely across the nucleus (Figure 4). Several factors were critical for the general behavior of the system. As in two dimensions, the size of the gap~ ...
B6 Brain and Mind revised - Blackpool Aspire Academy
... The CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) enables us to react to our surroundings. It consists mainly of the brain, the spinal chord, nerve cells (“neurones”) and receptors. Types of receptor: 1) Light receptors in the eyes 2) Sound receptors in the ears 3) Taste receptors on the tongue 4) Smell receptors in ...
... The CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) enables us to react to our surroundings. It consists mainly of the brain, the spinal chord, nerve cells (“neurones”) and receptors. Types of receptor: 1) Light receptors in the eyes 2) Sound receptors in the ears 3) Taste receptors on the tongue 4) Smell receptors in ...
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
... a normal person. This is because neurons start to break down and die causing a decrease in brain matter. The neurons that are affected are noticed to be in different parts of the brain. ...
... a normal person. This is because neurons start to break down and die causing a decrease in brain matter. The neurons that are affected are noticed to be in different parts of the brain. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Neuroglia - 4 types in the CNS (continued) Ependymal cells • range in shape from squamous to columnar; many are ciliated • line the dorsal body cavity housing the brain and spinal cord • form a barrier between the neurons and the rest of the body ...
... • Neuroglia - 4 types in the CNS (continued) Ependymal cells • range in shape from squamous to columnar; many are ciliated • line the dorsal body cavity housing the brain and spinal cord • form a barrier between the neurons and the rest of the body ...
Ch. 7 - The Nervous System
... a. Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system b. Connect sensory and motor neurons D. Structural Classification of Neurons 1. Multipolar neurons - many extensions from the cell body 2. Bipolar neurons - one axon and one dendrite 3. Unipolar neurons - have a short single process leaving t ...
... a. Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system b. Connect sensory and motor neurons D. Structural Classification of Neurons 1. Multipolar neurons - many extensions from the cell body 2. Bipolar neurons - one axon and one dendrite 3. Unipolar neurons - have a short single process leaving t ...
"Touch". In: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (ELS)
... patterns. The anatomical arrangement of these receptors in the fingertip skin provides a precise grid for detection of spatial features such as Braille dots. The hairy skin of the hand dorsum and the other parts of the body senses touch with hair follicle afferents, field receptors and Merkel cells. To ...
... patterns. The anatomical arrangement of these receptors in the fingertip skin provides a precise grid for detection of spatial features such as Braille dots. The hairy skin of the hand dorsum and the other parts of the body senses touch with hair follicle afferents, field receptors and Merkel cells. To ...
Nervous System
... • Neurons in the brain or spinal cord synthesize neuropeptides. • These neuropeptides act as neurotransmitters or neuromodulators. •Alter the neuron’s response to the neurotransmitter or block neurotransmitter’s release • Examples include: • Enkephalins • Beta endorphin • Substance P ...
... • Neurons in the brain or spinal cord synthesize neuropeptides. • These neuropeptides act as neurotransmitters or neuromodulators. •Alter the neuron’s response to the neurotransmitter or block neurotransmitter’s release • Examples include: • Enkephalins • Beta endorphin • Substance P ...
BIOLOGICAL AND CULTURAL SHAPING OF MIND AND BEHAVIOUR
... (3) The axon is a long fibre that leads away from the cell body. The axons send signals to the dendrites, other neurons or to muscles and glands. The axons make neural pathways in the (CNS). The axons are insulated by myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is made up of glial cells. The Nerve Impulse An infor ...
... (3) The axon is a long fibre that leads away from the cell body. The axons send signals to the dendrites, other neurons or to muscles and glands. The axons make neural pathways in the (CNS). The axons are insulated by myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is made up of glial cells. The Nerve Impulse An infor ...
A1981LQ21400002
... But there was no reason to expect the receptor to be present in the neuronal cells of brain tissue. "To support the hypothesis that the colchicine-binding receptor was important in cell division, we attempted to correlate colchicine-binding activity with mitotic index. What a surprise, then, to find ...
... But there was no reason to expect the receptor to be present in the neuronal cells of brain tissue. "To support the hypothesis that the colchicine-binding receptor was important in cell division, we attempted to correlate colchicine-binding activity with mitotic index. What a surprise, then, to find ...


![NERVOUS SYSTEM1.ppt [Recovered]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016266408_1-c10f66de9e30a67756061e0fd6bdcbe1-300x300.png)