Spindle-Like Thalamocortical Synchronization in a Rat Brain Slice
... potential recordings were obtained. Moreover, to limit possible activity-dependent variabilities in oscillation shape and/or duration, we used stimuli delivered every 10 –30 s, and we avoided the occurrence of stimuli immediately after a spontaneous oscillatory sequence. As shown in Fig. 3A, kynuren ...
... potential recordings were obtained. Moreover, to limit possible activity-dependent variabilities in oscillation shape and/or duration, we used stimuli delivered every 10 –30 s, and we avoided the occurrence of stimuli immediately after a spontaneous oscillatory sequence. As shown in Fig. 3A, kynuren ...
Remapping of Border Ownership in the Visual Cortex
... The following analysis is based on a sample of 140 neurons recorded in four hemispheres of two monkeys, which we refer to as JA (54 neurons) and JO (86 neurons). All but one of these were assigned to area V2, the other to V1. Note, however, that some of our recordings were close to the V1/V2 border, ...
... The following analysis is based on a sample of 140 neurons recorded in four hemispheres of two monkeys, which we refer to as JA (54 neurons) and JO (86 neurons). All but one of these were assigned to area V2, the other to V1. Note, however, that some of our recordings were close to the V1/V2 border, ...
Inkwell @ SMUG - Indiana University
... • Evolution of higher-order, ethological-level behaviors observed • Selection for use of vision observed • This approach to evolution of neural architectures generates a broad range of network designs ...
... • Evolution of higher-order, ethological-level behaviors observed • Selection for use of vision observed • This approach to evolution of neural architectures generates a broad range of network designs ...
Full version (PDF file)
... subfamily of CaBP. The gene for CR is located on chromosome 16 (Parmentier et al. 1991). CR is composed of 269-271 amino acid residues and contains six EF-hand domains. Four of them bind Ca2+ with high affinity in a cooperative manner, one with low affinity and the last one is non-functional, withou ...
... subfamily of CaBP. The gene for CR is located on chromosome 16 (Parmentier et al. 1991). CR is composed of 269-271 amino acid residues and contains six EF-hand domains. Four of them bind Ca2+ with high affinity in a cooperative manner, one with low affinity and the last one is non-functional, withou ...
BETA ACTIVITY: A CARRIER FOR VISUAL ATTENTION
... repetitive stimulation of the visual pathway evoked synchronous responses at the cortical level with gain depending on frequency: oscillations within relevant bands were less damped at subsequent processing levels then others. Our current results show that in the cat, cortico-geniculate feedback has ...
... repetitive stimulation of the visual pathway evoked synchronous responses at the cortical level with gain depending on frequency: oscillations within relevant bands were less damped at subsequent processing levels then others. Our current results show that in the cat, cortico-geniculate feedback has ...
PN - Neurobiologie, FU Berlin
... About equal numbers of FUAs increased and decreased rate responses (+/- stanfard deviation) More for CS+ than for CS- and Ctr. Out of 110 FUAs: 13 switched responses (mostly for CS+); 3 were recruited t o CS+, 2 did not respond to CS+ any more after conditioning. ...
... About equal numbers of FUAs increased and decreased rate responses (+/- stanfard deviation) More for CS+ than for CS- and Ctr. Out of 110 FUAs: 13 switched responses (mostly for CS+); 3 were recruited t o CS+, 2 did not respond to CS+ any more after conditioning. ...
Physiological Mechanisms of Behavior
... dimension of the discipline of psychology. A great deal of factual information is provided in this section of the course, and a variety of scientific technologies are introduced and described. Additionally, a number of biological, chemical, and physical principles are discussed throughout the course ...
... dimension of the discipline of psychology. A great deal of factual information is provided in this section of the course, and a variety of scientific technologies are introduced and described. Additionally, a number of biological, chemical, and physical principles are discussed throughout the course ...
Low vision and brain plasticity Symposium abstract
... Visual field defects are considered irreversible because the retina and optic nerve do no regenerate. Yet, there is some potential for neural repair and recovery of the visual fields. This is accomplished by the brain which analyses and interprets visual information and is able to amplify residual s ...
... Visual field defects are considered irreversible because the retina and optic nerve do no regenerate. Yet, there is some potential for neural repair and recovery of the visual fields. This is accomplished by the brain which analyses and interprets visual information and is able to amplify residual s ...
chapter 3 powerpoint
... either the neuron fires or it does not- no part way firing. • Like a gun ...
... either the neuron fires or it does not- no part way firing. • Like a gun ...
Chapter 8 - Cloudfront.net
... • A group of nerve cells in the brain or spinal cord is a nerve center. • The nerve center in the medulla oblongata of the brain stem controls your breathing. ...
... • A group of nerve cells in the brain or spinal cord is a nerve center. • The nerve center in the medulla oblongata of the brain stem controls your breathing. ...
1 Introduction to Nerve Cells and Nervous Systems
... experiments. It is the remaining ability of the nervous system that is being tested under such circumstances. Stimulation, by either electrical or chemical means,has also been much used and has been important in human studies (the brain can be stimulated in conscious patients under local anaesthesia ...
... experiments. It is the remaining ability of the nervous system that is being tested under such circumstances. Stimulation, by either electrical or chemical means,has also been much used and has been important in human studies (the brain can be stimulated in conscious patients under local anaesthesia ...
PDF
... We describe LOLLIbow, a Brainbow-based live imaging system with applications in developmental biology and neurobiology. The development of an animal, including the environmentally sensitive adaptation of its brain, is thought to proceed through continual orchestration among diverse cell types as the ...
... We describe LOLLIbow, a Brainbow-based live imaging system with applications in developmental biology and neurobiology. The development of an animal, including the environmentally sensitive adaptation of its brain, is thought to proceed through continual orchestration among diverse cell types as the ...
Live imaging of multicolor-labeled cells in Drosophila
... We describe LOLLIbow, a Brainbow-based live imaging system with applications in developmental biology and neurobiology. The development of an animal, including the environmentally sensitive adaptation of its brain, is thought to proceed through continual orchestration among diverse cell types as the ...
... We describe LOLLIbow, a Brainbow-based live imaging system with applications in developmental biology and neurobiology. The development of an animal, including the environmentally sensitive adaptation of its brain, is thought to proceed through continual orchestration among diverse cell types as the ...
Biological Cybernetics
... • Simple models explaining the rhythmicity of the EEG • Based on Wilson and Cowan model • A feedback loop through a third set of neurons – Lopes da Silva et al. • Positive and negative feedback loops with two excitatory and one inhibitory subsets of neurons – Zetterberg et al. ...
... • Simple models explaining the rhythmicity of the EEG • Based on Wilson and Cowan model • A feedback loop through a third set of neurons – Lopes da Silva et al. • Positive and negative feedback loops with two excitatory and one inhibitory subsets of neurons – Zetterberg et al. ...
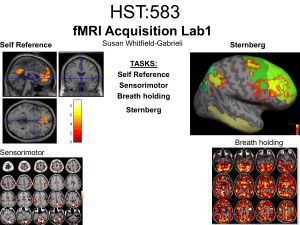
HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
... additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
... additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
Endocrine_Lecture
... This material IS testable. I would expect Multiple Choice questions, true false questions and a matching section based upon this summary. (1) Hormones are chemical signals synthesized and released by SOURCE cells/glands into the bloodstream so that they can be carried to the TARGET cells. To be a ta ...
... This material IS testable. I would expect Multiple Choice questions, true false questions and a matching section based upon this summary. (1) Hormones are chemical signals synthesized and released by SOURCE cells/glands into the bloodstream so that they can be carried to the TARGET cells. To be a ta ...
Purinergic signalling in neuroregeneration
... Purinergic signalling in neuroregeneration Purinergic signalling, adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) as an extracellular signalling molecule, was proposed in 1972 (Burnstock, 1972). However, it was not generally accepted until the early 1990s when receptors for ATP and its breakdown product adenosine w ...
... Purinergic signalling in neuroregeneration Purinergic signalling, adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) as an extracellular signalling molecule, was proposed in 1972 (Burnstock, 1972). However, it was not generally accepted until the early 1990s when receptors for ATP and its breakdown product adenosine w ...
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF NERVOUS SYSTEM DISEASES
... Ultimately, mute and paralyzed Death comes from infection ...
... Ultimately, mute and paralyzed Death comes from infection ...
B6 Brain and Mind
... When the brain is asked to do certain tasks different areas are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... When the brain is asked to do certain tasks different areas are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... hemisphere. What was the result? While he is paralyzed on his right side he grew up to have above average intelligence, completed college and grad school and is now a business executive. ...
... hemisphere. What was the result? While he is paralyzed on his right side he grew up to have above average intelligence, completed college and grad school and is now a business executive. ...
Nervous System - Mrs. Riggs Online
... multiple sclerosis (MS): body's immune system attacks glial cells; myelin sheaths deteriorate and are replaced by scar tissue which slows nerve impulses action potential [Fig 8.11 p.128]: wave of electrical activity in which a brief (+) charge sweeps through neuron and races down axon; propagated by ...
... multiple sclerosis (MS): body's immune system attacks glial cells; myelin sheaths deteriorate and are replaced by scar tissue which slows nerve impulses action potential [Fig 8.11 p.128]: wave of electrical activity in which a brief (+) charge sweeps through neuron and races down axon; propagated by ...
Mirror neurons in monkey area F5 do not adapt to the observation of
... These studies have suggested that adaptation in IT may either depend on a decrease of synaptic efficacy of the afferents carrying visual information to temporal lobe neurons8,12 or it might be the result of improved predictions of experienced visual stimuli (that is, a top–down effect), leading to de ...
... These studies have suggested that adaptation in IT may either depend on a decrease of synaptic efficacy of the afferents carrying visual information to temporal lobe neurons8,12 or it might be the result of improved predictions of experienced visual stimuli (that is, a top–down effect), leading to de ...
ANIMAL RESPONSES TO ENVIRONMENT
... environment occurs to maintain stability/balance within the organism. • Organisms sense changes in the environment as a stimulus. • These impulses are send to the brain which interpret the information and sends a different message back to the part of the body telling it how to react. ...
... environment occurs to maintain stability/balance within the organism. • Organisms sense changes in the environment as a stimulus. • These impulses are send to the brain which interpret the information and sends a different message back to the part of the body telling it how to react. ...
Nervous System
... (b–d) In axons with a myelin sheath, ions flow across the neural membrane at nodes, or small gaps between the cells that make up the sheath. Many gated channels for sodium ions are exposed to extracellular fluid at the nodes. When excitation caused by an action potential reaches a node, the gates o ...
... (b–d) In axons with a myelin sheath, ions flow across the neural membrane at nodes, or small gaps between the cells that make up the sheath. Many gated channels for sodium ions are exposed to extracellular fluid at the nodes. When excitation caused by an action potential reaches a node, the gates o ...
BAD-LAMP defines a subset of early endocytic organelles in
... site of initial contact between axons and dendrites. These vesicles, containing the different proteins necessary for proper establishment and function of synapses, are the results of complex interplay between the secretion and the endocytic membrane transport pathways (Kennedy and Ehlers, 2006). Ano ...
... site of initial contact between axons and dendrites. These vesicles, containing the different proteins necessary for proper establishment and function of synapses, are the results of complex interplay between the secretion and the endocytic membrane transport pathways (Kennedy and Ehlers, 2006). Ano ...