Nervous Systems
... extracellular ion concentrations (important when we talk about membrane potentials) • Oligodendrocytes (in the CNS) and Schwann cells (in the PNS): responsible for creating the myelin sheath on the axon ...
... extracellular ion concentrations (important when we talk about membrane potentials) • Oligodendrocytes (in the CNS) and Schwann cells (in the PNS): responsible for creating the myelin sheath on the axon ...
Ne_plas_cause
... visual, auditory and olfactory) signals that regulate social behavior, or relate then to their own affective states (moods), which regulate approach to or avoidance of other members of the group and are thus the building blocks of social interactions. They avoid other members of the group and seem a ...
... visual, auditory and olfactory) signals that regulate social behavior, or relate then to their own affective states (moods), which regulate approach to or avoidance of other members of the group and are thus the building blocks of social interactions. They avoid other members of the group and seem a ...
A1983QW37500002
... whether or not a neuron cell body projected an axon to a particular site by simple light microscopic histochemistry. Such an experiment usually took only a day or two to complete as compared to the weeks or months necessary to obtain the same kind of information using other techniques. Previously we ...
... whether or not a neuron cell body projected an axon to a particular site by simple light microscopic histochemistry. Such an experiment usually took only a day or two to complete as compared to the weeks or months necessary to obtain the same kind of information using other techniques. Previously we ...
Cellular localization of RNA expression in central and peripheral
... especially low abundance targets. And not only can RNAscope® technology be used to discern if your gene of interest is in a neuronal or glial cell, but it can also show its subcellular localization. The multiplexing capabilities of RNAscope® assay allows for detection of multiple markers at once, en ...
... especially low abundance targets. And not only can RNAscope® technology be used to discern if your gene of interest is in a neuronal or glial cell, but it can also show its subcellular localization. The multiplexing capabilities of RNAscope® assay allows for detection of multiple markers at once, en ...
Look at brain imaging article.
... detected via a wide-field camera (25, 26). One advantage of this approach is that it can acquire images of many cells simultaneously, giving higher throughput for functional imaging than otherwise possible (27) but with less depth penetration than 2P imaging. Activity or its suppression can be optic ...
... detected via a wide-field camera (25, 26). One advantage of this approach is that it can acquire images of many cells simultaneously, giving higher throughput for functional imaging than otherwise possible (27) but with less depth penetration than 2P imaging. Activity or its suppression can be optic ...
Overview of the Nervous System
... Aging and the Nervous System • Decrease in the number of neurons – Decreased brain weight and size ...
... Aging and the Nervous System • Decrease in the number of neurons – Decreased brain weight and size ...
PDF
... its core, I postulate the cell assemblies are not random, but rather should conform to the power-of-two based equation, N = 2i −1, to form the pre-configured building block termed as the functional connectivity motif (FCM). Instead of using a single neuron as the computational unit in some extremely ...
... its core, I postulate the cell assemblies are not random, but rather should conform to the power-of-two based equation, N = 2i −1, to form the pre-configured building block termed as the functional connectivity motif (FCM). Instead of using a single neuron as the computational unit in some extremely ...
Regulation of Stroke-Induced Neurogenesis in Adult Brain—Recent
... damaged striatum (Arvidsson and others 2002; Parent and others 2002; Jin and others 2003; Zhang R, Zhang Z, Wang, and others 2004), a region in which neurogenesis does not occur in the intact brain. After differentiation, a substantial proportion of the new neurons express markers characteristic of ...
... damaged striatum (Arvidsson and others 2002; Parent and others 2002; Jin and others 2003; Zhang R, Zhang Z, Wang, and others 2004), a region in which neurogenesis does not occur in the intact brain. After differentiation, a substantial proportion of the new neurons express markers characteristic of ...
The Human Body in Health and Illness
... • Electrical signals convey information along a neuron • Also called action potential • Move along sensory or motor neurons ...
... • Electrical signals convey information along a neuron • Also called action potential • Move along sensory or motor neurons ...
Module_3vs9_Final - Doral Academy Preparatory
... axon, the action potential will continue at the _________________ segment to segment to the very end of the axon ...
... axon, the action potential will continue at the _________________ segment to segment to the very end of the axon ...
Communication Workbook
... What can I do to improve: _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
... What can I do to improve: _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
Work toward real-time control of a cortical neural prothesis
... Research being conducted at Arizona State University, as a part of the NIH’s Neural Prosthesis Program, is attempting to develop a cortical motor prosthesis. The goal is to design a system to record and analyze the activity of neurons in the motor cortex, and implement this to control a robotic arm. ...
... Research being conducted at Arizona State University, as a part of the NIH’s Neural Prosthesis Program, is attempting to develop a cortical motor prosthesis. The goal is to design a system to record and analyze the activity of neurons in the motor cortex, and implement this to control a robotic arm. ...
Synaptic and cellular organization of layer 1 of the
... Cells whose regression line had a slope greater than or equal to 1 and whose sum of the Root Mean Square (RMS) error was less than 30 (mean = 28.76), were classified as Accommodating Cells. Cells whose regression line had a slope less than 1 and whose sum of the RMS errors were less than 30 (mean = ...
... Cells whose regression line had a slope greater than or equal to 1 and whose sum of the Root Mean Square (RMS) error was less than 30 (mean = 28.76), were classified as Accommodating Cells. Cells whose regression line had a slope less than 1 and whose sum of the RMS errors were less than 30 (mean = ...
Identified Serotonergic Neurons LCBI and RCBI in the Cerebral
... preparations showed positive 5-HT histofluorescence. The results of these experiments were consistent with the idea that one of the cells in the B cluster of each cerebral ganglion is a serotonergic facilitator. However, to be more confident of that conclusion, it was necessary to identify that cell ...
... preparations showed positive 5-HT histofluorescence. The results of these experiments were consistent with the idea that one of the cells in the B cluster of each cerebral ganglion is a serotonergic facilitator. However, to be more confident of that conclusion, it was necessary to identify that cell ...
The Nervous System - El Camino College
... rate as well as respiration, activate sweat glands, etc. In the diagram below you can see how the sympathetic spinal nerves are all close to each other as they exit the spinal cord – if part becomes activated, the whole system responds as well – that’s the “in sympathy” part The Parasympathetic Nerv ...
... rate as well as respiration, activate sweat glands, etc. In the diagram below you can see how the sympathetic spinal nerves are all close to each other as they exit the spinal cord – if part becomes activated, the whole system responds as well – that’s the “in sympathy” part The Parasympathetic Nerv ...
Relative sparing of primary auditory cortex in Williams Syndrome
... features include musical ability, heightened sound sensitivity, and specific patterns of auditory evoked potentials. These features have led to the hypothesis that the dorsal forebrain is more affected than the ventral. Previously, we reported primary visual area 17 abnormalities in rostral striate ...
... features include musical ability, heightened sound sensitivity, and specific patterns of auditory evoked potentials. These features have led to the hypothesis that the dorsal forebrain is more affected than the ventral. Previously, we reported primary visual area 17 abnormalities in rostral striate ...
Relative sparing of primary auditory cortex in Williams Syndrome
... features include musical ability, heightened sound sensitivity, and specific patterns of auditory evoked potentials. These features have led to the hypothesis that the dorsal forebrain is more affected than the ventral. Previously, we reported primary visual area 17 abnormalities in rostral striate ...
... features include musical ability, heightened sound sensitivity, and specific patterns of auditory evoked potentials. These features have led to the hypothesis that the dorsal forebrain is more affected than the ventral. Previously, we reported primary visual area 17 abnormalities in rostral striate ...
Ch19 Lecture
... night, may elicit an active immobility so profound that the frightened person can hardly speak or even breathe (i.e., freezing). However, if the danger source has been localized and an avenue for flight or concealment is plausible, the person will probably try to flee or hide. Actual contact with th ...
... night, may elicit an active immobility so profound that the frightened person can hardly speak or even breathe (i.e., freezing). However, if the danger source has been localized and an avenue for flight or concealment is plausible, the person will probably try to flee or hide. Actual contact with th ...
biological bases of behavior
... (hunger, thirst) and emotions such as pleasure, fear, rage, and sexuality c. Amygdala and Hippocampus- two arms surrounding the thalamus, important in how we process and perceive memory and emotion ...
... (hunger, thirst) and emotions such as pleasure, fear, rage, and sexuality c. Amygdala and Hippocampus- two arms surrounding the thalamus, important in how we process and perceive memory and emotion ...
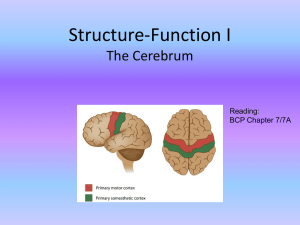
Structure-Function I
... layers differ in thickness, cell density and type pyramidal cells (output neurons; excitatory) vs stellate cells (local circuit; both excitatory and inhibitory) vertical axons and dendrites give rise to columnar organization layer thickness differs from brain area to area ...
... layers differ in thickness, cell density and type pyramidal cells (output neurons; excitatory) vs stellate cells (local circuit; both excitatory and inhibitory) vertical axons and dendrites give rise to columnar organization layer thickness differs from brain area to area ...
Biological Implementation of the Temporal Difference Algorithm for
... The actor– critic architecture (Barto et al., 1983) has the interesting property that the actor and critic units differ in only a relatively minor way that is nevertheless critical. Both units use the same neuromodulatory signal (the TD error, which has been linked to the signaling of DA neurons) an ...
... The actor– critic architecture (Barto et al., 1983) has the interesting property that the actor and critic units differ in only a relatively minor way that is nevertheless critical. Both units use the same neuromodulatory signal (the TD error, which has been linked to the signaling of DA neurons) an ...
The “Conscious” Dorsal Stream - Università degli Studi di Parma
... determines mild but consistent contralesional neglect for peri-personal space. No changes were observed in ocular saccades, pursuit and optokinetik nistagmus. Tactile stimuli applied to the contralesional side of the face also failed to elicit orienting responses. Single neurons studies showed that ...
... determines mild but consistent contralesional neglect for peri-personal space. No changes were observed in ocular saccades, pursuit and optokinetik nistagmus. Tactile stimuli applied to the contralesional side of the face also failed to elicit orienting responses. Single neurons studies showed that ...