cerebellum student copy 2010
... It is worth noting , in this regard , that each Purkinje cell receives inputs from 250,000 to 1,000,000 Mossy fibers. By contrast , each Purkinje cell receives only a single ( only one ) Climbing fiber from the inferior olive , and this fiber makes 200-3000 synapses on the Purkinje cell . Climbing f ...
... It is worth noting , in this regard , that each Purkinje cell receives inputs from 250,000 to 1,000,000 Mossy fibers. By contrast , each Purkinje cell receives only a single ( only one ) Climbing fiber from the inferior olive , and this fiber makes 200-3000 synapses on the Purkinje cell . Climbing f ...
THE NEURON
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. ...
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. ...
Action potentials
... • Sensory-motor integration is the process by which the PNS relays sensory input to the CNS; the CNS interprets this information and then sends out an appropriate motor signal to elicit the desired motor response • Sensory input can terminate at various levels of the CNS (Spinal cord, Lower regions ...
... • Sensory-motor integration is the process by which the PNS relays sensory input to the CNS; the CNS interprets this information and then sends out an appropriate motor signal to elicit the desired motor response • Sensory input can terminate at various levels of the CNS (Spinal cord, Lower regions ...
Anatomy of the Sympathetic (Thoracolumbar) Division
... running parallel to the spinal cord. These connecting branches may be referred to as interganglionic rami (ramus = branch). Together with the ganglia, they form the sympathetic trunk on either side (bilateral) of the vertebral column. Its cephalic end continues into the skull through the carotid can ...
... running parallel to the spinal cord. These connecting branches may be referred to as interganglionic rami (ramus = branch). Together with the ganglia, they form the sympathetic trunk on either side (bilateral) of the vertebral column. Its cephalic end continues into the skull through the carotid can ...
Ch 3 Biological Bases of Behavior
... impulses. These impulses are sent to your brain. Your brain "sees" the words and gives meaning to them. Your brain then decides whether or not to carry out what it has read. If it decides yes, your brain's motor cortex, a small area that exists on the outer part of your brain, calls for messages to ...
... impulses. These impulses are sent to your brain. Your brain "sees" the words and gives meaning to them. Your brain then decides whether or not to carry out what it has read. If it decides yes, your brain's motor cortex, a small area that exists on the outer part of your brain, calls for messages to ...
The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... Amobarbital Test; Language on Two Sides of the Brain? ➤ Exercises: Neuroscience and Moral Judgments; The Sensory Homunculus ➤ Project: The Human Brain Coloring Book ➤ ActivePsych: Scientific American Frontiers, 3rd ed.: Brain and Behavior: Phineas Gage Revisited and Brain Plasticity: Rewiring the Vi ...
... Amobarbital Test; Language on Two Sides of the Brain? ➤ Exercises: Neuroscience and Moral Judgments; The Sensory Homunculus ➤ Project: The Human Brain Coloring Book ➤ ActivePsych: Scientific American Frontiers, 3rd ed.: Brain and Behavior: Phineas Gage Revisited and Brain Plasticity: Rewiring the Vi ...
The promise of stem cells in the therapy of
... Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a common neurodegenerative disorder associated with gradually to dramatic neuronal death, synaptic loss and dementia, is considered to be one of the most obscure and intractable brain disorders in medicine. Currently, there is no therapy clinically available to induce marke ...
... Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a common neurodegenerative disorder associated with gradually to dramatic neuronal death, synaptic loss and dementia, is considered to be one of the most obscure and intractable brain disorders in medicine. Currently, there is no therapy clinically available to induce marke ...
ii. neuro-embryology
... Making Neuronal Connections: o Sometimes a neuron will reel out its axon as it grows. o At other times, a neuron will use physical or chemical (chemotaxis) cues to grow toward a target. Synaptic Plasticity: Modifications to neuronal connections made after development is complete. o They can be m ...
... Making Neuronal Connections: o Sometimes a neuron will reel out its axon as it grows. o At other times, a neuron will use physical or chemical (chemotaxis) cues to grow toward a target. Synaptic Plasticity: Modifications to neuronal connections made after development is complete. o They can be m ...
Elements of the nervous system
... form of heat. It depends on th size of the animals: - Heat produced by bigger animals is larger - Heat produced per body weight decreases with the size of the animal Rubner’s surface area law: heat produced by the basal metabolism of animals is proportional with their surface area rather than their ...
... form of heat. It depends on th size of the animals: - Heat produced by bigger animals is larger - Heat produced per body weight decreases with the size of the animal Rubner’s surface area law: heat produced by the basal metabolism of animals is proportional with their surface area rather than their ...
AP Psychology Brain Review- Have A Ball! Learning Target: Identify
... Option 1 “Round Robin Brain”: Each student will be given a different brain part to represent (see cards below). Students will stand in a circle so that all class members can see the brain part each person is representing. A ball will start in the center of the circle, the teacher will read the first ...
... Option 1 “Round Robin Brain”: Each student will be given a different brain part to represent (see cards below). Students will stand in a circle so that all class members can see the brain part each person is representing. A ball will start in the center of the circle, the teacher will read the first ...
Lecture 9B
... travelling lengths. Nevertheless, action potentials in the thalamic neurons arrive almost simultaneously at each target cortical neuron. This isochronicity (to within 2ms) is achieved by changing the conduction velocity within the individual axons by differential myelination (Salami M, 2003 – JC1). ...
... travelling lengths. Nevertheless, action potentials in the thalamic neurons arrive almost simultaneously at each target cortical neuron. This isochronicity (to within 2ms) is achieved by changing the conduction velocity within the individual axons by differential myelination (Salami M, 2003 – JC1). ...
An Optogenetic Approach to Understanding the Neural Circuits of Fear
... revealed a great deal about the neural mechanisms of fear learning (1–7,11–13). Despite this progress, much remains to be understood about the fundamental principles by which fear conditioning is implemented at the level of defined neural circuits. In addition, information processing by neurons in t ...
... revealed a great deal about the neural mechanisms of fear learning (1–7,11–13). Despite this progress, much remains to be understood about the fundamental principles by which fear conditioning is implemented at the level of defined neural circuits. In addition, information processing by neurons in t ...
Chapter 2
... At this stage in the developmental process, cells have been created, they have migrated into position, and they have become differentiated in their morphology by growing axons and dendrites. The next stage is for these neurons to connect up to each other, and to other structures, and form synapses. ...
... At this stage in the developmental process, cells have been created, they have migrated into position, and they have become differentiated in their morphology by growing axons and dendrites. The next stage is for these neurons to connect up to each other, and to other structures, and form synapses. ...
Photon Microscopy in Living Brain Tissue
... both stationary and moving states, in the latter instance showing an ovoid or peanut-like shape (Fig. 2A; movie 2A). Stationary T cells were mostly round (Fig. 2B, arrow) and often found in clusters showing search-like behavior (Fig. 2B; movie 2B). Cells leaving clusters initiated their movement as ...
... both stationary and moving states, in the latter instance showing an ovoid or peanut-like shape (Fig. 2A; movie 2A). Stationary T cells were mostly round (Fig. 2B, arrow) and often found in clusters showing search-like behavior (Fig. 2B; movie 2B). Cells leaving clusters initiated their movement as ...
Gaurav Anand - UMKC School of Medicine
... Figure 2: Calcein cell viability assay of cortical neurons treated with NAE 16:0 and exposed to oxidative stress. Primary rat cortical neurons were pre-treated for 1-2 hours with media, vehicle, or increasing concentrations of NAE 16:0. Cells were either exposed to oxidative stress initiated by the ...
... Figure 2: Calcein cell viability assay of cortical neurons treated with NAE 16:0 and exposed to oxidative stress. Primary rat cortical neurons were pre-treated for 1-2 hours with media, vehicle, or increasing concentrations of NAE 16:0. Cells were either exposed to oxidative stress initiated by the ...
Ions in Your Life
... excitation occurs and neurotransmitter stops being produced by the body itself. Neurotransmitters are blocked from going through reuptake transporters by original neuron. Extra excitation occurs and body stops producing neurotransmitter. ...
... excitation occurs and neurotransmitter stops being produced by the body itself. Neurotransmitters are blocked from going through reuptake transporters by original neuron. Extra excitation occurs and body stops producing neurotransmitter. ...
Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions
... B) Fibrillations: • As degeneration of the injured axon continues, the axon terminals are now separate from the main axon and hence, from each other. • Injury potentials are still generated along the terminals leading to asynchronous contraction of the individual ms fibers attached to terminals. • ...
... B) Fibrillations: • As degeneration of the injured axon continues, the axon terminals are now separate from the main axon and hence, from each other. • Injury potentials are still generated along the terminals leading to asynchronous contraction of the individual ms fibers attached to terminals. • ...
File
... • Receive inputs from multiple sensory areas • Send outputs to multiple areas, including the premotor cortex • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to ...
... • Receive inputs from multiple sensory areas • Send outputs to multiple areas, including the premotor cortex • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to ...
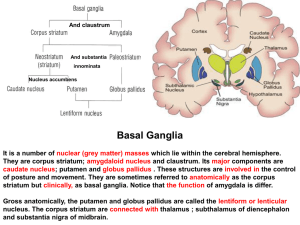
21. Basal ganglion
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
nervous system notes
... Significance of synapses Advantages: Allows transit of Impulses. Permit impulses in one direction only – neurotransmitters only present on one side of the synapse. Allow localisation of a response rather than a total body response (chaos!). Protect against over-stimulation, as they will slow ...
... Significance of synapses Advantages: Allows transit of Impulses. Permit impulses in one direction only – neurotransmitters only present on one side of the synapse. Allow localisation of a response rather than a total body response (chaos!). Protect against over-stimulation, as they will slow ...
CMM/BIO4350
... Closure of neural tube have around 125,000 cells. At birth, the human brain contains around 100 billion neurons We can infer from this information that new neurons are being generated at the rate of about 250,000 per minute during the nine months of gestation. (Cowan, 1979) ...
... Closure of neural tube have around 125,000 cells. At birth, the human brain contains around 100 billion neurons We can infer from this information that new neurons are being generated at the rate of about 250,000 per minute during the nine months of gestation. (Cowan, 1979) ...
Presentation 5: The Role of the Nervous System
... Filled with fluid and intrafusal muscle fibers Nucleated and supplied with afferent neuron ...
... Filled with fluid and intrafusal muscle fibers Nucleated and supplied with afferent neuron ...