The Fine Structure of Slow-Wave Sleep Oscillations: from Single
... particular, the deafferented RE nucleus in vivo can exhibit spindle rhythmicity in extracellular recordings. In contrast, the RE nucleus does not display autonomous oscillations in vitro, but spindles have been observed in thalamic slices based on TCRE interactions (see Steriade et al. 1997 a detail ...
... particular, the deafferented RE nucleus in vivo can exhibit spindle rhythmicity in extracellular recordings. In contrast, the RE nucleus does not display autonomous oscillations in vitro, but spindles have been observed in thalamic slices based on TCRE interactions (see Steriade et al. 1997 a detail ...
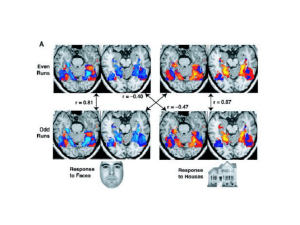
Visuospatial processing and the right
... speech and dominates language functions, has greater fine motor control, and superior cognitive abilities in general. Split-brain researchers have suggested that the left hemisphere often over-rules the right, even when it does not possess task-relevant information, and that it is ‘‘in control’’ most ...
... speech and dominates language functions, has greater fine motor control, and superior cognitive abilities in general. Split-brain researchers have suggested that the left hemisphere often over-rules the right, even when it does not possess task-relevant information, and that it is ‘‘in control’’ most ...
Contributions of the Basal Amygdala Nuclei to Conditioned Fear
... aid breathing. In aseptic conditions, rats were placed in a stereotaxic apparatus with nonpuncture ear bars. A local anesthetic (bupivacaine, subcutaneous) was injected in the region to be incised. The scalp was incised, small holes were drilled in the skull above the amygdala, and movable bundles o ...
... aid breathing. In aseptic conditions, rats were placed in a stereotaxic apparatus with nonpuncture ear bars. A local anesthetic (bupivacaine, subcutaneous) was injected in the region to be incised. The scalp was incised, small holes were drilled in the skull above the amygdala, and movable bundles o ...
Evidence for topographically organized endogenous 5‐HT‐1A
... on the left. Bars depict average number of TPOH-containing cells dually labeled with Fos per section for different groups + SEM (C, control; W, WAY-100635; S, swim; S+W, swim + WAY-100635). Each area was analyzed with a 2 · 2 factorial anova. Significant differences as compared to controls as determi ...
... on the left. Bars depict average number of TPOH-containing cells dually labeled with Fos per section for different groups + SEM (C, control; W, WAY-100635; S, swim; S+W, swim + WAY-100635). Each area was analyzed with a 2 · 2 factorial anova. Significant differences as compared to controls as determi ...
Developmental mechanics of the primate cerebral cortex
... plate with the sub-plate during development (Armstrong et al. 1995). However, these general factors do not explain the specific placement, orientation, and characteristic shape of convolutions. Thus, it has been suggested that convolutions could be formed individually by tailored growth processes (We ...
... plate with the sub-plate during development (Armstrong et al. 1995). However, these general factors do not explain the specific placement, orientation, and characteristic shape of convolutions. Thus, it has been suggested that convolutions could be formed individually by tailored growth processes (We ...
Neuropeptide-Mediated Facilitation and Inhibition of Sensory Inputs
... GABAB agonists] were studied on reflex responses evoked by cutaneous stimulation in the lamprey. Reflex responses were elicited in an isolated spinal cord preparation by electrical stimulation of the attached tail fin. To be able to separate modulator-induced effects at the sensory level from that a ...
... GABAB agonists] were studied on reflex responses evoked by cutaneous stimulation in the lamprey. Reflex responses were elicited in an isolated spinal cord preparation by electrical stimulation of the attached tail fin. To be able to separate modulator-induced effects at the sensory level from that a ...
Electrical stimulation of neural tissue to evoke behavioral responses
... overlap. When the stimulation fields begin to overlap (at short interpulse intervals), the fibers exhibiting refractoriness should be those with low current-distance constants. When the stimulation fields are overlapped considerably, the fibers exhibiting refractoriness should include those with low ...
... overlap. When the stimulation fields begin to overlap (at short interpulse intervals), the fibers exhibiting refractoriness should be those with low current-distance constants. When the stimulation fields are overlapped considerably, the fibers exhibiting refractoriness should include those with low ...
PDF
... The AN was stimulated with a bipolar stainless steel electrode inserted into the nerve stump. The stimulation protocol consisted of presenting rectangular (monophasic or biphasic) electrical pulses of 0.2-ms duration in 50-ms trains with pulse rates of 100, 200, 300, 500, 800 and 1000 pps. The time ...
... The AN was stimulated with a bipolar stainless steel electrode inserted into the nerve stump. The stimulation protocol consisted of presenting rectangular (monophasic or biphasic) electrical pulses of 0.2-ms duration in 50-ms trains with pulse rates of 100, 200, 300, 500, 800 and 1000 pps. The time ...
NIH Public Access
... cells nmol/L concentrations of α-tocotrienol (TCT), but not α-tocopherol (TCP), blocked glutamateinduced death by suppressing early activation of c-Src kinase (J Biol Chem 275:13049) and 12lipoxygenase (12-Lox;J Biol Chem 278:43508). Methods—Single neuron microinjection technique was employed to com ...
... cells nmol/L concentrations of α-tocotrienol (TCT), but not α-tocopherol (TCP), blocked glutamateinduced death by suppressing early activation of c-Src kinase (J Biol Chem 275:13049) and 12lipoxygenase (12-Lox;J Biol Chem 278:43508). Methods—Single neuron microinjection technique was employed to com ...
Leap 2 - Entire - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... known as the axon tip or terminal. There is not a direct connection between the axon tip of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Surprisingly, a gap (synapse) exists (Figure 3). The impulse is in an electrical form when it reaches the synapse and cannot cross in that form. What happens to ...
... known as the axon tip or terminal. There is not a direct connection between the axon tip of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Surprisingly, a gap (synapse) exists (Figure 3). The impulse is in an electrical form when it reaches the synapse and cannot cross in that form. What happens to ...
ppt - BIAC – Duke
... In this period of intense research in the neurosciences, nothing is more promising than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) methods, which localize brain activities. These functional imaging methodologies map neurophysiological responses to cognitive, ...
... In this period of intense research in the neurosciences, nothing is more promising than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) methods, which localize brain activities. These functional imaging methodologies map neurophysiological responses to cognitive, ...
Responses to stimulating multiple inputs
... 12) (6 pts) Many sensory systems use a ‘range-fractionated’ coding scheme. What are 3 main features of range-fractionated coding that distinguish it from other coding schemes? (consider the nature of the stimulus that is being encoded, and the receptive fields of the sensory cells). ...
... 12) (6 pts) Many sensory systems use a ‘range-fractionated’ coding scheme. What are 3 main features of range-fractionated coding that distinguish it from other coding schemes? (consider the nature of the stimulus that is being encoded, and the receptive fields of the sensory cells). ...
Synchronisation hubs in the visual cortex may arise from strong
... responses, we computed the oscillation score, as described previously (Muresan et al., 2008). In brief, this measure is based on analysing the power spectrum of autocorrelation histograms (ACHs) computed with 1-ms resolution (see below). The oscillation score is defined as the ratio between the peak ...
... responses, we computed the oscillation score, as described previously (Muresan et al., 2008). In brief, this measure is based on analysing the power spectrum of autocorrelation histograms (ACHs) computed with 1-ms resolution (see below). The oscillation score is defined as the ratio between the peak ...
Lack of response suppression follows repeated ventral tegmental
... Abstract—Cannabinoid compounds have been reported to excite ventral tegmental neurons through activation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors. More recently, biochemical and whole-cell voltage-clamp studies carried out on CB1-transfected AtT20 cells have shown a rapid desensitization of these receptors foll ...
... Abstract—Cannabinoid compounds have been reported to excite ventral tegmental neurons through activation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors. More recently, biochemical and whole-cell voltage-clamp studies carried out on CB1-transfected AtT20 cells have shown a rapid desensitization of these receptors foll ...
Broca`s Area in Language, Action, and Music
... monkey acts on an object and when it observes another monkey or the experimenter making a similar goal-directed action, therefore being identical to canonical neurons in terms of motor properties. However, mirror neurons radically differ from canonical neurons as far as visual properties are concern ...
... monkey acts on an object and when it observes another monkey or the experimenter making a similar goal-directed action, therefore being identical to canonical neurons in terms of motor properties. However, mirror neurons radically differ from canonical neurons as far as visual properties are concern ...
Print
... Phillips and Irvine 1982; Phillips and Orman 1984; Rauschecker et al. 1995, 1997); these appear physiologically as gradient reversals in tonotopic organization or by the virtual absence of tonotopic organization (Merzenich and Schreiner 1992; Rauschecker et al. 1995, 1997; Schreiner and Cynader 1984 ...
... Phillips and Irvine 1982; Phillips and Orman 1984; Rauschecker et al. 1995, 1997); these appear physiologically as gradient reversals in tonotopic organization or by the virtual absence of tonotopic organization (Merzenich and Schreiner 1992; Rauschecker et al. 1995, 1997; Schreiner and Cynader 1984 ...
Anatomy Review - Interactive Physiology
... ________ or __________, and the signal can be modified as it passes from one neuron to the next. a. electrical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory b. chemical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory 29. (Page 7.) Chemical synapses are the most common type of ________, and they are associated with the most com ...
... ________ or __________, and the signal can be modified as it passes from one neuron to the next. a. electrical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory b. chemical synapses, excitatory, inhibitory 29. (Page 7.) Chemical synapses are the most common type of ________, and they are associated with the most com ...
the premotor cortex of the monkey
... (Macaca mulatta), 7 and 9 kg, were used in the present experiments. Although the motor tasks for the two monkeys were somewhat different, the basic behavioral patterns were comparable. The description of methods and results will focus on one of these animals. However, all of the conclusions and obse ...
... (Macaca mulatta), 7 and 9 kg, were used in the present experiments. Although the motor tasks for the two monkeys were somewhat different, the basic behavioral patterns were comparable. The description of methods and results will focus on one of these animals. However, all of the conclusions and obse ...
Topography of Modular Subunits in the Mushroom Bodies of the
... particular slab throughout the length of the pedunculus and the lobes. Thus, the sheet is a component forming the slab. In the pedunculus and the b lobe, a class of Golgi-impregnated extrinsic neurons exhibit segmented dendritelike arbors that interact with every other slab, i.e., either with only d ...
... particular slab throughout the length of the pedunculus and the lobes. Thus, the sheet is a component forming the slab. In the pedunculus and the b lobe, a class of Golgi-impregnated extrinsic neurons exhibit segmented dendritelike arbors that interact with every other slab, i.e., either with only d ...
The Beautiful Brain - Weisman Art Museum
... discoveries was the idea that the brain is made up of individual cells called neurons. The most commonly held idea among scientists of Cajal’s time was that the brain was a continuous, interconnected network. All research on the brain and brain related diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, ...
... discoveries was the idea that the brain is made up of individual cells called neurons. The most commonly held idea among scientists of Cajal’s time was that the brain was a continuous, interconnected network. All research on the brain and brain related diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, ...
PDF
... from the venom of Vipera russelli, on the growth of dispersed cells from the sensory ganglia of the embryonic chick. The main effects were to increase the viability of the sensory neurons in culture and to promote the regeneration of nerve fibres. In the presence of NGF a higher proportion of neuron ...
... from the venom of Vipera russelli, on the growth of dispersed cells from the sensory ganglia of the embryonic chick. The main effects were to increase the viability of the sensory neurons in culture and to promote the regeneration of nerve fibres. In the presence of NGF a higher proportion of neuron ...
Nociceptive sensation
... Pain reception Damage stimuli perception created by the brain from electrochemical nerve impulses delivered to it from sensory receptors. These receptors transfuse (or change) different influences of both internal processes in organism and surrounding environment into the electric impulses. ► Pai ...
... Pain reception Damage stimuli perception created by the brain from electrochemical nerve impulses delivered to it from sensory receptors. These receptors transfuse (or change) different influences of both internal processes in organism and surrounding environment into the electric impulses. ► Pai ...
the neural impulse
... A neuron, or nerve cell, is the most basic component of the nervous system (Figure 1). To understand how neurons send messages, it is important to become familiar with their specialized structures. The soma (or cell body) is the neuron’s control centre. It contains the nucleus and other organelles w ...
... A neuron, or nerve cell, is the most basic component of the nervous system (Figure 1). To understand how neurons send messages, it is important to become familiar with their specialized structures. The soma (or cell body) is the neuron’s control centre. It contains the nucleus and other organelles w ...
Two different lateral amygdala cell populations contribute to the
... Persistence of conditioned response The averaged neural response of plastic cells reached maximum levels during the first two 4-trial blocks of conditioning, and then tended to diminish during later conditioning trials (Fig. 5b). To determine how individual cells contributed to this pattern, a ‘pers ...
... Persistence of conditioned response The averaged neural response of plastic cells reached maximum levels during the first two 4-trial blocks of conditioning, and then tended to diminish during later conditioning trials (Fig. 5b). To determine how individual cells contributed to this pattern, a ‘pers ...