Trends Towards Progress of Brains and Sense Organs
... we must confess that a classification is very difficult. We can only distinguish between general and more specific trends. The former are of much greater interest for the understanding of evolution as they govern the development of many branches of the phylogeny of animals. However, by using the ter ...
... we must confess that a classification is very difficult. We can only distinguish between general and more specific trends. The former are of much greater interest for the understanding of evolution as they govern the development of many branches of the phylogeny of animals. However, by using the ter ...
Eye Movements - Center for Neural Science
... evolved specialized retinas that can be effectively employed only if the direction of gaze can be shifted. Primates, for example, have a highly specialized central region of the retina known as the fovea. The fovea can gather visual information from only 18 of the visual world, but the photoreceptor ...
... evolved specialized retinas that can be effectively employed only if the direction of gaze can be shifted. Primates, for example, have a highly specialized central region of the retina known as the fovea. The fovea can gather visual information from only 18 of the visual world, but the photoreceptor ...
Effect of Tactile Inputs on Thalamic Responses to Noxious
... colorectal sensory processing is more important than that of the ventrolateral pathways to the thalamic ventrobasal complex. Most DC-ML neurons that respond to visceral painful stimuli are also sensitive to gentle skin manipulation, such as brushing (Al-Chaer et al. 1996a,b, 1997a, 1998); therefore ...
... colorectal sensory processing is more important than that of the ventrolateral pathways to the thalamic ventrobasal complex. Most DC-ML neurons that respond to visceral painful stimuli are also sensitive to gentle skin manipulation, such as brushing (Al-Chaer et al. 1996a,b, 1997a, 1998); therefore ...
Differential Temporal Storage Capacity in the Baseline Activity of
... the central spot on the display during this period and they had no information about the forthcoming array, baseline activity was virtually free of any specific eye movements and visual stimulus. This allowed us to examine temporal storage capacity under conditions when visual sensory stimuli and ey ...
... the central spot on the display during this period and they had no information about the forthcoming array, baseline activity was virtually free of any specific eye movements and visual stimulus. This allowed us to examine temporal storage capacity under conditions when visual sensory stimuli and ey ...
THE REGULATION OF SLEEP AND WAKEFULNESS BY THE
... toxin (TTC) and the cholera toxin B subunit (CT-B), were utilized to show synaptic connections involving orexin neurons. Sakurai et al. (2005) generated a transgenic mouse line expressing a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labeled TTC. The construct was expressed exclusively in orexin neurons using t ...
... toxin (TTC) and the cholera toxin B subunit (CT-B), were utilized to show synaptic connections involving orexin neurons. Sakurai et al. (2005) generated a transgenic mouse line expressing a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labeled TTC. The construct was expressed exclusively in orexin neurons using t ...
The Science of Psychology
... the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the involuntary muscles, organs, and glands sensory pathway nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS consisting of sensory neurons. • Sympathetic division (fight-or-flight system) - part of the ANS that is responsible for reacting to stressful ...
... the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the involuntary muscles, organs, and glands sensory pathway nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS consisting of sensory neurons. • Sympathetic division (fight-or-flight system) - part of the ANS that is responsible for reacting to stressful ...
Learning Innate Face Preferences
... addition to the primary visual cortex. The same model allows preferences for low-level features such as orientation or spatial frequency, and high-level features such as faces. to be compared, in order to account for the different categories of preferences found in experiments with newborns. Very fe ...
... addition to the primary visual cortex. The same model allows preferences for low-level features such as orientation or spatial frequency, and high-level features such as faces. to be compared, in order to account for the different categories of preferences found in experiments with newborns. Very fe ...
Neurotransmitter Parameter Definitions
... Taurine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in neuromodulatory and neuroprotective actions. Supplementing with taurine can have a specific effect on GABA function.There are two primary ways in which taurine affects GABA.; First, it can inhibit GABA transaminase, an enzyme that metabolizes GAB ...
... Taurine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in neuromodulatory and neuroprotective actions. Supplementing with taurine can have a specific effect on GABA function.There are two primary ways in which taurine affects GABA.; First, it can inhibit GABA transaminase, an enzyme that metabolizes GAB ...
General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal
... mice, to test the importance of the receptor to the in vivo anaesthetic phenotype18–20. Because anaesthetic binding potentiates the actions of GABA, any anaesthetic-binding site must also be closely coupled to receptor gating. Consequently, it is difficult to identify anaesthetic-binding sites by st ...
... mice, to test the importance of the receptor to the in vivo anaesthetic phenotype18–20. Because anaesthetic binding potentiates the actions of GABA, any anaesthetic-binding site must also be closely coupled to receptor gating. Consequently, it is difficult to identify anaesthetic-binding sites by st ...
Contribution of Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Neurons to
... cerebellar peduncle, and reached PPTN. PPTN was located 3–5 mm lateral from midline and 3–7 mm deeper than where auditory responses were observed. We recorded single units in that location and confirmed high-frequency tonic fiber activity (⬎20 Hz) within 3–5 mm from single units, since PPTN is close ...
... cerebellar peduncle, and reached PPTN. PPTN was located 3–5 mm lateral from midline and 3–7 mm deeper than where auditory responses were observed. We recorded single units in that location and confirmed high-frequency tonic fiber activity (⬎20 Hz) within 3–5 mm from single units, since PPTN is close ...
projecting to oculomotor regions of the pons Activity of monkey
... frontal eye field caused omnipause neurons to stop firing. The cessation in firing appeared to be immediate, within ~5 ms. The time that the omnipause neuron remained quiet depended on the intensity of the cortical stimulus and lasted up to 30 ms after a train of three stimulus pulses lasting a tota ...
... frontal eye field caused omnipause neurons to stop firing. The cessation in firing appeared to be immediate, within ~5 ms. The time that the omnipause neuron remained quiet depended on the intensity of the cortical stimulus and lasted up to 30 ms after a train of three stimulus pulses lasting a tota ...
Rebound spiking properties of mouse medial entorhinal cortex neurons in vivo NEUROSYSTEMS
... Fig. 3. Hyperpolarizing current stimulation at specific input phases of the oscillation increased the probability of subsequent spikes at the peak of the oscillation in some neurons. (A) Polar plot of the input phase of hyperpolarizing current stimulation that elicited subsequent spikes of a putative ...
... Fig. 3. Hyperpolarizing current stimulation at specific input phases of the oscillation increased the probability of subsequent spikes at the peak of the oscillation in some neurons. (A) Polar plot of the input phase of hyperpolarizing current stimulation that elicited subsequent spikes of a putative ...
Firing characteristics of deep layer neurons in prefrontal cortex in
... trial (eight correct arm choices) all arms were made inaccessible so that the animal had to wait at the center platform until the next trial. The animals typically ran 10 trials within 30 min. (B) Figure-eight maze, delayed spatial alternation task. Starting from the center of the maze, the animal h ...
... trial (eight correct arm choices) all arms were made inaccessible so that the animal had to wait at the center platform until the next trial. The animals typically ran 10 trials within 30 min. (B) Figure-eight maze, delayed spatial alternation task. Starting from the center of the maze, the animal h ...
Skeletal System
... Recall that the somatic motor system innervates skeletal muscles Each somatic motor neuron runs from the central nervous system all the way to the muscle being innervated, and that each motor unit consists of a single neuron plus the skeletal muscle cells it innervates Typical somatic motor axons ar ...
... Recall that the somatic motor system innervates skeletal muscles Each somatic motor neuron runs from the central nervous system all the way to the muscle being innervated, and that each motor unit consists of a single neuron plus the skeletal muscle cells it innervates Typical somatic motor axons ar ...
Antennal Mechanosensory Neurons Mediate Wing Motor Reflexes
... the subset of these neurons that are driven by the JO-AB or JO-CE GAL4 driver. This intersectional strategy has been used successfully in a previous study to genetically ablate JO neurons (Yorozu et al., 2009). To further validate the selective expression of ricin A and the lack of leaky expression ...
... the subset of these neurons that are driven by the JO-AB or JO-CE GAL4 driver. This intersectional strategy has been used successfully in a previous study to genetically ablate JO neurons (Yorozu et al., 2009). To further validate the selective expression of ricin A and the lack of leaky expression ...
Slide 1
... controls their timing (reviewed by Deurveilher and Semba, 2005) Without photic stimulation or nonphotic zeitgebers, circadian rhythm is freerunning: SCN is an endogenous pacemaker Transgenic mice that lack rods and cones are functionally blind but are still able to show photic entrainment (reviewe ...
... controls their timing (reviewed by Deurveilher and Semba, 2005) Without photic stimulation or nonphotic zeitgebers, circadian rhythm is freerunning: SCN is an endogenous pacemaker Transgenic mice that lack rods and cones are functionally blind but are still able to show photic entrainment (reviewe ...
CELL MIGRATION IN THE FOREBRAIN
... of highly coordinated stages and is thought to involve at least two different modes of cell movement. The first cohort of neurons that migrate out of the cortical VZ constitutes the preplate (reviewed in Allendoerfer & Shatz 1994), originally described in Golgi-stained preparations as the primordial ...
... of highly coordinated stages and is thought to involve at least two different modes of cell movement. The first cohort of neurons that migrate out of the cortical VZ constitutes the preplate (reviewed in Allendoerfer & Shatz 1994), originally described in Golgi-stained preparations as the primordial ...
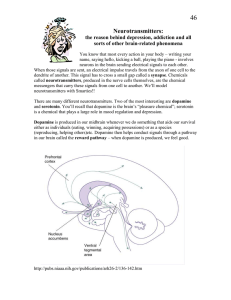
Neurotransmitters:
... We’ll arrange some of our neurons as part of a dopamine pathway. Using your neuron models, try to model these steps in the normal dopamine process: 1. Dopamine is made in a cell body. 2. Dopamine travels down the axon to the synapse. 3. Dopamine is released from the cell and floats into the synapse. ...
... We’ll arrange some of our neurons as part of a dopamine pathway. Using your neuron models, try to model these steps in the normal dopamine process: 1. Dopamine is made in a cell body. 2. Dopamine travels down the axon to the synapse. 3. Dopamine is released from the cell and floats into the synapse. ...
Chapter 15
... • how can different autonomic neurons have different effects? constricting some vessels but dilating others – effects determined by types of neurotransmitters released and types of receptors found on target cells ...
... • how can different autonomic neurons have different effects? constricting some vessels but dilating others – effects determined by types of neurotransmitters released and types of receptors found on target cells ...
accepted manuscript - Radboud Repository
... in humans is involved in a multiplicity of higher functions, such as face (Haxby et al., 2000) and word (Xue et al., 2010) recognition. As a consequence, topographic assignment is not always informative about the functional role of a particular brain area, which may be partially due to the poor and ...
... in humans is involved in a multiplicity of higher functions, such as face (Haxby et al., 2000) and word (Xue et al., 2010) recognition. As a consequence, topographic assignment is not always informative about the functional role of a particular brain area, which may be partially due to the poor and ...
Mesodermal and neuronal retinoids regulate the induction and
... neurons (Jessell, 2000). All motor neurons derive from a distinct ventral progenitor domain, set up in part by sonic hedgehog secreted by the notochord and floorplate (Jessell, 2000; Shirasaki and Pfaff, 2002; Price and Briscoe, 2004). The cell bodies of motor neurons are organized into distinct col ...
... neurons (Jessell, 2000). All motor neurons derive from a distinct ventral progenitor domain, set up in part by sonic hedgehog secreted by the notochord and floorplate (Jessell, 2000; Shirasaki and Pfaff, 2002; Price and Briscoe, 2004). The cell bodies of motor neurons are organized into distinct col ...
Parallel Processing of Appetitive Short- and Long
... [22, 24] and in ab neurons to form LTM [24], suggesting an independence of these two memory phases. However, several results suggest that aversive STM and LTM are not processed by fully independent neuronal pathways. Thus, a more efficient rescue of rut STM or LTM defect is observed when RUT is expr ...
... [22, 24] and in ab neurons to form LTM [24], suggesting an independence of these two memory phases. However, several results suggest that aversive STM and LTM are not processed by fully independent neuronal pathways. Thus, a more efficient rescue of rut STM or LTM defect is observed when RUT is expr ...
Centrosome Motility Is Essential for Initial Axon Formation in the Neocortex
... the HSN motor neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans (Adler et al., 2006). Several studies have also demonstrated that efficient axonal growth is dependent on extracellular contact (Polleux et al., 1998; Esch et al., 1999; Hilliard and Bargmann, 2006; Prasad and Clark, 2006; Shelly et al., 2007; Zhang et ...
... the HSN motor neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans (Adler et al., 2006). Several studies have also demonstrated that efficient axonal growth is dependent on extracellular contact (Polleux et al., 1998; Esch et al., 1999; Hilliard and Bargmann, 2006; Prasad and Clark, 2006; Shelly et al., 2007; Zhang et ...
The role of mirror neurons in cognition
... With this thesis I strive to open the debate and point the reader towards a critical reconsideration of what we currently know and think about the mirror neurons. I commence my efforts by providing a thorough introduction to the neurobiological background of the primate action observation–execution ...
... With this thesis I strive to open the debate and point the reader towards a critical reconsideration of what we currently know and think about the mirror neurons. I commence my efforts by providing a thorough introduction to the neurobiological background of the primate action observation–execution ...
Millisecond Timescale Synchrony among Hippocampal Neurons
... power was selected for cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) calculations, whereas one electrode with maximal power between 25 and 90 Hz was selected for subsequent ␥ detection on each shank, to ensure that the oscillation was local. To determine CA3 ␥ phase for CA1 units, we used the electrode corresponding to t ...
... power was selected for cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) calculations, whereas one electrode with maximal power between 25 and 90 Hz was selected for subsequent ␥ detection on each shank, to ensure that the oscillation was local. To determine CA3 ␥ phase for CA1 units, we used the electrode corresponding to t ...