the Handout set ( format)
... Equation of a Straight Line passing through two known points Say the points are (p,q) and (r,s) The equation will be of the form ax – by = c, where a, b and c have to be found Procedure: 1. To find a, i.e. coefficient of x, find the difference of y coordinates [q – s] 2. To find b, i.e. coefficient ...
... Equation of a Straight Line passing through two known points Say the points are (p,q) and (r,s) The equation will be of the form ax – by = c, where a, b and c have to be found Procedure: 1. To find a, i.e. coefficient of x, find the difference of y coordinates [q – s] 2. To find b, i.e. coefficient ...
3-6 Solving Equations Containing Decimals
... 40-yard dashes as part of a fitness test. The slowest time in the class was 3.84 seconds slower than the fastest time of 7.2 seconds. ...
... 40-yard dashes as part of a fitness test. The slowest time in the class was 3.84 seconds slower than the fastest time of 7.2 seconds. ...
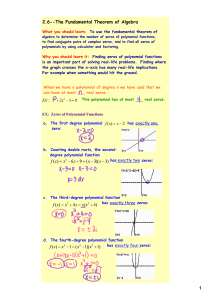
5.7 Introduction to Square Roots
... Fractions and Decimals We can also find square roots of fractions and decimals. You Try It! Simplify: q ...
... Fractions and Decimals We can also find square roots of fractions and decimals. You Try It! Simplify: q ...
FINITE FIELDS OF THE FORM GF(p)
... Let set S of polynomial coefficients is a finite field Zp, and polynomials have degree from 0 to n-1. There are totally pn different such polynomials. The definition consists of the following elements: 1. Arithmetic follows the ordinary rules of polynomial arithmetic using the basic rules of algebra ...
... Let set S of polynomial coefficients is a finite field Zp, and polynomials have degree from 0 to n-1. There are totally pn different such polynomials. The definition consists of the following elements: 1. Arithmetic follows the ordinary rules of polynomial arithmetic using the basic rules of algebra ...
FINITE FIELDS OF THE FORM GF(p)
... Let set S of polynomial coefficients is a finite field Zp, and polynomials have degree from 0 to n-1. There are totally pn different such polynomials. The definition consists of the following elements: 1. Arithmetic follows the ordinary rules of polynomial arithmetic using the basic rules of algebra ...
... Let set S of polynomial coefficients is a finite field Zp, and polynomials have degree from 0 to n-1. There are totally pn different such polynomials. The definition consists of the following elements: 1. Arithmetic follows the ordinary rules of polynomial arithmetic using the basic rules of algebra ...
Robust Ray Intersection with Interval Arithmetic
... F(x, y, z) = F(S x + tD x , S y + tD y , S z + tD z ) ...
... F(x, y, z) = F(S x + tD x , S y + tD y , S z + tD z ) ...
Guidelines for Equations, Units, and Mathematical Notation 1
... B. The standard free energy change for a reversible reaction is related to its equilibrium constant K at a given temperature T as ∆G° = –RTlnK, where R is the gas constant. ...
... B. The standard free energy change for a reversible reaction is related to its equilibrium constant K at a given temperature T as ∆G° = –RTlnK, where R is the gas constant. ...