6.1 Solving Equations by Using Inverse Operations
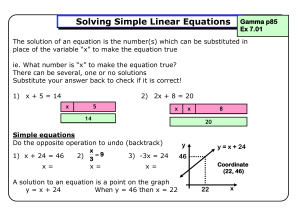
... Lesson 1 – 6.1 Solving Equations by Using Inverse Operations What is an equation? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ You can use ____________________________ to solve equations. For example: ...
... Lesson 1 – 6.1 Solving Equations by Using Inverse Operations What is an equation? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ You can use ____________________________ to solve equations. For example: ...
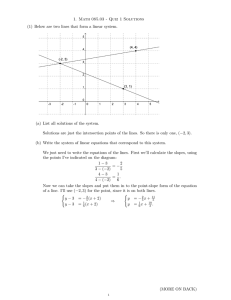
Review for System of Equations Quiz 1. Which ordered pair is the
... Name: ___________________________________________ ...
... Name: ___________________________________________ ...
Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables
... A linear equation in three variables x, y, and z is an equation of the form Ax + By + Cz = D , where A, B, C, and D are real numbers with A, B, and C not all equal to zero. (For example, x + 2y + z = 6) A solution to a linear equation in three variables is an ordered triple of real numbers in the fo ...
... A linear equation in three variables x, y, and z is an equation of the form Ax + By + Cz = D , where A, B, C, and D are real numbers with A, B, and C not all equal to zero. (For example, x + 2y + z = 6) A solution to a linear equation in three variables is an ordered triple of real numbers in the fo ...
Unit 1 Assignment 7 Notes
... 2. If there are any parentheses, remove them by using the distributive property 3. Combine any like terms that are on the same side of the equation 4. Sort variables to one side and numbers (constants) to the other side of the equation by adding or subtracting terms. 5. Divide both sides by the coef ...
... 2. If there are any parentheses, remove them by using the distributive property 3. Combine any like terms that are on the same side of the equation 4. Sort variables to one side and numbers (constants) to the other side of the equation by adding or subtracting terms. 5. Divide both sides by the coef ...
Equation

In mathematics, an equation is an equality containing one or more variables. Solving the equation consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. In this situation, variables are also known as unknowns and the values which satisfy the equality are known as solutions. An equation differs from an identity in that an equation is not necessarily true for all possible values of the variable.There are many types of equations, and they are found in all areas of mathematics; the techniques used to examine them differ according to their type.Algebra studies two main families of equations: polynomial equations and, among them, linear equations. Polynomial equations have the form P(X) = 0, where P is a polynomial. Linear equations have the form a(x) + b = 0, where a is a linear function and b is a vector. To solve them, one uses algorithmic or geometric techniques, coming from linear algebra or mathematical analysis. Changing the domain of a function can change the problem considerably. Algebra also studies Diophantine equations where the coefficients and solutions are integers. The techniques used are different and come from number theory. These equations are difficult in general; one often searches just to find the existence or absence of a solution, and, if they exist, to count the number of solutions.Geometry uses equations to describe geometric figures. The objective is now different, as equations are used to describe geometric properties. In this context, there are two large families of equations, Cartesian equations and parametric equations.Differential equations are equations involving one or more functions and their derivatives. They are solved by finding an expression for the function that does not involve derivatives. Differential equations are used to model real-life processes in areas such as physics, chemistry, biology, and economics.The ""="" symbol was invented by Robert Recorde (1510–1558), who considered that nothing could be more equal than parallel straight lines with the same length.