
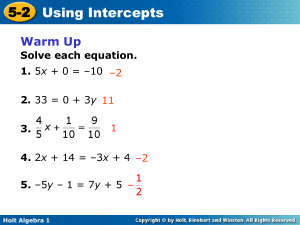
Sec 4.5
... The Equations: a sinx + b = c and a cosx + b = c If the sine or cosine is not isolated (i.e. all by itself on one side of the equation) carry out the algebra to isolate the sine or cosine. Solve: 2 cos(5 x) 2 0 2 cos(5 x) 2 0 2 cos(5 x) 2 cos(5 x) ...
... The Equations: a sinx + b = c and a cosx + b = c If the sine or cosine is not isolated (i.e. all by itself on one side of the equation) carry out the algebra to isolate the sine or cosine. Solve: 2 cos(5 x) 2 0 2 cos(5 x) 2 0 2 cos(5 x) 2 cos(5 x) ...
Mathematics Set 3 Yearly Overview Mr Jones
... Use formulae and equations (algebra) to solve problems. (see also week 7). Solve simple linear equations. Week 6 Consolidate the rapid recall of number facts, including multiplication facts to 12 × 12 and the associated division facts Week 7 Generate sequences and describe the general term in simple ...
... Use formulae and equations (algebra) to solve problems. (see also week 7). Solve simple linear equations. Week 6 Consolidate the rapid recall of number facts, including multiplication facts to 12 × 12 and the associated division facts Week 7 Generate sequences and describe the general term in simple ...
Pyramid diffraction in parity-time-symmetric optical lattices Sean Nixon and Jianke Yang*
... in both X and Y directions, which we term pyramid diffraction. For the initial condition in Eq. (15), this pattern is illustrated in Fig. 1 for both the envelope and full equations. Using the explicit formula of An for this initial condition, the fine structure in this diffraction pattern (such as t ...
... in both X and Y directions, which we term pyramid diffraction. For the initial condition in Eq. (15), this pattern is illustrated in Fig. 1 for both the envelope and full equations. Using the explicit formula of An for this initial condition, the fine structure in this diffraction pattern (such as t ...



















![A) Area Between Curves in [a , b]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010244503_1-8d5ca7e45bea07d60196d1e4f510559f-300x300.png)

