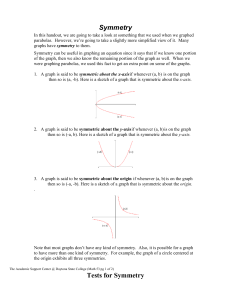
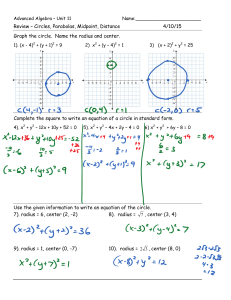
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM)
... Definition : Left-Unit : An element a ǂ 0 in a field Gr-Algebra ( A, +, ., / ) with L-identity is said to be a Left-Unit of the Gr-Algebra or simply a L-Unit of the Gr-Algebra if there exists an element a’ǂ 0 in A such that a’/ a = 1’. 2.14.1 Example : ( R , + , . ÷ ), where + is the usual addition, ...
... Definition : Left-Unit : An element a ǂ 0 in a field Gr-Algebra ( A, +, ., / ) with L-identity is said to be a Left-Unit of the Gr-Algebra or simply a L-Unit of the Gr-Algebra if there exists an element a’ǂ 0 in A such that a’/ a = 1’. 2.14.1 Example : ( R , + , . ÷ ), where + is the usual addition, ...
Orthogonal bases are Schauder bases and a characterization
... for every x e A and « E N . Since / is continuous and nonzero, we have f{ek) Φ 0 for some k eTS. It follows that f = e£. 2. Locally m-convex algebras with orthogonal bases. Let A be a complete locally m-convex algebra with an orthogonal basis and an identity. Husain and Watson [7] showed that A is t ...
... for every x e A and « E N . Since / is continuous and nonzero, we have f{ek) Φ 0 for some k eTS. It follows that f = e£. 2. Locally m-convex algebras with orthogonal bases. Let A be a complete locally m-convex algebra with an orthogonal basis and an identity. Husain and Watson [7] showed that A is t ...
The Digit Factory
... Down yonder are three numerical expressions. The value of each expression is exactly 1,000,000. To be sure, we entered each expression into our TI-84 Plus and got 1,000,000 every time. We show each expression using operation symbols for keys (+, –, , , ^) and symbols displayed on the calculator's ...
... Down yonder are three numerical expressions. The value of each expression is exactly 1,000,000. To be sure, we entered each expression into our TI-84 Plus and got 1,000,000 every time. We show each expression using operation symbols for keys (+, –, , , ^) and symbols displayed on the calculator's ...
Grade 6 – Number and Operation
... Construct and solve systems of linear equations and inequalities in two variables by various methods. CLE 3102.3.8 Solve and understand solutions of quadratic equations with real roots. CLE 3102.3.9 Understand and use exponential functions to solve contextual problems. ...
... Construct and solve systems of linear equations and inequalities in two variables by various methods. CLE 3102.3.8 Solve and understand solutions of quadratic equations with real roots. CLE 3102.3.9 Understand and use exponential functions to solve contextual problems. ...
Atom structures of cylindric algebras and relation algebras
... given, their cylindric algebra structure is determined by the way the diagonal and cylindrification operations behave on their atoms — i.e., by their atom structure. Of course, they have the same atom structure. Now the difficulties in finding representations for cylindric algebras mostly arise from ...
... given, their cylindric algebra structure is determined by the way the diagonal and cylindrification operations behave on their atoms — i.e., by their atom structure. Of course, they have the same atom structure. Now the difficulties in finding representations for cylindric algebras mostly arise from ...