Business English, 9e
... Chapter 2, Guffey-Seefer, Business English, 10e, Copyright 2011 Cengage Learning, All Rights Reserved ...
... Chapter 2, Guffey-Seefer, Business English, 10e, Copyright 2011 Cengage Learning, All Rights Reserved ...
at this moment
... way. rather use syntactic, formal criteria to identify compounds, Show that words are ‘frozen’ together, even if the meaning of the combination is relatively ‘transparent’. ...
... way. rather use syntactic, formal criteria to identify compounds, Show that words are ‘frozen’ together, even if the meaning of the combination is relatively ‘transparent’. ...
grade 3 grammar glossary
... adverb (e.g., more slowly). It is used to show who (or what) has performed an action in a specific manner to the greater or lesser degree. An expression formed from the adverb (e.g., most carefully). It is used to show who (or what) has performed an action in a specific manner to the greatest or lea ...
... adverb (e.g., more slowly). It is used to show who (or what) has performed an action in a specific manner to the greater or lesser degree. An expression formed from the adverb (e.g., most carefully). It is used to show who (or what) has performed an action in a specific manner to the greatest or lea ...
Adverbs Worksheet - NordoniaEnglish9CP
... nearby, there, around, outside, inside rather, quite, extremely, very almost, extremely, quite, so, usually, especially, nearly, really, too, very ...
... nearby, there, around, outside, inside rather, quite, extremely, very almost, extremely, quite, so, usually, especially, nearly, really, too, very ...
Year 5 Programme of Study for English
... last three is clearly related to finance, commerce and province). Use –ant and –ance/–ancy if there is a related word with a /æ/ or /e?/ sound in the right position; –ation endings are often a clue. Use –ent and –ence/–ency after soft c (/s/ sound), soft g (/dʒ/ sound) and qu, or if there is a relat ...
... last three is clearly related to finance, commerce and province). Use –ant and –ance/–ancy if there is a related word with a /æ/ or /e?/ sound in the right position; –ation endings are often a clue. Use –ent and –ence/–ency after soft c (/s/ sound), soft g (/dʒ/ sound) and qu, or if there is a relat ...
Year 6 Programme of Study for English
... last three is clearly related to finance, commerce and province). Use –ant and –ance/–ancy if there is a related word with a /æ/ or /e?/ sound in the right position; –ation endings are often a clue. Use –ent and –ence/–ency after soft c (/s/ sound), soft g (/dʒ/ sound) and qu, or if there is a relat ...
... last three is clearly related to finance, commerce and province). Use –ant and –ance/–ancy if there is a related word with a /æ/ or /e?/ sound in the right position; –ation endings are often a clue. Use –ent and –ence/–ency after soft c (/s/ sound), soft g (/dʒ/ sound) and qu, or if there is a relat ...
Russian sentence analysis - Machine Translation Archive
... it is comparatively slight, it causes substantial ...
... it is comparatively slight, it causes substantial ...
Phrases - Cardinal Newman High School
... Verbal: a verb form that functions in a sentence as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Verbal Phrase: a verbal plus any complements and modifiers. Participles: verb form that functions as an adjective. Gerunds: verb form that ends in –ing that functions as a noun. Infinitives: verb form that is pre ...
... Verbal: a verb form that functions in a sentence as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Verbal Phrase: a verbal plus any complements and modifiers. Participles: verb form that functions as an adjective. Gerunds: verb form that ends in –ing that functions as a noun. Infinitives: verb form that is pre ...
An introduction to the Ancient Language
... There are two types of articles: definite and indefinite articles. The indefinite article is aí “a”, and is only used for indefinite singular nouns. The definite article du “the” is used for as well singular nouns as plural ones. Indefinite plural nouns do not have articles. The articles are placed ...
... There are two types of articles: definite and indefinite articles. The indefinite article is aí “a”, and is only used for indefinite singular nouns. The definite article du “the” is used for as well singular nouns as plural ones. Indefinite plural nouns do not have articles. The articles are placed ...
Français (8)
... The passé composé uses être conjugated in the present tense as the auxiliary verb with intransitive and reflexive verbs. Intransitive verbs are verbs that do not take an object. Reflexive verbs (e.g., “Je m’appelle”) have an extra pronoun to show that the action of the verb is being reflected back o ...
... The passé composé uses être conjugated in the present tense as the auxiliary verb with intransitive and reflexive verbs. Intransitive verbs are verbs that do not take an object. Reflexive verbs (e.g., “Je m’appelle”) have an extra pronoun to show that the action of the verb is being reflected back o ...
Word Choice
... E.g., The effect of her decision to network the computers was better communication among team members. Effect can occasionally be used as a verb meaning “accomplish.” E.g., We plan to effect those changes by December. The word affect is usually used as a verb. E.g., The attitude of management affect ...
... E.g., The effect of her decision to network the computers was better communication among team members. Effect can occasionally be used as a verb meaning “accomplish.” E.g., We plan to effect those changes by December. The word affect is usually used as a verb. E.g., The attitude of management affect ...
Tree Syntax of Natural Language
... In linguistics and natural language processing, it is common to attribute labeled tree structures called syntactic trees or parse trees to phrases and sentences of human languages. An example is found above. The tree consists of a set of vertices (also known as nodes or addresses), including a uniqu ...
... In linguistics and natural language processing, it is common to attribute labeled tree structures called syntactic trees or parse trees to phrases and sentences of human languages. An example is found above. The tree consists of a set of vertices (also known as nodes or addresses), including a uniqu ...
Verbs Nouns and Basic Sentences
... nouns or pronouns, but they can also be adjectives (and sometimes other word classes). Subject Complements give us more information about the Subject, so they refer to the same person or thing as the Subject. For example: ...
... nouns or pronouns, but they can also be adjectives (and sometimes other word classes). Subject Complements give us more information about the Subject, so they refer to the same person or thing as the Subject. For example: ...
Morphological - School of Computer Science, University of
... Derivation: Examples • Making adjectives into adverbs by suffixing with “ly”. • Making nouns (etc.) into adverbs by suffixing with “wards”, as in “sidewards”. • Nominalizing (= “nounifying”) verbs by suffixing with “ation” or “ment” (as in “payment”), “ee” (as in “payee”), “er” (as in “payer”). • M ...
... Derivation: Examples • Making adjectives into adverbs by suffixing with “ly”. • Making nouns (etc.) into adverbs by suffixing with “wards”, as in “sidewards”. • Nominalizing (= “nounifying”) verbs by suffixing with “ation” or “ment” (as in “payment”), “ee” (as in “payee”), “er” (as in “payer”). • M ...
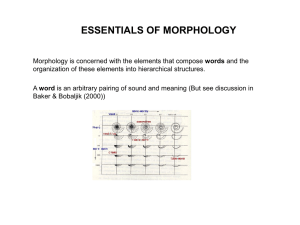
essentials of morphology
... long, random list, but is structured into special subgroups of words identified by the grammatical/syntactic categories (=the traditional “parts-of-speech”) The basic parts-of-speech of English: ...
... long, random list, but is structured into special subgroups of words identified by the grammatical/syntactic categories (=the traditional “parts-of-speech”) The basic parts-of-speech of English: ...
MEMOIR
... F5. Overuse. Symbols, codes, and decorations are doing more of the talking than the words. If you feel the need to add an exclamation point (or several), bolding a word, or writing in ALL CAPS – consider using stronger language instead to get your point across to the reader. G. Verb Error. (on your ...
... F5. Overuse. Symbols, codes, and decorations are doing more of the talking than the words. If you feel the need to add an exclamation point (or several), bolding a word, or writing in ALL CAPS – consider using stronger language instead to get your point across to the reader. G. Verb Error. (on your ...
Conjugating –ar verbs
... All Spanish verbs fit into one of three categories: -ar, -er, or -ir verbs. In this section we will learn to conjugate regular –ar verbs. But let’s review a little first. Verb – A word that represents an action or a state of being. Infinitive - the simple or basic form of the verb, the unchanged ver ...
... All Spanish verbs fit into one of three categories: -ar, -er, or -ir verbs. In this section we will learn to conjugate regular –ar verbs. But let’s review a little first. Verb – A word that represents an action or a state of being. Infinitive - the simple or basic form of the verb, the unchanged ver ...
Grammar Link
... An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. EXAMPLE: Grendel slowly stirs in his murky and vile lair. ...
... An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. EXAMPLE: Grendel slowly stirs in his murky and vile lair. ...
simple subject
... sentence—a noun or a pronoun that tells who or what is being talked about—and all of the words that describe it. ...
... sentence—a noun or a pronoun that tells who or what is being talked about—and all of the words that describe it. ...
simple subject
... sentence—a noun or a pronoun that tells who or what is being talked about—and all of the words that describe it. ...
... sentence—a noun or a pronoun that tells who or what is being talked about—and all of the words that describe it. ...
Manange, a Sino-Tibetan Language of Nepal Kristine A. Hildebrandt, SIU Edwardsville 1 Introduction
... apply to other lexical classes. Nouns may be plural marked with the clitic =tse, and they may take case enclitics. Nouns may also be marked with the definiteness enclitics =ko or =ri, which indicate the degree to which a referent (a noun) is already introduced or known in a discourse context. None o ...
... apply to other lexical classes. Nouns may be plural marked with the clitic =tse, and they may take case enclitics. Nouns may also be marked with the definiteness enclitics =ko or =ri, which indicate the degree to which a referent (a noun) is already introduced or known in a discourse context. None o ...
Action verbs
... Wally gave the new nurse the patient’s chart. Wally gave the patient’s chart to the new nurse. ...
... Wally gave the new nurse the patient’s chart. Wally gave the patient’s chart to the new nurse. ...
Reported Speech-12º
... “I suppose you have heard the latest news about Lampedusa ”, she said. Reporting someone’s actual words (statements and questions) by using verbs say, reply, ask…) Reporting their emotions, tones by using specific reporting verbs like: (add, admit, advise, agree, announce, answer, ask, beg, clai ...
... “I suppose you have heard the latest news about Lampedusa ”, she said. Reporting someone’s actual words (statements and questions) by using verbs say, reply, ask…) Reporting their emotions, tones by using specific reporting verbs like: (add, admit, advise, agree, announce, answer, ask, beg, clai ...
So - INFOP Virtual
... More future tenses: future perfect The future perfect tense is formed with will have + past participle, as in, “I will have left by tomorrow” or “They will have been friends for a long time.” The form stays the same no matter what subject you use. We use the future perfect tense to talk about an act ...
... More future tenses: future perfect The future perfect tense is formed with will have + past participle, as in, “I will have left by tomorrow” or “They will have been friends for a long time.” The form stays the same no matter what subject you use. We use the future perfect tense to talk about an act ...
Complement Notes
... • A direct object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of a verb. • A direct object follows an action verb. • You can find the direct object by asking what? or whom? after the action verb. • Formula for finding DO: subject + verb + what? or whom? = direct object • Examples: My older brother ...
... • A direct object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of a verb. • A direct object follows an action verb. • You can find the direct object by asking what? or whom? after the action verb. • Formula for finding DO: subject + verb + what? or whom? = direct object • Examples: My older brother ...