Transcript
... modern theories of mind and the way in which different regions of the brain control our thoughts, our memories, and our actions. I'm going to continue, pick up on some of these themes but in two slightly different ways. I'm going to look at the brain at a higher focus and I'm going to move backwards ...
... modern theories of mind and the way in which different regions of the brain control our thoughts, our memories, and our actions. I'm going to continue, pick up on some of these themes but in two slightly different ways. I'm going to look at the brain at a higher focus and I'm going to move backwards ...
Brain and Nervous System— Your Information Superhighway
... sclera: The white of the eye; acts as a protective coating to the rest of the eyeball. somatic nervous system (SNS): The part of the PNS that involves voluntary movement because it allows conscious control of body movements. static equilibrium: The position of the head in respect to the pull of grav ...
... sclera: The white of the eye; acts as a protective coating to the rest of the eyeball. somatic nervous system (SNS): The part of the PNS that involves voluntary movement because it allows conscious control of body movements. static equilibrium: The position of the head in respect to the pull of grav ...
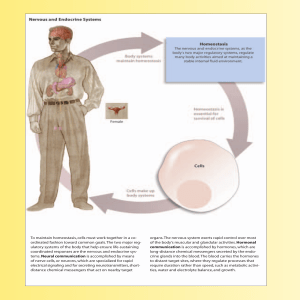
To maintain homeostasis, cells must work together in a co
... ❚ Electrical signals are produced by changes in ion movement across the plasma membrane. Changes in membrane potential are brought about by changes in ion movement across the membrane. For example, if the net inward flow of positively charged ions increases compared to the resting state, the membran ...
... ❚ Electrical signals are produced by changes in ion movement across the plasma membrane. Changes in membrane potential are brought about by changes in ion movement across the membrane. For example, if the net inward flow of positively charged ions increases compared to the resting state, the membran ...
Introduction_to_the_Nervous_System1
... (CNS); that is, to either the brain or the spinal cord. Over any particular period of time, the excitatory state generated by the multitude of active receptors of the body results in a varying pattern of excitation arriving at the central nervous system. Within the central nervous system, the differ ...
... (CNS); that is, to either the brain or the spinal cord. Over any particular period of time, the excitatory state generated by the multitude of active receptors of the body results in a varying pattern of excitation arriving at the central nervous system. Within the central nervous system, the differ ...
Skeletal System
... limited exceptions do exist in the CNS as neural stem cells have been identified ...
... limited exceptions do exist in the CNS as neural stem cells have been identified ...
Done by : Noor Bjant.hala Dr: loai zghol
... 2) Also our brain block some sensation in this case . ...
... 2) Also our brain block some sensation in this case . ...
Coding Rate and Duration of Vocalizations of the Frog, Xenopus laevis
... expressed NMDARs, we first applied 1 M tetrodotoxin (TTX) (SigmaAldrich) to block all spike-mediated synaptic transmission. The effectiveness of TTX treatment was confirmed when action potentials could no longer be produced by either the FTNs or vocal motoneurons (determined by the loss of activity ...
... expressed NMDARs, we first applied 1 M tetrodotoxin (TTX) (SigmaAldrich) to block all spike-mediated synaptic transmission. The effectiveness of TTX treatment was confirmed when action potentials could no longer be produced by either the FTNs or vocal motoneurons (determined by the loss of activity ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... the body. • It is subdivided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. ...
... the body. • It is subdivided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. ...
Effects of Correlated Input on Development of Structure in an
... with a mean rate of 0.07 events per second, corresponding to the figure of 251.7±55.1 events per hour measured by Hartley et al. (2012). The duration for each event was taken to be 5 seconds, as per the findings of Anderson et al. (1985). Figure 3.2 shows the effect that such a process has on the sa ...
... with a mean rate of 0.07 events per second, corresponding to the figure of 251.7±55.1 events per hour measured by Hartley et al. (2012). The duration for each event was taken to be 5 seconds, as per the findings of Anderson et al. (1985). Figure 3.2 shows the effect that such a process has on the sa ...
Document
... derived from studies of patients with brain damage. • Aphasia – language deficit caused by brain damage • Broca’s area – involved in speech production • Wernicke’s area – involved in speech comprehension ...
... derived from studies of patients with brain damage. • Aphasia – language deficit caused by brain damage • Broca’s area – involved in speech production • Wernicke’s area – involved in speech comprehension ...
STOCHASTIC GENERATION OF BIOLOGICALLY - G
... The “Network Statistical Analyzer ” can be used to mine through the biologically observed XwebDB neurons and their YwebDB projections to derive statistical estimates of the parameters groups, which can in turn be used to produce more accurate brain network models. D. Background and rationale This se ...
... The “Network Statistical Analyzer ” can be used to mine through the biologically observed XwebDB neurons and their YwebDB projections to derive statistical estimates of the parameters groups, which can in turn be used to produce more accurate brain network models. D. Background and rationale This se ...
Modeling and Detecting Deep Brain Activity with MEG
... related disorders (memory, emotions, motor control, epilepsy, Parkinson, Huntington and Alzheimer diseases, etc.). They form with the cortex a dense array of interconnected functional networks that are essential to be explored using functional brain imaging. The millisecond time resolution asset of ...
... related disorders (memory, emotions, motor control, epilepsy, Parkinson, Huntington and Alzheimer diseases, etc.). They form with the cortex a dense array of interconnected functional networks that are essential to be explored using functional brain imaging. The millisecond time resolution asset of ...
Your Nervous System - Springfield Public Schools
... the diameter of a ping-pong ball is 3.8 cm. (The length of the model’s axon can be calculated using the ratio: 0.1 mm/1,000 mm ⫽ 38 mm/x. When solving for x, x ⫽ (38 ⫻ 1,000) ⫼ 0.1 ⫽ 380,000 mm. The axon would be 380 m long.) ...
... the diameter of a ping-pong ball is 3.8 cm. (The length of the model’s axon can be calculated using the ratio: 0.1 mm/1,000 mm ⫽ 38 mm/x. When solving for x, x ⫽ (38 ⫻ 1,000) ⫼ 0.1 ⫽ 380,000 mm. The axon would be 380 m long.) ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 12-03
... Conscious cortical control of motor activity Myelinated innervation of skeletal muscles No synapses outside of CNS – innervation by lower motor neurons (LMN) Active only when stimulated Acetylcholine excitatory input to target Autonomic Terminology Preganglionic neurons – visceral motor ...
... Conscious cortical control of motor activity Myelinated innervation of skeletal muscles No synapses outside of CNS – innervation by lower motor neurons (LMN) Active only when stimulated Acetylcholine excitatory input to target Autonomic Terminology Preganglionic neurons – visceral motor ...
Genetic analysis of dopaminergic system development in zebrafish
... are devoid of FGF8, revealed that FGF8 contributes both to specification of DA and NA neurons. Locus coeruleus NA neurons are completely absent in ace mutant embryos. Within the ventral diencephalon, the caudal DA groups form, but the anteriormost cluster of DA cells, corresponding to group 1 neurons ...
... are devoid of FGF8, revealed that FGF8 contributes both to specification of DA and NA neurons. Locus coeruleus NA neurons are completely absent in ace mutant embryos. Within the ventral diencephalon, the caudal DA groups form, but the anteriormost cluster of DA cells, corresponding to group 1 neurons ...
5-NeuralNetworks
... membrane exhibits spikes called action potentials. Spike originates in cell body, travels down axon, and causes synaptic terminals to release neurotransmitters. Chemical diffuses across synapse to dendrites of other neurons. Neurotransmitters can be excititory or inhibitory. If net input of neurotra ...
... membrane exhibits spikes called action potentials. Spike originates in cell body, travels down axon, and causes synaptic terminals to release neurotransmitters. Chemical diffuses across synapse to dendrites of other neurons. Neurotransmitters can be excititory or inhibitory. If net input of neurotra ...
New Insights into Neuron-Glia Communication
... Terminal Schwann cells affect synaptic signaling networks in the terminal Schwann strength by regulating neurotransmitter recell integrate the activity of the synapse and lease from the presynaptic neuron, but astrobalance the strength of the connection. cytes can influence synaptic strength by thei ...
... Terminal Schwann cells affect synaptic signaling networks in the terminal Schwann strength by regulating neurotransmitter recell integrate the activity of the synapse and lease from the presynaptic neuron, but astrobalance the strength of the connection. cytes can influence synaptic strength by thei ...
Notes to Resp. 4
... Control of Ventilation (see Fig. 13.30 to 13.37) Due to the different solubilities of O2 and CO2 in air and water, the basic chemo-chemistry of control of respiration is different in water versus air breathers. Control of respiration and thus ventilation is necessary in order to match the oxygen upt ...
... Control of Ventilation (see Fig. 13.30 to 13.37) Due to the different solubilities of O2 and CO2 in air and water, the basic chemo-chemistry of control of respiration is different in water versus air breathers. Control of respiration and thus ventilation is necessary in order to match the oxygen upt ...
PDF
... both Vldlr and Apoer2, exhibit identical behavior and neuroanatomy and provide strong evidence for the involvement of these proteins in the same signaling pathway (22). The Reln-positive CR neuron is one of the first neurons to mature during early cortical development. It was initially described in ...
... both Vldlr and Apoer2, exhibit identical behavior and neuroanatomy and provide strong evidence for the involvement of these proteins in the same signaling pathway (22). The Reln-positive CR neuron is one of the first neurons to mature during early cortical development. It was initially described in ...
3 Anatomy of the Nervous System
... The vertebrate nervous system is composed of two divisions: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system (see Figure 3.1). Roughly speaking, the central nervous system (CNS) is the division of the nervous system that is located within the skull and spine; the peripheral nervous syste ...
... The vertebrate nervous system is composed of two divisions: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system (see Figure 3.1). Roughly speaking, the central nervous system (CNS) is the division of the nervous system that is located within the skull and spine; the peripheral nervous syste ...
xiao-ying-lu-southeast-university
... With the invention of MEA in the early 1970s, related technologies have also been developed. MEA has been applied in : Neuroscience Drug screening Pharmacology, toxicology Etc. ...
... With the invention of MEA in the early 1970s, related technologies have also been developed. MEA has been applied in : Neuroscience Drug screening Pharmacology, toxicology Etc. ...
Schwann cells
... A. Neurons - electrical signals to transmit information 1. basic structural unit of the nervous system 2. can send an “action potential” (nerve impulse) down its axon 3. Longevity - can live and function for a lifetime 4. amitotic - fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem ce ...
... A. Neurons - electrical signals to transmit information 1. basic structural unit of the nervous system 2. can send an “action potential” (nerve impulse) down its axon 3. Longevity - can live and function for a lifetime 4. amitotic - fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem ce ...
Level 3 Pharmaceutical Science
... Impulses need to move from one neuron to another. The journey of an impulse from the finger crosses 3 junctions before reaching the brain. These junctions are called synapses. A synapse is a gap between two neurons. In an electrical circuit you might expect a gap to result in a failure of the circui ...
... Impulses need to move from one neuron to another. The journey of an impulse from the finger crosses 3 junctions before reaching the brain. These junctions are called synapses. A synapse is a gap between two neurons. In an electrical circuit you might expect a gap to result in a failure of the circui ...
Curriculum Vitae
... molecular mechanisms underlying the proper migration and distribution of different types of neurons in developing brain, one of the key steps for brain morphogenesis. Currently, we focus on the guidance mechanism for the radial migration of cortical neurons by diffusible guidance factors and the int ...
... molecular mechanisms underlying the proper migration and distribution of different types of neurons in developing brain, one of the key steps for brain morphogenesis. Currently, we focus on the guidance mechanism for the radial migration of cortical neurons by diffusible guidance factors and the int ...
Neural Networks – An Introduction
... A neurone has a cell body, a branching input structure (the dendrIte) and a branching output structure (th axOn) –Axons connect to dendrites via synapses. –Electro-chemical signals are propagated from the dendritic input, through the cell body, and down the axon to other neurons ...
... A neurone has a cell body, a branching input structure (the dendrIte) and a branching output structure (th axOn) –Axons connect to dendrites via synapses. –Electro-chemical signals are propagated from the dendritic input, through the cell body, and down the axon to other neurons ...