Complete Nervous System Worksheet
... -presynaptic means anything before the synapse and postsynaptic means anything after the synapse. Therefore the cell transmitting the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell and the cell receiving the information is called the postsynaptic cell. -nerve impulses reaching the presynaptic ending c ...
... -presynaptic means anything before the synapse and postsynaptic means anything after the synapse. Therefore the cell transmitting the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell and the cell receiving the information is called the postsynaptic cell. -nerve impulses reaching the presynaptic ending c ...
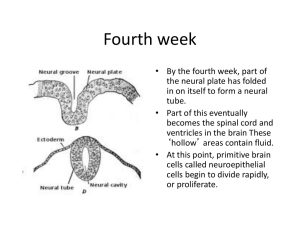
Fourth week
... undergoes the most complicated changes. • The forebrain divides into two distinct structures: the diencephalon and telencephalon. • The diencephalon develops into the thalamus and hypothalamus, which will affect everything from emotions to sensory perception. ...
... undergoes the most complicated changes. • The forebrain divides into two distinct structures: the diencephalon and telencephalon. • The diencephalon develops into the thalamus and hypothalamus, which will affect everything from emotions to sensory perception. ...
Module 4 - Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receives messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receives messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
File
... Depolarization is stopped When the membrane voltage reaches 35 mV, the inactivation gates close in response to depolarization and the sodium ions can’t enter the cell anymore. The Na+ can only come in during a brief period when both activation and inactivation ...
... Depolarization is stopped When the membrane voltage reaches 35 mV, the inactivation gates close in response to depolarization and the sodium ions can’t enter the cell anymore. The Na+ can only come in during a brief period when both activation and inactivation ...
Nervous System
... pass their signal to a single connecting neuron. • Such cells may be “decision-making” cells that may determine an appropriate output. ...
... pass their signal to a single connecting neuron. • Such cells may be “decision-making” cells that may determine an appropriate output. ...
How Ca2+ triggers neurotransmitter release
... previous events and that constitutes the minimal information processing unit in brain. Thomas Südhof began his inquiry into synaptic transmission by focusing on the presynaptic nerve terminal. When he started, scientists knew that calcium ions stimulate the release of neurotransmitters from membrane ...
... previous events and that constitutes the minimal information processing unit in brain. Thomas Südhof began his inquiry into synaptic transmission by focusing on the presynaptic nerve terminal. When he started, scientists knew that calcium ions stimulate the release of neurotransmitters from membrane ...
Biology
... organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
... organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
Biology The Nervous System
... spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
... spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
Dr. Carlos Paladini
... within the ventral mesencephalon, encode perhaps one of the most important signals for reinforcement learning in the brain: reward prediction error. This signal is encoded by the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons, which controls the release of dopamine at target regions. Specifically, transient ...
... within the ventral mesencephalon, encode perhaps one of the most important signals for reinforcement learning in the brain: reward prediction error. This signal is encoded by the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons, which controls the release of dopamine at target regions. Specifically, transient ...
The Nervous System Lesson Outline LESSON 1 A.
... 4. The part of the brain that coordinates voluntary muscle movement and regulates balance and posture is the ...
... 4. The part of the brain that coordinates voluntary muscle movement and regulates balance and posture is the ...
Neuroscience: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... The neuron that sends a signal across the gap is called the presynaptic neuron. The neuron that receives the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... The neuron that sends a signal across the gap is called the presynaptic neuron. The neuron that receives the signal is called the postsynaptic neuron. ...
Na + - Tufts
... • How do you think Novocain works??? – Novocain stops our neurons from signaling electrically. – But how do our neurons signal electrically??? ...
... • How do you think Novocain works??? – Novocain stops our neurons from signaling electrically. – But how do our neurons signal electrically??? ...
AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology
... a. Dendrites- bushy fibers that receive information b. Axon- fibers that pass message along to other neurons, muscles or glands. c. Myelin Sheath- fatty tissue insulates axon to speed info. d. Axon terminals- form junctions with other cells ...
... a. Dendrites- bushy fibers that receive information b. Axon- fibers that pass message along to other neurons, muscles or glands. c. Myelin Sheath- fatty tissue insulates axon to speed info. d. Axon terminals- form junctions with other cells ...
Unit M - Notes #1 Neurons - Mr. Lesiuk
... -Conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body. 4. Myelin Sheath -Protective lipid coating of Schwann cells (type of neuroglial cell) forms insulating layer around longer axons and dendrites. OMIT "Larger __________" 5. Nodes of Ranvier -Interrupted areas of the Myelin Sheath due to gaps between o ...
... -Conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body. 4. Myelin Sheath -Protective lipid coating of Schwann cells (type of neuroglial cell) forms insulating layer around longer axons and dendrites. OMIT "Larger __________" 5. Nodes of Ranvier -Interrupted areas of the Myelin Sheath due to gaps between o ...
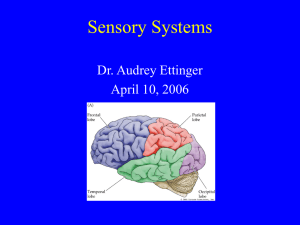
Sensory Systems - Cedar Crest College
... • “What kind” information is transmitted by which neurons respond to the signal • “How much” information is transmitted by the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
... • “What kind” information is transmitted by which neurons respond to the signal • “How much” information is transmitted by the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
From Implantation to Neural Tube
... inner cell mass becomes the embryo. • The single-layer embryo begins to fold itself into three layers. • A U-shaped groove forms down the center of the top layer. ...
... inner cell mass becomes the embryo. • The single-layer embryo begins to fold itself into three layers. • A U-shaped groove forms down the center of the top layer. ...
1 From Implantation to Neural Tube From Implantation to Neural
... inner cell mass becomes the embryo. • The single-layer embryo begins to fold itself into three layers. • A U-shaped groove forms down the center of the top layer. ...
... inner cell mass becomes the embryo. • The single-layer embryo begins to fold itself into three layers. • A U-shaped groove forms down the center of the top layer. ...
Neurology - Porterville College
... Excitatory Neurotransmitters • Dopamine – Gross subconscious movement – Fine motor skills – Emotional responses ...
... Excitatory Neurotransmitters • Dopamine – Gross subconscious movement – Fine motor skills – Emotional responses ...
Nervous System
... 2. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)- affects neurons; slows nerve impulses, causing muscle weakness, possibly paralysis. 3. Alzheimer’s- brain tissue deteriorates; severe memory loss 4. Stroke- a blockage in a blood vessel in the brain, causing brain damage 5. Concussion- a bruise to the brain when the brain ...
... 2. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)- affects neurons; slows nerve impulses, causing muscle weakness, possibly paralysis. 3. Alzheimer’s- brain tissue deteriorates; severe memory loss 4. Stroke- a blockage in a blood vessel in the brain, causing brain damage 5. Concussion- a bruise to the brain when the brain ...
the nervous system - Miss Gleason`s Science
... Memory is controlled by the HIPPOCAMPUS The hippocampus plays a major role in forging memories. ...
... Memory is controlled by the HIPPOCAMPUS The hippocampus plays a major role in forging memories. ...
Chapter 2
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...











![AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008569681_1-9cf3b4caa50d34e12653d8840c008c05-300x300.png)