Course HRD 2101: COMMUNICATION SKILLS
... complex sentence. We need to be familiar with these forms of sentences so that we may be able to construct them with ease when we write English compositions. A sentence normally has a subject and a predicate. The subject identifies a place, a person or thing. The predicate tells what the subject doe ...
... complex sentence. We need to be familiar with these forms of sentences so that we may be able to construct them with ease when we write English compositions. A sentence normally has a subject and a predicate. The subject identifies a place, a person or thing. The predicate tells what the subject doe ...
Lexical Semantics … cont`d
... up of a verb followed by a preposition or an adverbial particle or both, and usually the meaning is slightly or considerably different from the literal meaning of the words. We come across something: to see or discover it. Look down on something: scorn or despise it Put up with: tolerate, endure Loo ...
... up of a verb followed by a preposition or an adverbial particle or both, and usually the meaning is slightly or considerably different from the literal meaning of the words. We come across something: to see or discover it. Look down on something: scorn or despise it Put up with: tolerate, endure Loo ...
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
... master vocabulary and develop their skill. It suggests that vocabulary has important role in learning a language. River (1978: 462) says that it would be impossible to learn language without vocabulary. Because vocabulary is the foundation to learn a language, it comes first when we start learning a ...
... master vocabulary and develop their skill. It suggests that vocabulary has important role in learning a language. River (1978: 462) says that it would be impossible to learn language without vocabulary. Because vocabulary is the foundation to learn a language, it comes first when we start learning a ...
English Reading, Speaking and Listening Plan
... making inferences on the basis of what is being said and done answering and asking questions predicting what might happen on the basis of what has been read so far participate in discussion about books, poems and other works that are read to them and those that they can read for themselves, taking t ...
... making inferences on the basis of what is being said and done answering and asking questions predicting what might happen on the basis of what has been read so far participate in discussion about books, poems and other works that are read to them and those that they can read for themselves, taking t ...
Learning Syntax — A Neurocogitive Approach
... more units as lexemes than are usually considered. The cognitive orientation forces us to accept that people learn as units any combination that has occurred with sufficient frequency or to which sufficient attention has been given, as a consequence of the brain’s natural tendency to “absorb” repeat ...
... more units as lexemes than are usually considered. The cognitive orientation forces us to accept that people learn as units any combination that has occurred with sufficient frequency or to which sufficient attention has been given, as a consequence of the brain’s natural tendency to “absorb” repeat ...
Syntactic category information and the semantics of
... This is broadly in line with Berg’s (2003:300) finding that “both prefixes and suffixes combine with an average of 1.4 word-classes”, which was based on a much smaller data-base (only CELEX, Baayen et al. 1995) and which did not include roots as a base category. In (6b) we see that many different wo ...
... This is broadly in line with Berg’s (2003:300) finding that “both prefixes and suffixes combine with an average of 1.4 word-classes”, which was based on a much smaller data-base (only CELEX, Baayen et al. 1995) and which did not include roots as a base category. In (6b) we see that many different wo ...
kencan terus
... Language is used to express our inner thoughts and emotions, to make sense of complex and abstract thought, to learn to communicate with others, to fulfill our wants and needs, as well as to establish rules and maintain our culture. People need language to communicate with each other. Communications ...
... Language is used to express our inner thoughts and emotions, to make sense of complex and abstract thought, to learn to communicate with others, to fulfill our wants and needs, as well as to establish rules and maintain our culture. People need language to communicate with each other. Communications ...
Exercises for Developing Prediction Skills in Reading Latin Sentences
... attention on the form and the direct association of the form with the concept in a way that does not require translation or grammatical terms. English translations may be ambiguous, especially in this example, since “in” is often used for “into.” While knowledge of grammatical terms is important for ...
... attention on the form and the direct association of the form with the concept in a way that does not require translation or grammatical terms. English translations may be ambiguous, especially in this example, since “in” is often used for “into.” While knowledge of grammatical terms is important for ...
General English Mahmoud Alimohammadi Hassan Khalili
... The general aim and behavioral objectives are listed at the beginning of each unit to draw your attention to the main points and activities on which you are expected to concentrate. ...
... The general aim and behavioral objectives are listed at the beginning of each unit to draw your attention to the main points and activities on which you are expected to concentrate. ...
Using Commas After Introductory Words, Phrases, and Clauses
... Note: This section includes some common examples that signal to a writer that a comma is usually needed after an introductory element. These examples are based on the ELAR TEKS for grades 6–8. This section does not represent all of the different types of introductory words, phrases, or clauses that ...
... Note: This section includes some common examples that signal to a writer that a comma is usually needed after an introductory element. These examples are based on the ELAR TEKS for grades 6–8. This section does not represent all of the different types of introductory words, phrases, or clauses that ...
Grammar on mathematical principles
... propertv is not their having a common meaning: it is hard to say what me aning is common to prefer and promise but not to beg or deseroe. Rather, it is the likelihoocl that the subject, or object, under that verb be the same as the subject, or object, of the verb itself. It is reasonable to expect t ...
... propertv is not their having a common meaning: it is hard to say what me aning is common to prefer and promise but not to beg or deseroe. Rather, it is the likelihoocl that the subject, or object, under that verb be the same as the subject, or object, of the verb itself. It is reasonable to expect t ...
Spelling progression
... or not they have seen these words before. Spelling, however, is a very different matter. Once pupils have learnt more than one way of spelling particular sounds, choosing the right letter or letters depends on their either having made a conscious effort to learn the words or having absorbed them les ...
... or not they have seen these words before. Spelling, however, is a very different matter. Once pupils have learnt more than one way of spelling particular sounds, choosing the right letter or letters depends on their either having made a conscious effort to learn the words or having absorbed them les ...
1 What is Paradigm Function Morphology?
... The leading ideas of PFM are fairly few in number, but they impose important constraints on any formal instantiation of the theory. Some of these leading ideas are shared with other morphological theories, but no other theory shares the full set of core assumptions constituting PFM. ...
... The leading ideas of PFM are fairly few in number, but they impose important constraints on any formal instantiation of the theory. Some of these leading ideas are shared with other morphological theories, but no other theory shares the full set of core assumptions constituting PFM. ...
Languages of India and India as a Linguistic Area
... the first is the main or predicating verb and the second member, although, homophonous with an independent verb in the language, does not appear in its primary lexical meaning; V2 only occurs in the sequence to mark the main verb for certain ‘grammatical’ features. Thus an ...
... the first is the main or predicating verb and the second member, although, homophonous with an independent verb in the language, does not appear in its primary lexical meaning; V2 only occurs in the sequence to mark the main verb for certain ‘grammatical’ features. Thus an ...
chapter 2 theoretical background
... components of fluency are Accuracy, or accurate in decoding the words in text, second is Automaticity, or decoding words with minimal use of attentional resources, and Prosody, or the appropriate use of phrasing and expression to convey meaning. Dowhower (1997) says beginning readers are nonautomat ...
... components of fluency are Accuracy, or accurate in decoding the words in text, second is Automaticity, or decoding words with minimal use of attentional resources, and Prosody, or the appropriate use of phrasing and expression to convey meaning. Dowhower (1997) says beginning readers are nonautomat ...
Nominalizations in Ojibwe
... transparency can give us a window into the internal structure of nominalizations in a way that non-agglutinative languages cannot and this is why it is interesting to study nominalizations in such a language (see Bliss, this volume and Wiltschko, this volume, for an analysis of nominalizations in Bl ...
... transparency can give us a window into the internal structure of nominalizations in a way that non-agglutinative languages cannot and this is why it is interesting to study nominalizations in such a language (see Bliss, this volume and Wiltschko, this volume, for an analysis of nominalizations in Bl ...
Preview the Teacher`s Guide and Student Workbook
... Mechanics Practice Answers: Chris’ (or Chris’s) coat was black, and so was Mike’s. ...
... Mechanics Practice Answers: Chris’ (or Chris’s) coat was black, and so was Mike’s. ...
Document
... cognitive linguistic approaches (e.g. Croft and Cruse, 2004) which maintain that the semantic input of words is construed in context. Words are envisaged not to have pre ‑specified meanings as presumed by Lakoff, but only a “meaning potential” or general “purport” activated by the context on the ba ...
... cognitive linguistic approaches (e.g. Croft and Cruse, 2004) which maintain that the semantic input of words is construed in context. Words are envisaged not to have pre ‑specified meanings as presumed by Lakoff, but only a “meaning potential” or general “purport” activated by the context on the ba ...
Key Stage 1 Presentation - St Nicolas and St Mary CE Primary School
... What is phonics? Phonics is a way of teaching children to read quickly and skilfully. Children are taught how to recognise the sounds each individual letter makes and to identify the sounds that different combinations of letters make such as ‘sh’ and ‘oo’. Children are taught to read by breaking dow ...
... What is phonics? Phonics is a way of teaching children to read quickly and skilfully. Children are taught how to recognise the sounds each individual letter makes and to identify the sounds that different combinations of letters make such as ‘sh’ and ‘oo’. Children are taught to read by breaking dow ...
On the Role of Analogy Mechanism in Meaning Evolution of
... the language itself. And in order to achieve language analogy, there must be a “model”, namely “category”. Therefore, the form of analogy can only be deduced with one or more other forms as model, that is, category is the basis and starting point of reasoning. There exist a great number of such mode ...
... the language itself. And in order to achieve language analogy, there must be a “model”, namely “category”. Therefore, the form of analogy can only be deduced with one or more other forms as model, that is, category is the basis and starting point of reasoning. There exist a great number of such mode ...
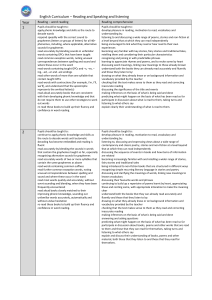
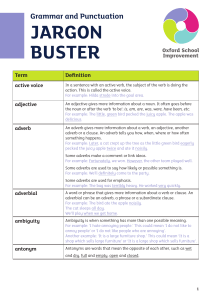
JarGon Buster
... A comma can be used to separate items in a list. For example: I like peas, carrots, beans and pizza. Some texts use the serial, or Oxford, comma after the penultimate item in a list. For example: I ate an orange, an apple, and raspberries. A comma can be used to change the meaning of a sentence. For ...
... A comma can be used to separate items in a list. For example: I like peas, carrots, beans and pizza. Some texts use the serial, or Oxford, comma after the penultimate item in a list. For example: I ate an orange, an apple, and raspberries. A comma can be used to change the meaning of a sentence. For ...
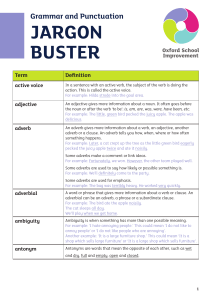
jargon buster - Cuddington and Dinton School
... A comma can be used to separate items in a list. For example: I like peas, carrots, beans and pizza. Some texts use the serial, or Oxford, comma after the penultimate item in a list. For example: I ate an orange, an apple, and raspberries. A comma can be used to change the meaning of a sentence. For ...
... A comma can be used to separate items in a list. For example: I like peas, carrots, beans and pizza. Some texts use the serial, or Oxford, comma after the penultimate item in a list. For example: I ate an orange, an apple, and raspberries. A comma can be used to change the meaning of a sentence. For ...
Syntactic notions of the first level
... » Dominational connection can be achieved with the help of various forms of the word (agreement, government), the connective words (prepositional government), wordorder. » The dominational connection can be two-way (reciprocal) and one-way. » Two-way domination is performed in predicative connectio ...
... » Dominational connection can be achieved with the help of various forms of the word (agreement, government), the connective words (prepositional government), wordorder. » The dominational connection can be two-way (reciprocal) and one-way. » Two-way domination is performed in predicative connectio ...
Sentence Structure
... grammatical categories and meaning is more complex than these few examples suggest. For example, some nouns refer to events (marriage and destruction) and others to states (happiness, loneliness). We can use abstract nouns such as honor and beauty, rather than adjectives, to refer to properties and ...
... grammatical categories and meaning is more complex than these few examples suggest. For example, some nouns refer to events (marriage and destruction) and others to states (happiness, loneliness). We can use abstract nouns such as honor and beauty, rather than adjectives, to refer to properties and ...
Joint Parameterization of Honorifics and Terms of Address in
... relevant; but this does not imply that linguistic means themselves are just an appropriate inventory and nothing else. In this paper we argue that mechanisms and rules, provided by a language, are basic in these cases. This can be highlighted with the study of honorifics and terms of address in Kart ...
... relevant; but this does not imply that linguistic means themselves are just an appropriate inventory and nothing else. In this paper we argue that mechanisms and rules, provided by a language, are basic in these cases. This can be highlighted with the study of honorifics and terms of address in Kart ...