HEAD/NECK: Cranial Nerves
... • Parasympathetic to most of gut • Taste to back posterior pharynx XI: (Spinal) • Motor to traps, Accesory sternocleidomastoid IX: Glosso- • Sensory to carotid body/sinus pharyngeal • Taste to posterior tongue • Sensory to ear opening/middle ear • Parotid salivary gland X: Vagus ...
... • Parasympathetic to most of gut • Taste to back posterior pharynx XI: (Spinal) • Motor to traps, Accesory sternocleidomastoid IX: Glosso- • Sensory to carotid body/sinus pharyngeal • Taste to posterior tongue • Sensory to ear opening/middle ear • Parotid salivary gland X: Vagus ...
Lecture 12b - Spinal Cord
... • Gray matter is central • Thick layer of white matter covers it: – consists of ascending and descending axons – organized in columns – containing axon bundles with specific ...
... • Gray matter is central • Thick layer of white matter covers it: – consists of ascending and descending axons – organized in columns – containing axon bundles with specific ...
Lecture 12b - Spinal Cord
... • Gray matter is central • Thick layer of white matter covers it: – consists of ascending and descending axons – organized in columns – containing axon bundles with specific ...
... • Gray matter is central • Thick layer of white matter covers it: – consists of ascending and descending axons – organized in columns – containing axon bundles with specific ...
MOTOR ph226 2015
... •Cortical representation of each body part is proportionate in size to the skill of that part being used for fine voluntary movement •Therefore the area involved in hand movement and in speech have large representation in the cortex (more than half of primary motor cortex) •Both individual muscles a ...
... •Cortical representation of each body part is proportionate in size to the skill of that part being used for fine voluntary movement •Therefore the area involved in hand movement and in speech have large representation in the cortex (more than half of primary motor cortex) •Both individual muscles a ...
The Nervous System
... 32. Nerves of this portion of the nervous system get the internal organs of body ready for action, the so-called “fight or flight” reflex. 33. Sensory nerves in the skin would be part of this portion of the nervous system. 34. This portion of the nervous system increases digestive system activity. 3 ...
... 32. Nerves of this portion of the nervous system get the internal organs of body ready for action, the so-called “fight or flight” reflex. 33. Sensory nerves in the skin would be part of this portion of the nervous system. 34. This portion of the nervous system increases digestive system activity. 3 ...
Ramon y Cajal deduced basic functioning of neuron
... Regulates levels of awareness and emotional aspects of sensory experiences through wide variety of effects on cortex. http://thalamus.wustl.edu/course/bassens.html ...
... Regulates levels of awareness and emotional aspects of sensory experiences through wide variety of effects on cortex. http://thalamus.wustl.edu/course/bassens.html ...
Physiology Study Guide 12
... ____ 2. A sensation is usually perceived as originating at the site where that particular sensory pathway begins. ____ 3. The semicircular canals of the vestibular apparatus provide information about the tilt of the head while standing in place. ____ 4. Rod photoreceptors are more sensitive to light ...
... ____ 2. A sensation is usually perceived as originating at the site where that particular sensory pathway begins. ____ 3. The semicircular canals of the vestibular apparatus provide information about the tilt of the head while standing in place. ____ 4. Rod photoreceptors are more sensitive to light ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and
... • Electromagnetic receptors- detect light on the retina ...
... • Electromagnetic receptors- detect light on the retina ...
Document
... -ridges = gyri (gyrus) -specific gyri are for the processing of sensation, area of voluntary movement, speech, all thought processes -called motor and sensory areas ...
... -ridges = gyri (gyrus) -specific gyri are for the processing of sensation, area of voluntary movement, speech, all thought processes -called motor and sensory areas ...
Lecture
... -ridges = gyri (gyrus) -specific gyri are for the processing of sensation, area of voluntary movement, speech, all thought processes -called motor and sensory areas ...
... -ridges = gyri (gyrus) -specific gyri are for the processing of sensation, area of voluntary movement, speech, all thought processes -called motor and sensory areas ...
Human Nervous system
... network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions and transmit signals between different parts of human body. In Human nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous system contains the brain, spinal cord, and retina. The peripheral nervous sy ...
... network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions and transmit signals between different parts of human body. In Human nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous system contains the brain, spinal cord, and retina. The peripheral nervous sy ...
Nerve activates contraction
... There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each vertebrae for a total of 31 pairs Spinal nerves are formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord Spinal nerves are named for the region from which they arise ...
... There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each vertebrae for a total of 31 pairs Spinal nerves are formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord Spinal nerves are named for the region from which they arise ...
the organization of the arthropod central nervous system
... tion between primary sensory fibers and final motor fibers, are present in all animals. Because the delay times involved are the shortest possible, monosynaptic reflexes are common in quick withdrawal movements, which generally have priority over all other responses. However it is quite incorrect to ...
... tion between primary sensory fibers and final motor fibers, are present in all animals. Because the delay times involved are the shortest possible, monosynaptic reflexes are common in quick withdrawal movements, which generally have priority over all other responses. However it is quite incorrect to ...
STUDY GUIDE 8
... reaching a synaptic knob causes the release of a ____11____ into the ____12____ . The ____13____ binds with ____14___ on the postsynaptic neuron, causing an ____15___ to be formed. An enzyme quickly breaks down the ____16___ and restores the synapse to its resting ...
... reaching a synaptic knob causes the release of a ____11____ into the ____12____ . The ____13____ binds with ____14___ on the postsynaptic neuron, causing an ____15___ to be formed. An enzyme quickly breaks down the ____16___ and restores the synapse to its resting ...
File
... The Peripheral Nervous System includes a- somatic and bautonomic nerves. Somatic nerves mediate voluntary movement. The autonomic nerves serve the involuntary action. At the cellular level The nervous system is defined by the presence of a special type of cell, called the neuron, also known as a "n ...
... The Peripheral Nervous System includes a- somatic and bautonomic nerves. Somatic nerves mediate voluntary movement. The autonomic nerves serve the involuntary action. At the cellular level The nervous system is defined by the presence of a special type of cell, called the neuron, also known as a "n ...
Divisions of the Nervous System Section 35-3 pgs 901-904
... Although the commands to move muscles come from the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum ___________________________________________________ the actions of the muscles so that the body can move gracefully and efficiently. ...
... Although the commands to move muscles come from the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum ___________________________________________________ the actions of the muscles so that the body can move gracefully and efficiently. ...
The ABCs of VEPs and ERGs Visual Testing Systems Clinical
... Structural Loss by Several Years in Glaucoma Suspects. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, March 2013, Vol. 54, No. 3, 2346-2352. ...
... Structural Loss by Several Years in Glaucoma Suspects. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, March 2013, Vol. 54, No. 3, 2346-2352. ...
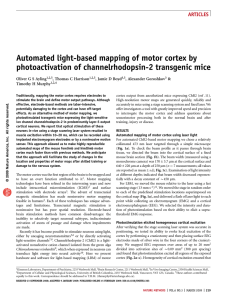
Nat Methods 6:219-224 - University of British Columbia
... in four mice, unpaired t-test; Fig. 2d). We also found that targeting the laser at the exposed EEG electrode caused a large photoelectric artifact that was different in kinetics from the results of cortical tissue excitation and was restricted to periods when the laser was activated. As expected, wi ...
... in four mice, unpaired t-test; Fig. 2d). We also found that targeting the laser at the exposed EEG electrode caused a large photoelectric artifact that was different in kinetics from the results of cortical tissue excitation and was restricted to periods when the laser was activated. As expected, wi ...
Lecture notes for October 9, 2015 FINAL
... Communication to and from the brain involves tracts Ascending tracts are sensory o Deliver information to the brain Descending tracts are motor o Deliver information to the periphery Naming the tracts o If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract deliv ...
... Communication to and from the brain involves tracts Ascending tracts are sensory o Deliver information to the brain Descending tracts are motor o Deliver information to the periphery Naming the tracts o If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract deliv ...
Document
... 29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Sponge 5 1) Sensory neurons: detect stimuli and transmit signals to the brain and the spinal cord 2) Interneurons: receive signals from sensory neurons and relay them within the brain and spinal cord 3) Motor neurons: pass messages from the nervous system ...
... 29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Sponge 5 1) Sensory neurons: detect stimuli and transmit signals to the brain and the spinal cord 2) Interneurons: receive signals from sensory neurons and relay them within the brain and spinal cord 3) Motor neurons: pass messages from the nervous system ...
sensor
... the skin it diffuses into the electrolyte. It reacts with water forming carbonic acid and immediately dissociates by the following equation. The changes in H in the electrolyte imply changes in pH. As the pH in the electrolyte changes, the voltage between the glass electrode and reference electrode ...
... the skin it diffuses into the electrolyte. It reacts with water forming carbonic acid and immediately dissociates by the following equation. The changes in H in the electrolyte imply changes in pH. As the pH in the electrolyte changes, the voltage between the glass electrode and reference electrode ...
Sensors in the field of Sleep
... For the pO2 reading oxygen diffuses to the platinum cathode through the electrodes membrane. A reduction in oxygen occurs as a result of the current generating process.This reduction generates a current which is fed into the pO2 channel and converted to a voltage, digitalized then passed to the micr ...
... For the pO2 reading oxygen diffuses to the platinum cathode through the electrodes membrane. A reduction in oxygen occurs as a result of the current generating process.This reduction generates a current which is fed into the pO2 channel and converted to a voltage, digitalized then passed to the micr ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... electromagnetic signals from the brain, these devices are not yet practical for BCI use. Currently, the four primary recording modalities are electroencephalography (EEG), electrocorticography (ECoG), local field potentials (LFPs), and single-neuron action potential recordings (single units). All of ...
... electromagnetic signals from the brain, these devices are not yet practical for BCI use. Currently, the four primary recording modalities are electroencephalography (EEG), electrocorticography (ECoG), local field potentials (LFPs), and single-neuron action potential recordings (single units). All of ...