Heading Glossary of grammatical terms
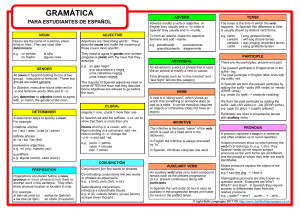
... an article or a pronoun has to ‘agree’ with the gender, number and (usually) case of the noun or pronoun it accompanies or replaces. ■ article There are two types of article in English and German: definite (the) and indefinite (a, an). However, in German the form of both definite and indefinite arti ...
... an article or a pronoun has to ‘agree’ with the gender, number and (usually) case of the noun or pronoun it accompanies or replaces. ■ article There are two types of article in English and German: definite (the) and indefinite (a, an). However, in German the form of both definite and indefinite arti ...
Parts of Speech - Hewlett
... -ing present progressive believing have… present perfect have believed had… past perfect had believed ...
... -ing present progressive believing have… present perfect have believed had… past perfect had believed ...
gramática - Light Bulb Languages
... The tense is the time in which the verb happens. In Spanish this difference in time is usually shown by distinct verb forms. ...
... The tense is the time in which the verb happens. In Spanish this difference in time is usually shown by distinct verb forms. ...
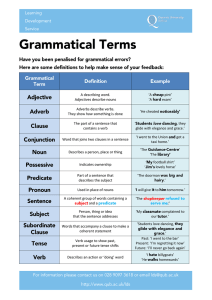
REV Grammar Handout
... Misplaced Modifier: a modifier that is placed far from the word it modifies, a modifier whose placement changes the meaning of a sentence, or a split infinitive (437-38) Dangling Modifier: a phrase or clause (often using “-ed” or “-ing”) that is not correctly attached to the object it describes (438 ...
... Misplaced Modifier: a modifier that is placed far from the word it modifies, a modifier whose placement changes the meaning of a sentence, or a split infinitive (437-38) Dangling Modifier: a phrase or clause (often using “-ed” or “-ing”) that is not correctly attached to the object it describes (438 ...
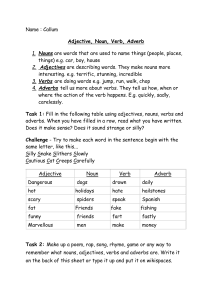
Name : Callum Adjective, Noun, Verb, Adverb Nouns are words that
... things) e.g. car, boy, house 2. Adjectives are describing words. They make nouns more interesting. e.g. terrific, stunning, incredible 3. Verbs are doing words e.g. jump, run, walk, chop 4. Adverbs tell us more about verbs. They tell us how, when or where the action of the verb happens. E.g. quickly ...
... things) e.g. car, boy, house 2. Adjectives are describing words. They make nouns more interesting. e.g. terrific, stunning, incredible 3. Verbs are doing words e.g. jump, run, walk, chop 4. Adverbs tell us more about verbs. They tell us how, when or where the action of the verb happens. E.g. quickly ...
A describing word. Adjectives describe nouns `A pint` `A exam
... Adverbs describe verbs. They show how something is done ...
... Adverbs describe verbs. They show how something is done ...
What is a VERB? - partsofspeech4
... What is an ADJECTIVE? • An adjective DESCRIBES a noun or pronoun. • Listen carefully and try to find three adjectives. Write them on the lines. To review parts of speech-visit http://partsofspeech4.wikispaces.com ...
... What is an ADJECTIVE? • An adjective DESCRIBES a noun or pronoun. • Listen carefully and try to find three adjectives. Write them on the lines. To review parts of speech-visit http://partsofspeech4.wikispaces.com ...
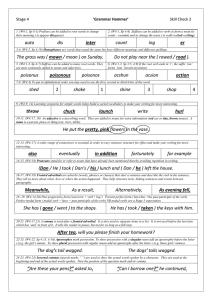
Stage 4 Check 2 – Answers
... 1. (W4:1, Sp 4:1) Prefixes can be added to root words to change their meaning ( ie appear-disappear) ...
... 1. (W4:1, Sp 4:1) Prefixes can be added to root words to change their meaning ( ie appear-disappear) ...
Stage 4 Check 2 – Answers
... 1. (W4:1, Sp 4:1) Prefixes can be added to root words to change their meaning ( ie appear-disappear) ...
... 1. (W4:1, Sp 4:1) Prefixes can be added to root words to change their meaning ( ie appear-disappear) ...
APP-Writing-Glossary-L1-and-2
... The word technique consists of only one morpheme having two syllables. Even though the word has two syllables, it is a single morpheme because it cannot be broken down into smaller meaningful parts. ...
... The word technique consists of only one morpheme having two syllables. Even though the word has two syllables, it is a single morpheme because it cannot be broken down into smaller meaningful parts. ...
A verb is a word that expresses an action, a happening, a process or
... Names of people and places are called Proper Nouns In the sentence ‘My older sister won some money in a competition’, ‘sister’, ‘money’ and ‘competition’ are nouns. ...
... Names of people and places are called Proper Nouns In the sentence ‘My older sister won some money in a competition’, ‘sister’, ‘money’ and ‘competition’ are nouns. ...
Slide 1
... Linking - connect the subject to an adjective or noun. Auxiliary - work to form verb phrases that can give more information about when something occurred. (also called helping verbs) Irregulars– form tenses in unusual ways Great writers know a well chosen verb is more powerful than the over use of a ...
... Linking - connect the subject to an adjective or noun. Auxiliary - work to form verb phrases that can give more information about when something occurred. (also called helping verbs) Irregulars– form tenses in unusual ways Great writers know a well chosen verb is more powerful than the over use of a ...
Document
... appear, feel, smell, seem, sound, taste, become, grow, remain look, stay, turn, (Linking verbs / or action) (green list) Verb phrase- the main verb and all its helpers 5. ADVERB- describes (modifies) a verb, adverb, or a adjective Answers the questions – How? When? Where? How much? (To what degree) ...
... appear, feel, smell, seem, sound, taste, become, grow, remain look, stay, turn, (Linking verbs / or action) (green list) Verb phrase- the main verb and all its helpers 5. ADVERB- describes (modifies) a verb, adverb, or a adjective Answers the questions – How? When? Where? How much? (To what degree) ...
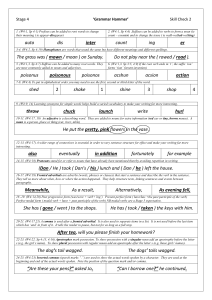
Stage 4 Check 5 - Tranmere Park Primary School
... 18 -19. (W4:14,20) Past progressive form (was/were + verb+’ing’) Present perfect form ( have/has +the past participle of the verb) Perfect modal form ( modal verb + have + past participle of the verb) NB modal verbs are a Stage 5 expectation. ...
... 18 -19. (W4:14,20) Past progressive form (was/were + verb+’ing’) Present perfect form ( have/has +the past participle of the verb) Perfect modal form ( modal verb + have + past participle of the verb) NB modal verbs are a Stage 5 expectation. ...
Parts of Speech
... of language except for nouns: verbs, adjectives (including numbers), clauses, sentences and other adverbs. Adverbs typically answer such questions as how?, when?, where?, in what way?, or how often? ...
... of language except for nouns: verbs, adjectives (including numbers), clauses, sentences and other adverbs. Adverbs typically answer such questions as how?, when?, where?, in what way?, or how often? ...
File
... What about fight and laugh? Aren’t those verbs? The fight rattled the crowd. Her laugh rang, high-pitched, through the cafeteria. ...
... What about fight and laugh? Aren’t those verbs? The fight rattled the crowd. Her laugh rang, high-pitched, through the cafeteria. ...
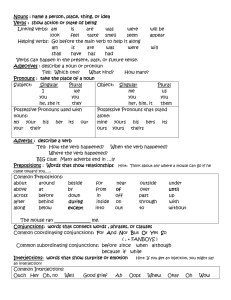
Nouns - name a person, place, thing, or idea
... is are was were will be look feel taste smell seem appear Helping verbs: Go before the main verb to help it along am is are was were will shall have has had Verbs can happen in the present, past, or future tense. Adjectives : describe a noun or pronoun Tell: Which one? What kind? How many? Pronouns ...
... is are was were will be look feel taste smell seem appear Helping verbs: Go before the main verb to help it along am is are was were will shall have has had Verbs can happen in the present, past, or future tense. Adjectives : describe a noun or pronoun Tell: Which one? What kind? How many? Pronouns ...
WOW Day 2 corrected
... 3. Subject-verb agreement – if the subject of the sentence is singular, then the verb is also singular - Example: My dog is cute (dog = subject, is = verb) 4. Irregular verbs – in past tense we change the spelling (don’t just add –ed) Examples: tell – told teach – taught swim – swam ride – rode 5. A ...
... 3. Subject-verb agreement – if the subject of the sentence is singular, then the verb is also singular - Example: My dog is cute (dog = subject, is = verb) 4. Irregular verbs – in past tense we change the spelling (don’t just add –ed) Examples: tell – told teach – taught swim – swam ride – rode 5. A ...
Grammar: Verbs, Adjectives, and Nouns followed by Prepositions
... Grammar: Verbs, Adjectives, and Nouns followed by Prepositions The texts above contain verbs, adjectives, and nouns that are followed by prepositions. Learning to use the correct preposition following a verb, adjective or noun can be challenging; particularly when the preposition differs from, e.g. ...
... Grammar: Verbs, Adjectives, and Nouns followed by Prepositions The texts above contain verbs, adjectives, and nouns that are followed by prepositions. Learning to use the correct preposition following a verb, adjective or noun can be challenging; particularly when the preposition differs from, e.g. ...
subject-predicate-prepositional phrases
... • When you see –ed, it MIGHT mean it is a _________ ________ _________ ...
... • When you see –ed, it MIGHT mean it is a _________ ________ _________ ...
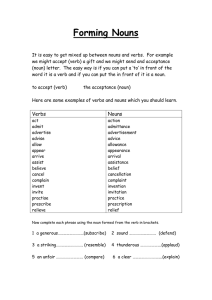
Forming nouns
... Forming Nouns It is easy to get mixed up between nouns and verbs. For example we might accept (verb) a gift and we might send and acceptance (noun) letter. The easy way is if you can put a ‘to’ in front of the word it is a verb and if you can put the in front of it is a noun. to accept (verb) ...
... Forming Nouns It is easy to get mixed up between nouns and verbs. For example we might accept (verb) a gift and we might send and acceptance (noun) letter. The easy way is if you can put a ‘to’ in front of the word it is a verb and if you can put the in front of it is a noun. to accept (verb) ...
The Nine Parts of Speech Verbs • Action Verb: tells what the subject
... word or words that describe it. has, have, had, do, does, did Nouns • Common Nouns: name a whole group or general person, place, thing, or idea. state, school, table, chair • Proper Nouns: name a specific person, place, thing, or idea. Missouri, Central High School, Emily Pronouns: a word that r ...
... word or words that describe it. has, have, had, do, does, did Nouns • Common Nouns: name a whole group or general person, place, thing, or idea. state, school, table, chair • Proper Nouns: name a specific person, place, thing, or idea. Missouri, Central High School, Emily Pronouns: a word that r ...
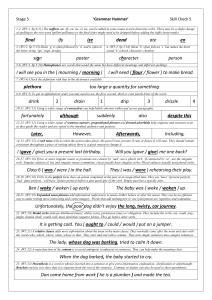
final ify ize dead ate en sign poster character person I will see you in
... verb. Singular subjects (I, he) and singular nouns (committee, class) usually have singular verbs. Plural subjects usually need plural verbs. ...
... verb. Singular subjects (I, he) and singular nouns (committee, class) usually have singular verbs. Plural subjects usually need plural verbs. ...
Inflection

In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. The inflection of verbs is also called conjugation, and the inflection of nouns, adjectives and pronouns is also called declension.An inflection expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. For example, the Latin verb ducam, meaning ""I will lead"", includes the suffix -am, expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense (future). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause ""I will lead"", the word lead is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb.The inflected form of a word often contains both a free morpheme (a unit of meaning which can stand by itself as a word), and a bound morpheme (a unit of meaning which cannot stand alone as a word). For example, the English word cars is a noun that is inflected for number, specifically to express the plural; the content morpheme car is unbound because it could stand alone as a word, while the suffix -s is bound because it cannot stand alone as a word. These two morphemes together form the inflected word cars.Words that are never subject to inflection are said to be invariant; for example, the English verb must is an invariant item: it never takes a suffix or changes form to signify a different grammatical category. Its categories can be determined only from its context.Requiring the inflections of more than one word in a sentence to be compatible according to the rules of the language is known as concord or agreement. For example, in ""the choir sings"", ""choir"" is a singular noun, so ""sing"" is constrained in the present tense to use the third person singular suffix ""s"".Languages that have some degree of inflection are synthetic languages. These can be highly inflected, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, or weakly inflected, such as English. Languages that are so inflected that a sentence can consist of a single highly inflected word (such as many American Indian languages) are called polysynthetic languages. Languages in which each inflection conveys only a single grammatical category, such as Finnish, are known as agglutinative languages, while languages in which a single inflection can convey multiple grammatical roles (such as both nominative case and plural, as in Latin and German) are called fusional. Languages such as Mandarin Chinese that never use inflections are called analytic or isolating.