Complex Sentence
... That’s magazine. It arrived this morning They’re the postcards. I sent them from Spain. They are the workmen. I paid them for the job. ...
... That’s magazine. It arrived this morning They’re the postcards. I sent them from Spain. They are the workmen. I paid them for the job. ...
Вопрос №1
... The principal language is Gothic. By the 3d century of our era, the Goths had left the region of Vistula where they lived and moved to the shore of the Black Sea. There in the 4th century they were christianized by a missionary called Ulfilas. For that purpose he translated into the Gothic language ...
... The principal language is Gothic. By the 3d century of our era, the Goths had left the region of Vistula where they lived and moved to the shore of the Black Sea. There in the 4th century they were christianized by a missionary called Ulfilas. For that purpose he translated into the Gothic language ...
Write-Brained Notions in a Left
... close to them to learn of this tragic event. Miss Scarlet, exwife of Apple’s Steve Jobs, felt her Apple stock would tumble when Professor Plum’s Vista vision came to fruition. Executives at Microsoft were inconsolable with this latest “Black Screen of Death.” ...
... close to them to learn of this tragic event. Miss Scarlet, exwife of Apple’s Steve Jobs, felt her Apple stock would tumble when Professor Plum’s Vista vision came to fruition. Executives at Microsoft were inconsolable with this latest “Black Screen of Death.” ...
Phrases - Belle Vernon Area School District
... ***Definition – A phrase is a group of words working together to function as a single part of speech. That means that an entire phrase can be for example a verb (ex. has been walking) or an adverb (ex. to the store). A phrase is NOT a sentence; therefore, it CANNOT contain a subject and a verb. I. ...
... ***Definition – A phrase is a group of words working together to function as a single part of speech. That means that an entire phrase can be for example a verb (ex. has been walking) or an adverb (ex. to the store). A phrase is NOT a sentence; therefore, it CANNOT contain a subject and a verb. I. ...
ENGLISH LESSON 3 CONTENTS TENSE KINDS OF VERBS THE
... verb in every sentence to make it understandable and that the verb has to agree with the subject of the sentence in both person and number. We have seen that verbs are generally the "doing" words; ie. they tell us what the subject does. We are now going to learn that verbs also tell us about the "ti ...
... verb in every sentence to make it understandable and that the verb has to agree with the subject of the sentence in both person and number. We have seen that verbs are generally the "doing" words; ie. they tell us what the subject does. We are now going to learn that verbs also tell us about the "ti ...
Lecture 03 - ELTE / SEAS
... It can’t be because the noun does not assign Case if we assume that such objects don’t have Case But the fact that the preposition makes it grammatical suggests that this is to do with Case Therefore we conclude that all nominals have (abstract) Case even if they show no morphological Case ...
... It can’t be because the noun does not assign Case if we assume that such objects don’t have Case But the fact that the preposition makes it grammatical suggests that this is to do with Case Therefore we conclude that all nominals have (abstract) Case even if they show no morphological Case ...
Uses - WordPress.com
... The Subjunctive Mood – Basics • many uses of the subjunctive mood, mostly in subordinate clauses • no uniform translation for subj. verbs – translation depends on clause in which it’s used • subj. mood = nonfactual; usually expresses doubt, uncertainty, possibility, or action as idea or wish ...
... The Subjunctive Mood – Basics • many uses of the subjunctive mood, mostly in subordinate clauses • no uniform translation for subj. verbs – translation depends on clause in which it’s used • subj. mood = nonfactual; usually expresses doubt, uncertainty, possibility, or action as idea or wish ...
Grammatical terminology recommended by the LAGB for use in
... shoot the man. Both interpretations are possible, and either makes sense. Ambiguity is often a source of humour. anaphora, anaphoric. Anaphora is the 'referring back' relation between one word and another, its antecedent. For example, in Bill hurt himself, the reflexive pronoun himself refers back a ...
... shoot the man. Both interpretations are possible, and either makes sense. Ambiguity is often a source of humour. anaphora, anaphoric. Anaphora is the 'referring back' relation between one word and another, its antecedent. For example, in Bill hurt himself, the reflexive pronoun himself refers back a ...
Agreement of the Predicator with the Subject
... In principle the predicator agrees with the subject in number and person – in Modern English agreement with the subject is restricted to the present tense forms. The bell rings. The verb be is an exception because it agrees with the subject not only in the present tense but in the past tense as well ...
... In principle the predicator agrees with the subject in number and person – in Modern English agreement with the subject is restricted to the present tense forms. The bell rings. The verb be is an exception because it agrees with the subject not only in the present tense but in the past tense as well ...
generate: a natural language sentence
... interesting exercise will be the inclusion of embedded sentences in the grammar. The semantic element will play an important role here, as well, but the transformations involved are fairly well understood. The program was written in BASIC because of its ready availability on microcomputers. GENERATE ...
... interesting exercise will be the inclusion of embedded sentences in the grammar. The semantic element will play an important role here, as well, but the transformations involved are fairly well understood. The program was written in BASIC because of its ready availability on microcomputers. GENERATE ...
Rules for subject verb agreement
... One-fourth of the books are gone. One-fourth of the sand is white. 31. Use singular verbs for the titles of single entities (books, novels, magazine, movies, newspaper, compositions, plays /films, organizations, nations, countries, etc.) as they are always singular. ...
... One-fourth of the books are gone. One-fourth of the sand is white. 31. Use singular verbs for the titles of single entities (books, novels, magazine, movies, newspaper, compositions, plays /films, organizations, nations, countries, etc.) as they are always singular. ...
AP STYLE ADDRESSES Use Ave., Blvd. and St. only with a
... ----Any parent who wants to enroll their child must provide a vaccination record. (incorrect) Any parent who wants to enroll her child must provide a vaccination record. (correct) Any parent who wants to enroll his child must provide a vaccination record. (correct) Any parent who wants to enroll his ...
... ----Any parent who wants to enroll their child must provide a vaccination record. (incorrect) Any parent who wants to enroll her child must provide a vaccination record. (correct) Any parent who wants to enroll his child must provide a vaccination record. (correct) Any parent who wants to enroll his ...
Presentation Exercise: Chapter 38
... Fill in the Blank. __________________________ is the term used for the phenomenon in which a speaker produces faulty grammar by importing a linguistic rule or feature associated elsewhere with valid grammar into a context where it does not apply. Fill in the Blank. The acronym SCID stands for “_____ ...
... Fill in the Blank. __________________________ is the term used for the phenomenon in which a speaker produces faulty grammar by importing a linguistic rule or feature associated elsewhere with valid grammar into a context where it does not apply. Fill in the Blank. The acronym SCID stands for “_____ ...
Micro-Skills - Tippie College of Business
... page for definitions of prepositions and conjunctions. Very often, complete sentences become fragments with the addition of one of these words. For instance, "I want a new job" is a complete sentence. "Because I want a new job" is a fragment; it leaves the reader without any information as to what h ...
... page for definitions of prepositions and conjunctions. Very often, complete sentences become fragments with the addition of one of these words. For instance, "I want a new job" is a complete sentence. "Because I want a new job" is a fragment; it leaves the reader without any information as to what h ...
Academic writing: sentence level
... A run-on sentence occurs when two independent clauses (of two complete thoughts) are blended into one without proper punctuation. Examples: The survey shows that more than 80% of the population agrees that racism is rife however only 12% of the population admits that they are racist. More than 80% o ...
... A run-on sentence occurs when two independent clauses (of two complete thoughts) are blended into one without proper punctuation. Examples: The survey shows that more than 80% of the population agrees that racism is rife however only 12% of the population admits that they are racist. More than 80% o ...
Word Detective Word Detective
... Word Detective Record your response in your Literacy Notebook/Folder Find and record 10 linking verbs. Remember, a linking verb is a verb that does not show action, but it does link the subject to words that tell something about the subject (Example: are, is, was, etc.). • Choose any three words fro ...
... Word Detective Record your response in your Literacy Notebook/Folder Find and record 10 linking verbs. Remember, a linking verb is a verb that does not show action, but it does link the subject to words that tell something about the subject (Example: are, is, was, etc.). • Choose any three words fro ...
Verbs
... The verbs am, is, are, was, and were are forms of the verb to be. They do not show action. They tell what someone or something is or was. Am, is, and are show present time. Was and were show past time. ...
... The verbs am, is, are, was, and were are forms of the verb to be. They do not show action. They tell what someone or something is or was. Am, is, and are show present time. Was and were show past time. ...
Reflexive Pronouns
... the action of the verb is occurring to the subject of the sentence. We use reflexive pronouns in such cases: 1.As the direct object or indirect object of the verb when we want to say that the object is the same person or thing as the subject of the verb in the same clause. 2.With transitive verbs. 3 ...
... the action of the verb is occurring to the subject of the sentence. We use reflexive pronouns in such cases: 1.As the direct object or indirect object of the verb when we want to say that the object is the same person or thing as the subject of the verb in the same clause. 2.With transitive verbs. 3 ...
Unit 1 - Types of Words and Word-Formation
... a. Lexical (content or referential) morphemes are free morphemes that have semantic content (or meaning) and usually refer to a thing, quality, state or action. For instance, in a language, these morphemes generally take the forms of nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs; e.g., dog, Peter, house, bui ...
... a. Lexical (content or referential) morphemes are free morphemes that have semantic content (or meaning) and usually refer to a thing, quality, state or action. For instance, in a language, these morphemes generally take the forms of nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs; e.g., dog, Peter, house, bui ...
File - MS. FORD and MS. PARKER
... • Compound sentence- sentence made up of two or more independent clauses joined by a conjunction. • Subordinate (dependent) clause- has a subject and a verb but DOES NOT express a complete thought • Subordinate clauses cannot stand alone; they are sentence fragments. ...
... • Compound sentence- sentence made up of two or more independent clauses joined by a conjunction. • Subordinate (dependent) clause- has a subject and a verb but DOES NOT express a complete thought • Subordinate clauses cannot stand alone; they are sentence fragments. ...
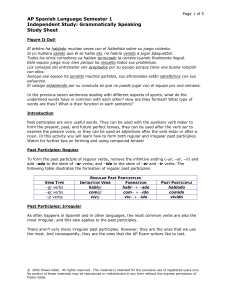
AP Spanish Language Semester 1 Independent Study
... In the previous seven sentences dealing with different aspects of sports, what do the underlined words have in common with each other? How are they formed? What type of words are they? What is their function in each sentence? Introduction Past participles are very useful words. They can be used with ...
... In the previous seven sentences dealing with different aspects of sports, what do the underlined words have in common with each other? How are they formed? What type of words are they? What is their function in each sentence? Introduction Past participles are very useful words. They can be used with ...
abbreviation - LAGB Education Committee
... brunch = breakfast + lunch borrow, borrowing. The speakers of one language may ‘borrow’ words from another. For instance, the word tsunami is a borrowing (or loan word) from Japanese, meaning that English speakers use the word as if it was an ordinary English word, even if they know that it was orig ...
... brunch = breakfast + lunch borrow, borrowing. The speakers of one language may ‘borrow’ words from another. For instance, the word tsunami is a borrowing (or loan word) from Japanese, meaning that English speakers use the word as if it was an ordinary English word, even if they know that it was orig ...
The Uses and Orthography of the Verb “Say”
... The words structure is agglutinative, and grammatical morphemes are suffixed to the root rather than prefixed. Andaandi also has some dialectical variation in different areas and sometimes in the same area. However, these differences are minor and do not have any grammatical or semantical effects. T ...
... The words structure is agglutinative, and grammatical morphemes are suffixed to the root rather than prefixed. Andaandi also has some dialectical variation in different areas and sometimes in the same area. However, these differences are minor and do not have any grammatical or semantical effects. T ...
4. Verbal Categories (Morphological forms. Transitivity. Reflexivity
... perfect, imperfect progressive, nonprogressive indicative, subjunctive, conditional ...
... perfect, imperfect progressive, nonprogressive indicative, subjunctive, conditional ...
Inflection

In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. The inflection of verbs is also called conjugation, and the inflection of nouns, adjectives and pronouns is also called declension.An inflection expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. For example, the Latin verb ducam, meaning ""I will lead"", includes the suffix -am, expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense (future). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause ""I will lead"", the word lead is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb.The inflected form of a word often contains both a free morpheme (a unit of meaning which can stand by itself as a word), and a bound morpheme (a unit of meaning which cannot stand alone as a word). For example, the English word cars is a noun that is inflected for number, specifically to express the plural; the content morpheme car is unbound because it could stand alone as a word, while the suffix -s is bound because it cannot stand alone as a word. These two morphemes together form the inflected word cars.Words that are never subject to inflection are said to be invariant; for example, the English verb must is an invariant item: it never takes a suffix or changes form to signify a different grammatical category. Its categories can be determined only from its context.Requiring the inflections of more than one word in a sentence to be compatible according to the rules of the language is known as concord or agreement. For example, in ""the choir sings"", ""choir"" is a singular noun, so ""sing"" is constrained in the present tense to use the third person singular suffix ""s"".Languages that have some degree of inflection are synthetic languages. These can be highly inflected, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, or weakly inflected, such as English. Languages that are so inflected that a sentence can consist of a single highly inflected word (such as many American Indian languages) are called polysynthetic languages. Languages in which each inflection conveys only a single grammatical category, such as Finnish, are known as agglutinative languages, while languages in which a single inflection can convey multiple grammatical roles (such as both nominative case and plural, as in Latin and German) are called fusional. Languages such as Mandarin Chinese that never use inflections are called analytic or isolating.