SBI4U - 9.2
... neurons and effectors • A single neuron may branch off and join with many different neurons • Involves neurotransmitters: chemicals release from vesicles to synapses • Presynaptic neuron: neuron that carries impulses to the synapse • Postsynaptic neuron: neuron that carries impulses away from the sy ...
... neurons and effectors • A single neuron may branch off and join with many different neurons • Involves neurotransmitters: chemicals release from vesicles to synapses • Presynaptic neuron: neuron that carries impulses to the synapse • Postsynaptic neuron: neuron that carries impulses away from the sy ...
Toward STDP-based population action in large networks of spiking
... when 2πf t = 0 mod 2π and P2 is redrawn when 2πf t = π2 mod 2π, which introduces novelty and cancels the periodicity. After a short relaxation (200 ms), the STDP plasticity is activated for 5 s on the excitatory synapses of excitatory neurons only. We represent in figure 1 the population response in ...
... when 2πf t = 0 mod 2π and P2 is redrawn when 2πf t = π2 mod 2π, which introduces novelty and cancels the periodicity. After a short relaxation (200 ms), the STDP plasticity is activated for 5 s on the excitatory synapses of excitatory neurons only. We represent in figure 1 the population response in ...
unit 2: biological bases of behavior
... Brain Imaging Techniques (p.66-68): Explain the techniques used to investigate the structures and functions of the brain. ...
... Brain Imaging Techniques (p.66-68): Explain the techniques used to investigate the structures and functions of the brain. ...
Nervous System Communication
... Sodium-Potassium Pump • Proteins embedded within cell membrane • Moves sodium to the outside ...
... Sodium-Potassium Pump • Proteins embedded within cell membrane • Moves sodium to the outside ...
Word version - World Book Encyclopedia
... World Book’s Building Blocks of Life Science The Nervous System Activity Sheet© ...
... World Book’s Building Blocks of Life Science The Nervous System Activity Sheet© ...
The Nervous System Activity Sheet
... World Book’s Building Blocks of Life Science The Nervous System Activity Sheet© ...
... World Book’s Building Blocks of Life Science The Nervous System Activity Sheet© ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... a. Thalamus- portion of the lower brain that functions primarily as a central relay station for incoming and outgoing messages from the body to the brain and the brain to the body b. Hypothalamus- portion of the lower brain that regulates basic needs (hunger, thirst) and emotions such as pleasure, f ...
... a. Thalamus- portion of the lower brain that functions primarily as a central relay station for incoming and outgoing messages from the body to the brain and the brain to the body b. Hypothalamus- portion of the lower brain that regulates basic needs (hunger, thirst) and emotions such as pleasure, f ...
fleming_Oct
... Hormones are chemicals secreted by endocrine organs in the body into the circulatory system Hormones act at a distance from where they are released NTs act close to release point Hormones act on receptors in other organs and in the brain Hormones act on general metabolism, arousal, and growth ...
... Hormones are chemicals secreted by endocrine organs in the body into the circulatory system Hormones act at a distance from where they are released NTs act close to release point Hormones act on receptors in other organs and in the brain Hormones act on general metabolism, arousal, and growth ...
3.13
... functioning of a neuron are sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions. The cell membrane of a neuron is impermeable to sodium and potassium ions when the cell is in a resting state. In a typical neuron in its resting state, the concentration of Na+ in the interior of the cell is about one-tenth of the ex ...
... functioning of a neuron are sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions. The cell membrane of a neuron is impermeable to sodium and potassium ions when the cell is in a resting state. In a typical neuron in its resting state, the concentration of Na+ in the interior of the cell is about one-tenth of the ex ...
Nervous System
... there are many layers of cell membrane insulating it. There are small gaps, called nodes of Ranvier, between individual Schwann cells. Conduction velocity goes from about 5m/s without the myelin sheath to ~150m/s with it. ...
... there are many layers of cell membrane insulating it. There are small gaps, called nodes of Ranvier, between individual Schwann cells. Conduction velocity goes from about 5m/s without the myelin sheath to ~150m/s with it. ...
Einstein`s Brain
... Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance an ...
... Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance an ...
einsteins-brain
... Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance an ...
... Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance an ...
PART 1: TRUE OR FALSE (1 point each)
... anatomical terms to the following descriptions of function. Words may be used more than once or not at all. Be as specific as possible. 13. contains primary somatosensory cortex 14. "relay station" for visual and auditory information 15. involved in transferring information to long-term memory 16. l ...
... anatomical terms to the following descriptions of function. Words may be used more than once or not at all. Be as specific as possible. 13. contains primary somatosensory cortex 14. "relay station" for visual and auditory information 15. involved in transferring information to long-term memory 16. l ...
Philosophy of the spike
... 2) ri(t) is the expected firing probability of neuron i. 3) spike trains (realizations) depend on r(t) only, through a private stochastic process (independent neurons) Example 1: random networks If true, then ri(t) can be found by writing self-consistent equations (cf. Brunel) This works for sparse ...
... 2) ri(t) is the expected firing probability of neuron i. 3) spike trains (realizations) depend on r(t) only, through a private stochastic process (independent neurons) Example 1: random networks If true, then ri(t) can be found by writing self-consistent equations (cf. Brunel) This works for sparse ...
Nervous System - s3.amazonaws.com
... contains about 50 million neurons (nerve cells)? • Each neuron may communicate with thousands of other neurons forming intricate networks that control our functions and store our thoughts. • The nervous system has 3 major functions. – Sensory input moves signals from our various sense organs to the ...
... contains about 50 million neurons (nerve cells)? • Each neuron may communicate with thousands of other neurons forming intricate networks that control our functions and store our thoughts. • The nervous system has 3 major functions. – Sensory input moves signals from our various sense organs to the ...
Chapter 2
... junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap Neurotransmitters chemical messengers that travel the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neuro-transmitters t ...
... junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap Neurotransmitters chemical messengers that travel the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neuro-transmitters t ...
Slide ()
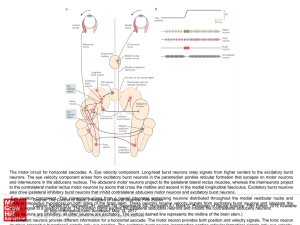
... nucleus prepositus hypoglossi on both sides of the brain stem. These neurons receive velocity signals from excitatory burst neurons and integrate this Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available velocity ...
... nucleus prepositus hypoglossi on both sides of the brain stem. These neurons receive velocity signals from excitatory burst neurons and integrate this Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available velocity ...
Chapter - Heartland Community College
... A. axons--outgoing signals B. sensory neuron--delivers signals to control sensory organs such as eye movement C. cell body--nucleus and organelles D. dendrites--incoming signals E. interneuron—conveys signals to other parts of the CNS 13. When a finger or other appendage is severed in an accident, i ...
... A. axons--outgoing signals B. sensory neuron--delivers signals to control sensory organs such as eye movement C. cell body--nucleus and organelles D. dendrites--incoming signals E. interneuron—conveys signals to other parts of the CNS 13. When a finger or other appendage is severed in an accident, i ...
Quiz - psychm5
... have a positive electric charge while neutrons have a negative charge. have neither a positive nor a negative electrical charge. can be found only inside the neuron, creating in your brain an electronic charge of about minus 90 millivolts. ...
... have a positive electric charge while neutrons have a negative charge. have neither a positive nor a negative electrical charge. can be found only inside the neuron, creating in your brain an electronic charge of about minus 90 millivolts. ...
Non- directed synapses
... • The nervous system is unique in the vast complexity of thought processes and control actions it can perform. • It receives each minute literally millions of bits of information from the different sensory nerves and sensory organs and then integrates all these to determine responses to be made by t ...
... • The nervous system is unique in the vast complexity of thought processes and control actions it can perform. • It receives each minute literally millions of bits of information from the different sensory nerves and sensory organs and then integrates all these to determine responses to be made by t ...
Name
... 4. _____ When repolarization has occurred, an impulse cannot be conducted. 5. _____ The action potential is an all-or-none response. 6. _____ In an adult, the nervous system is replete with both electrical and chemical synapses. 7. _____ Rapid succession stimulation of a postsynaptic neuron by a syn ...
... 4. _____ When repolarization has occurred, an impulse cannot be conducted. 5. _____ The action potential is an all-or-none response. 6. _____ In an adult, the nervous system is replete with both electrical and chemical synapses. 7. _____ Rapid succession stimulation of a postsynaptic neuron by a syn ...
Cell body
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...