(27)using approp. verb tense
... English has three simple tenses (past, present, and future) and three perfect tenses (present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect). In addition, each of these six tenses has a progressive form. SIMPLE TENSES The simple present tense is used primarily to describe habitual actions (Jane walks to ...
... English has three simple tenses (past, present, and future) and three perfect tenses (present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect). In addition, each of these six tenses has a progressive form. SIMPLE TENSES The simple present tense is used primarily to describe habitual actions (Jane walks to ...
Present simple - A general principle Talent shows usually allow
... happened, or refer to a current event or view. This means that the various forms of the future are less likely to be used in essays, although they might be used in reports. - ‘going to' future: They are going to research this next year. - future simple: They will research this next year. - future co ...
... happened, or refer to a current event or view. This means that the various forms of the future are less likely to be used in essays, although they might be used in reports. - ‘going to' future: They are going to research this next year. - future simple: They will research this next year. - future co ...
Tenses in academic writing Writers use tenses to give a particular
... happened, or refer to a current event or view. This means that the various forms of the future are less likely to be used in essays, although they might be used in reports. - ‘going to' future: They are going to research this next year. - future simple: They will research this next year. - future co ...
... happened, or refer to a current event or view. This means that the various forms of the future are less likely to be used in essays, although they might be used in reports. - ‘going to' future: They are going to research this next year. - future simple: They will research this next year. - future co ...
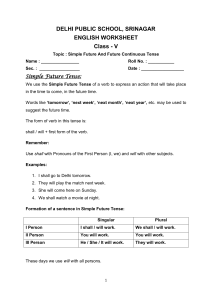
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL, SRINAGAR ENGLISH WORKSHEET
... 4. Something your family will do next vacations. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 5. Something your parents will buy for you on your birthday. ___________________________________________________________ ...
... 4. Something your family will do next vacations. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 5. Something your parents will buy for you on your birthday. ___________________________________________________________ ...
Imperfect tense
... In this little story, two slaves are returning home when they are confronted by a dog wandering loose in the streets. As with many wild street mongrols, this pooch doesn’t much like people, and so our two slaves find themselves in quite a pickle! You will also see the use of two different forms of p ...
... In this little story, two slaves are returning home when they are confronted by a dog wandering loose in the streets. As with many wild street mongrols, this pooch doesn’t much like people, and so our two slaves find themselves in quite a pickle! You will also see the use of two different forms of p ...
Verb Usage Notes - Garnet Valley School District
... Every verb has six tenses: _____________________________________________________________________ ...
... Every verb has six tenses: _____________________________________________________________________ ...
Yes/No Questions
... the simple future tense We can do the same thing with the verb To Be in the simple future tense. This time only the suffixe Will go in front of the subject. Susan will go to the dentist tomorrow afternoon Will Susan go to the dentist tomorrow afternoon? ...
... the simple future tense We can do the same thing with the verb To Be in the simple future tense. This time only the suffixe Will go in front of the subject. Susan will go to the dentist tomorrow afternoon Will Susan go to the dentist tomorrow afternoon? ...
1A The Greek Verb There are two important elements in the study of
... 2. number — whether a single individual is presented as engaging in the activity (the singular), or a group of people (the plural) [the difference, e.g., between “I” and “we,” or between “she” and “they”] 3. tense/aspect — when the action is thought of as having occurred (in the present, the future, ...
... 2. number — whether a single individual is presented as engaging in the activity (the singular), or a group of people (the plural) [the difference, e.g., between “I” and “we,” or between “she” and “they”] 3. tense/aspect — when the action is thought of as having occurred (in the present, the future, ...
Sheet1 Verbos de Indicativos
... Formed with the verb Estar in the Future Tense + Gerund. Similar to will be + -ing. Used to expresses an action that will be in progress at the moment in question. ...
... Formed with the verb Estar in the Future Tense + Gerund. Similar to will be + -ing. Used to expresses an action that will be in progress at the moment in question. ...
Conjugating –AR Verbs in the Preterite Tense
... The subjunctive tense is widely used in Spanish and expresses or implies different things from it’s English counterparts. It has a number of specific usages that we will look at one or two at a time in subsequent chapters. ...
... The subjunctive tense is widely used in Spanish and expresses or implies different things from it’s English counterparts. It has a number of specific usages that we will look at one or two at a time in subsequent chapters. ...
Tense, modality, and aspect define the status of the main verb
... notions of certainty, obligation, desire, necessity, promise, permission and even threat. Conditional concepts are concerned with events in the future. modals are sometimes said to express futurity Examples, I will visit my grandpa I will visit my grandpa tomorrow The verb following a mo ...
... notions of certainty, obligation, desire, necessity, promise, permission and even threat. Conditional concepts are concerned with events in the future. modals are sometimes said to express futurity Examples, I will visit my grandpa I will visit my grandpa tomorrow The verb following a mo ...
Verb Tenses: The Future Continuous
... Verb Tense Background • Verbs change their form to allow writers to accurately describe events. • Verbs alert the reader if the action is in the past, present or future. • Within these three main time frames, actions can be further broken down. ...
... Verb Tense Background • Verbs change their form to allow writers to accurately describe events. • Verbs alert the reader if the action is in the past, present or future. • Within these three main time frames, actions can be further broken down. ...
Using Participles
... A participle is a verb form that functions as an adjective. Used in a phrase, it may take objects, complements, and modifiers. Three forms of participles are common: present (ends in -ing), past (ends in -ed or, for irregular verbs, is the past participle form), and perfect (having + the past partic ...
... A participle is a verb form that functions as an adjective. Used in a phrase, it may take objects, complements, and modifiers. Three forms of participles are common: present (ends in -ing), past (ends in -ed or, for irregular verbs, is the past participle form), and perfect (having + the past partic ...
Grammar Workshop - American University
... When one action is happening at another particular time: It was snowing at noon. It was snowing during lunch. When one action is happening at the same time as another: It was raining while I was out walking. Remember NOT to use the past continuous tense with non-action verbs like seem and know ...
... When one action is happening at another particular time: It was snowing at noon. It was snowing during lunch. When one action is happening at the same time as another: It was raining while I was out walking. Remember NOT to use the past continuous tense with non-action verbs like seem and know ...
The Present Perfect Tense
... (hours, years, weeks, etc.). I have known him for six months. They have been married for twenty years. AJ has been in her office for almost an hour. ...
... (hours, years, weeks, etc.). I have known him for six months. They have been married for twenty years. AJ has been in her office for almost an hour. ...
Changing Verbs From Present to Past
... Many verbs have the helping verb “will” in front of them to show they will be happening. Clue words to look for are: tomorrow, some day, next time, or next week. Examples: Will play will lead will be happy Will have will eat will like ...
... Many verbs have the helping verb “will” in front of them to show they will be happening. Clue words to look for are: tomorrow, some day, next time, or next week. Examples: Will play will lead will be happy Will have will eat will like ...
Future Tense
... As the name implies the Future Tense expresses time in the future. In English this is done through the words "will" or "shall". I will be there tomorrow. What will he say? I will see you at the party. We shall wait for five minutes. Shall sounded odd, didn't it? This is because the standard rules of ...
... As the name implies the Future Tense expresses time in the future. In English this is done through the words "will" or "shall". I will be there tomorrow. What will he say? I will see you at the party. We shall wait for five minutes. Shall sounded odd, didn't it? This is because the standard rules of ...
Diapositiva 1 - teacheredgar
... used for past actions that happened either at a specific time, which can either be given by a time phrase (yesterday, last year, etc.) or understood from the context. Regular Verbs add -ed to the base form, or -d if the verbs ends with -e. Irregular verbs can change in many different ways. The verb ...
... used for past actions that happened either at a specific time, which can either be given by a time phrase (yesterday, last year, etc.) or understood from the context. Regular Verbs add -ed to the base form, or -d if the verbs ends with -e. Irregular verbs can change in many different ways. The verb ...