Vocabulary CHEM121
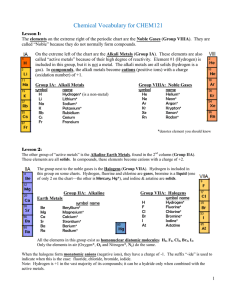
... 2. Ionic (contains ions) includes: Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently ...
... 2. Ionic (contains ions) includes: Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently ...
study material class X (science)
... 3. a) Why cannot a chemical change be normally reversed ? b) Why is it always essential to balance a chemical equation? c) What happens when CO2 gas is passed through lime water and why does it disappear on passing excess CO2? d) Can rusting of iron takes place in distilled water? Ans: a. In a chemi ...
... 3. a) Why cannot a chemical change be normally reversed ? b) Why is it always essential to balance a chemical equation? c) What happens when CO2 gas is passed through lime water and why does it disappear on passing excess CO2? d) Can rusting of iron takes place in distilled water? Ans: a. In a chemi ...
PDF of article - Crystallography Journals Online
... second, more gradual transition is observed, which ends at around 543 K. Phase 3 measured at 543 K is a hightemperature anhydrous form of the acid. The structures of phases 2 and 3 were solved from synchrotron powder diffraction data by simulated annealing using the DASH program and re®ned by the Ri ...
... second, more gradual transition is observed, which ends at around 543 K. Phase 3 measured at 543 K is a hightemperature anhydrous form of the acid. The structures of phases 2 and 3 were solved from synchrotron powder diffraction data by simulated annealing using the DASH program and re®ned by the Ri ...
File
... Calculations involving the Ion Product Constant for Water Kw Experiments have revealed that some water molecules react with each other to produce H3O+(aq) and OH-(aq) ions according to the following equation: H2O(l) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) - The production of ions occurs as the result of an i ...
... Calculations involving the Ion Product Constant for Water Kw Experiments have revealed that some water molecules react with each other to produce H3O+(aq) and OH-(aq) ions according to the following equation: H2O(l) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) - The production of ions occurs as the result of an i ...
158KB - NZQA
... Ethanoic acid does not dissociate before reacting with water, so produces fewer ions than ammonium chloride, due to the formation of ions being dependent on the position of equilibrium, which for a weak acid like ethanoic acid, lies to the left, resulting in only a small number of ions being formed ...
... Ethanoic acid does not dissociate before reacting with water, so produces fewer ions than ammonium chloride, due to the formation of ions being dependent on the position of equilibrium, which for a weak acid like ethanoic acid, lies to the left, resulting in only a small number of ions being formed ...
Chemical Equilibrium – Le Chatelier`s Principle
... constant temperature, then the equilibrium is “shifted to the right”, which means that the new equilibrium concentrations are obtained by a net increase of the forward reaction until the new equilibrium is established. The equilibrium constant remains unchanged. If, however, the temperature is chang ...
... constant temperature, then the equilibrium is “shifted to the right”, which means that the new equilibrium concentrations are obtained by a net increase of the forward reaction until the new equilibrium is established. The equilibrium constant remains unchanged. If, however, the temperature is chang ...
Spring 2002 - Kwantlen Polytechnic University
... b. The solution shows a positive deviation from Raoult’s Law. c. The solution shows a negative deviation from Raoult’s Law and possesses a minimum boiling point azeotrope. d. The solution shows a negative deviation from Raoult’s Law and possesses a maximum boiling point azeorope. e. The solution pro ...
... b. The solution shows a positive deviation from Raoult’s Law. c. The solution shows a negative deviation from Raoult’s Law and possesses a minimum boiling point azeotrope. d. The solution shows a negative deviation from Raoult’s Law and possesses a maximum boiling point azeorope. e. The solution pro ...
Question paper - Unit A173/02 - Module C7 - Higher tier
... whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our p ...
... whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our p ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
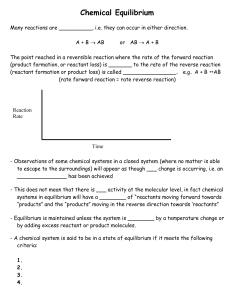
... ___________________________________________ which says that there is a ________________________________ between the concentrations of the products and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium ...
... ___________________________________________ which says that there is a ________________________________ between the concentrations of the products and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium ...
Give reasons for the following: (i) Bond enthalpy of F2
... negative charge in delocalized over two oxygen atoms (since O is more electronegative than C) which stabilizes the carboxylate ion. On the other hand, in phenoxide ion the charge is delocalized over entire molecule on the less electronegative atom (Carbon), thus resonance of phenoxide is not importa ...
... negative charge in delocalized over two oxygen atoms (since O is more electronegative than C) which stabilizes the carboxylate ion. On the other hand, in phenoxide ion the charge is delocalized over entire molecule on the less electronegative atom (Carbon), thus resonance of phenoxide is not importa ...
AP Chem Equations - Speedway High School
... strong (ionize completely) and which are weak (write as molecule). ...
... strong (ionize completely) and which are weak (write as molecule). ...
Soil-net.com Activity: Soil Chemistry Challenge
... is a 10-fold difference (because it is a logarithmic scale). There is a huge difference between each number on the scale A number above 7 is alkaline, below 7 is acid. Page 1 ...
... is a 10-fold difference (because it is a logarithmic scale). There is a huge difference between each number on the scale A number above 7 is alkaline, below 7 is acid. Page 1 ...
Solution FRQs Practice
... Two beakers, one containing 100 milliliters of a 0.10 molal solution of sucrose (a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte) the other containing 100 milliliters of pure water, are placed side by side in a closed system, such as under a bell jar. Explain in terms of the principles involved what changes, if any, o ...
... Two beakers, one containing 100 milliliters of a 0.10 molal solution of sucrose (a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte) the other containing 100 milliliters of pure water, are placed side by side in a closed system, such as under a bell jar. Explain in terms of the principles involved what changes, if any, o ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... ___________________________________________ which says that there is a ________________________________ between the concentrations of the products and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium ...
... ___________________________________________ which says that there is a ________________________________ between the concentrations of the products and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium ...
Acid-Base Equilibria and Activity
... 0.020 M OH− . In this case, there are two OH− for each Ca(OH)2 . We label this solution 0.010 M Ca(OH)2 , again recognizing that we are dealing with strong electrolytes and that there is essentially no undissociated Ca(OH)2 molecules in solution. This naming convention for solution concentration is ...
... 0.020 M OH− . In this case, there are two OH− for each Ca(OH)2 . We label this solution 0.010 M Ca(OH)2 , again recognizing that we are dealing with strong electrolytes and that there is essentially no undissociated Ca(OH)2 molecules in solution. This naming convention for solution concentration is ...
Basic Concepts - Department of Chemistry
... 1. that an exothermic reaction will shift to the left (toward reactants) if the temperature of the system is increased (heat is added); 2. that an endothermic reaction will shift to the right (toward the products) if the temperature of the system is increased; 3. that if DHrxn = 0, then a change in ...
... 1. that an exothermic reaction will shift to the left (toward reactants) if the temperature of the system is increased (heat is added); 2. that an endothermic reaction will shift to the right (toward the products) if the temperature of the system is increased; 3. that if DHrxn = 0, then a change in ...
Basic Concepts
... 1. that an exothermic reaction will shift to the left (toward reactants) if the temperature of the system is increased (heat is added); 2. that an endothermic reaction will shift to the right (toward the products) if the temperature of the system is increased; 3. that if DHrxn = 0, then a change in ...
... 1. that an exothermic reaction will shift to the left (toward reactants) if the temperature of the system is increased (heat is added); 2. that an endothermic reaction will shift to the right (toward the products) if the temperature of the system is increased; 3. that if DHrxn = 0, then a change in ...
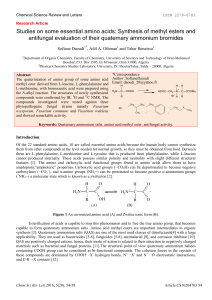
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
... Figure 1 An un-ionized amino acid (A) and Zwitter ionic form (B). Esterification of acids is capable to stop this phenomenon and to free the true amino group, that becomes capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quater ...
... Figure 1 An un-ionized amino acid (A) and Zwitter ionic form (B). Esterification of acids is capable to stop this phenomenon and to free the true amino group, that becomes capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quater ...
Sample 112 Final
... If 1.5 mol NO2, 3.0 mol O2and 2.0 mol NO3 are introduced into a 1.00 liter flask, what changes in concentration (if any) will be observed as the system reaches equilibrium? a) [NO2] increases; [O2] increases; [NO3] decreases b) [NO2] increases; [O2] decreases; [NO3] decreases c) [NO2] decreases; [O2 ...
... If 1.5 mol NO2, 3.0 mol O2and 2.0 mol NO3 are introduced into a 1.00 liter flask, what changes in concentration (if any) will be observed as the system reaches equilibrium? a) [NO2] increases; [O2] increases; [NO3] decreases b) [NO2] increases; [O2] decreases; [NO3] decreases c) [NO2] decreases; [O2 ...
GCE Chemistry Question Paper Unit 04 - Kinetics, Equilibria
... Use the data from Experiment 1 to calculate a value for the rate constant (k) at this temperature. Deduce the units of k. Calculation ......................................................................................................................... ...
... Use the data from Experiment 1 to calculate a value for the rate constant (k) at this temperature. Deduce the units of k. Calculation ......................................................................................................................... ...