Inclusive DIS in saturation models
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Collider: Step inside the World`s Greatest Experiment
... visible matter in a galaxy is far too insufficient to hold the stars and gas in its outer rim, again calling for the need for dark matter. We now know that about 85% of all matter in the universe is dark: it does not interact with light, and is thus transparent and invisible, but it gravitates. With ...
... visible matter in a galaxy is far too insufficient to hold the stars and gas in its outer rim, again calling for the need for dark matter. We now know that about 85% of all matter in the universe is dark: it does not interact with light, and is thus transparent and invisible, but it gravitates. With ...
Particle Physics - Atomic physics department
... particles properties and their interactions, including present-day acceleration complexes and multi-detector systems for particle registration and identification. The emphasis is on the specifics of high-energy particles (~GeV), short lifetimes (~ns) and large background of particles. Basics of quar ...
... particles properties and their interactions, including present-day acceleration complexes and multi-detector systems for particle registration and identification. The emphasis is on the specifics of high-energy particles (~GeV), short lifetimes (~ns) and large background of particles. Basics of quar ...
Glossary File
... Charm (c) is the fourth quark (in order of increasing mass), with an electric charge +2/3. ...
... Charm (c) is the fourth quark (in order of increasing mass), with an electric charge +2/3. ...
here - IFT
... Wulf designed and built himself, detected energetic charged particles. Knowing that radioactive minerals give off such charges, he expected that his electrometer would be less affected when he raised it high off the ground. But he was surprised to find an increased level of activity after he scaled ...
... Wulf designed and built himself, detected energetic charged particles. Knowing that radioactive minerals give off such charges, he expected that his electrometer would be less affected when he raised it high off the ground. But he was surprised to find an increased level of activity after he scaled ...
The relation of colour charge to electric charge (E/c) −P2 −Q2 −(mc
... This can also be done using 2x2 Pauli matrices (labelled K,L,M) because two inertial observers agree on the component of momentum Q orthogonal to the component of momentum P in the direction of a Lorentz boost. ...
... This can also be done using 2x2 Pauli matrices (labelled K,L,M) because two inertial observers agree on the component of momentum Q orthogonal to the component of momentum P in the direction of a Lorentz boost. ...
Lecture 1 What is physics? Physics, the most fundamental physical
... occupying the nucleus are two basic entities, protons and neutrons. and electrically neutral neutrons (was verified conclusively in 1932). The electrons of an atom are bound to the nucleus by the electromagnetic force. Protons, neutrons, and a host of other exotic particles are now known to be compo ...
... occupying the nucleus are two basic entities, protons and neutrons. and electrically neutral neutrons (was verified conclusively in 1932). The electrons of an atom are bound to the nucleus by the electromagnetic force. Protons, neutrons, and a host of other exotic particles are now known to be compo ...
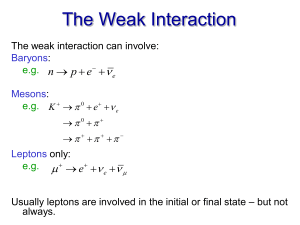
The Weak Interaction
... But the evidence of our observation of the real world is that gluons are not seen. Therefore, our world includes only the other eight gluons. These gluons cannot be seen as free particles since, if they leave a particle, they would leave behind a particle that is ...
... But the evidence of our observation of the real world is that gluons are not seen. Therefore, our world includes only the other eight gluons. These gluons cannot be seen as free particles since, if they leave a particle, they would leave behind a particle that is ...
What is matter? - National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory
... • The mass of the quarks that make up a proton is only a few percent of the mass. Most of the mass is in gluons (the carriers of the force). ...
... • The mass of the quarks that make up a proton is only a few percent of the mass. Most of the mass is in gluons (the carriers of the force). ...
Nuclear Physics - University of Houston
... in physics has been to connect microscopic theory to macroscopic (cosmology) For example, stellar burning and supernovae produce the nuclei of which the Universe is composed We can use this information to look back in time, as well as discuss the present features in our ...
... in physics has been to connect microscopic theory to macroscopic (cosmology) For example, stellar burning and supernovae produce the nuclei of which the Universe is composed We can use this information to look back in time, as well as discuss the present features in our ...
The Standard Model and Beyond
... Experiments at the Tevatron and other colliders have hunted for the Higgs for years and have not found it! ...
... Experiments at the Tevatron and other colliders have hunted for the Higgs for years and have not found it! ...
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
... protons and neutrons, with electrons circling around it. As experimental techniques evolved, and theoretical knowledge deepened, eventually the existence of quarks was proven. Protons and neutrons were no longer classified as elementary particles but as composite particles, consisting of quarks. By ...
... protons and neutrons, with electrons circling around it. As experimental techniques evolved, and theoretical knowledge deepened, eventually the existence of quarks was proven. Protons and neutrons were no longer classified as elementary particles but as composite particles, consisting of quarks. By ...
43. monte carlo particle numbering scheme
... assigned within the qq̄ model. Here nq2−3 and nJ are assigned according to the state’s likely flavors and spin; all such unassigned light isoscalar states are given the flavor code 22. Within these groups nL = 0, 1, 2, . . . is used to distinguish states of increasing mass. These states are flagged ...
... assigned within the qq̄ model. Here nq2−3 and nJ are assigned according to the state’s likely flavors and spin; all such unassigned light isoscalar states are given the flavor code 22. Within these groups nL = 0, 1, 2, . . . is used to distinguish states of increasing mass. These states are flagged ...
N-Body Dynamics of Strongly- Coupled (Nonideal) Plasmas
... Coulomb’s coupling parameter can be performed under the following assumptions: (1) the velocity fields are given by the model of uniform plasma cloud at the inertial stage of expansion, … ...
... Coulomb’s coupling parameter can be performed under the following assumptions: (1) the velocity fields are given by the model of uniform plasma cloud at the inertial stage of expansion, … ...
Strangeness production
Strangeness production is a signature and a diagnostic tool of quark–gluon plasma (or QGP) formation and properties. Unlike up and down quarks, from which everyday matter is made, strange quarks are formed in pair-production processes in collisions between constituents of the plasma. The dominant mechanism of production involves gluons only present when matter has become a quark–gluon plasma. When quark–gluon plasma disassembles into hadrons in a breakup process, the high availability of strange antiquarks helps to produce antimatter containing multiple strange quarks, which is otherwise rarely made. Similar considerations are at present made for the heavier charm flavor, which is made at the beginning of the collision process in the first interactions and is only abundant in the high-energy environments of CERN's Large Hadron Collider.