BIOL 241 Autonomic Nervous System 1 I. Visceral Reflexes A. All
... 2. cell bodies in lateral horns of spinal gray (T1-L2) 3. axons emerge from ventral roots ----> ganglia a. white communicating rami ...
... 2. cell bodies in lateral horns of spinal gray (T1-L2) 3. axons emerge from ventral roots ----> ganglia a. white communicating rami ...
Wagner for the Womb
... In fact, music increases neurogenesis, the regeneration and repair of neurons in the adult brain by altering androgen and estrogen levels. Pre-natal stress is also linked to learning deficits. Offspring from pregnant rodent mothers exposed to stress perform poorer in spatial memory tasks. Pre-natal ...
... In fact, music increases neurogenesis, the regeneration and repair of neurons in the adult brain by altering androgen and estrogen levels. Pre-natal stress is also linked to learning deficits. Offspring from pregnant rodent mothers exposed to stress perform poorer in spatial memory tasks. Pre-natal ...
slides
... background gray level (50% black) represents the region where dots had no (linear) effect on the neural response, with darker levels representing excitatory regions where dots increased the probability of firing and lighter levels representing regions where dots decreased the probability of firing. ...
... background gray level (50% black) represents the region where dots had no (linear) effect on the neural response, with darker levels representing excitatory regions where dots increased the probability of firing and lighter levels representing regions where dots decreased the probability of firing. ...
Fast and slow neurons in the nucleus of the
... Spatio-temporal contour plots for both the preferred and anti-preferred directions were obtained for all neurons. Because, for most neurons, large®eld motion in the preferred direction elicits excitation and motion in the anti-preferred direction inhibits the spontaneous activity, we refer to these ...
... Spatio-temporal contour plots for both the preferred and anti-preferred directions were obtained for all neurons. Because, for most neurons, large®eld motion in the preferred direction elicits excitation and motion in the anti-preferred direction inhibits the spontaneous activity, we refer to these ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... animals orient toward salient sounds and/or to filter out auditory effects of the animal’s own movements. The DCN is densely innervated by serotonergic fibers, which have been proposed to mediate context-dependent ...
... animals orient toward salient sounds and/or to filter out auditory effects of the animal’s own movements. The DCN is densely innervated by serotonergic fibers, which have been proposed to mediate context-dependent ...
1
... Satellite= are the same as a regular dish satellite, the way I see it, is as if it was on a roof the same way it is on the axon Schwann = close to swan which are also white, schwann cells form myelin ...
... Satellite= are the same as a regular dish satellite, the way I see it, is as if it was on a roof the same way it is on the axon Schwann = close to swan which are also white, schwann cells form myelin ...
Document
... • Substances synthesized or recycled in the neuron cell body are needed in the axon or at the axon terminals. Two types of transport systems carry materials from the cell body to the axon terminals and back. – Slow axonal transport conveys axoplasm in one direction only – from the cell body toward t ...
... • Substances synthesized or recycled in the neuron cell body are needed in the axon or at the axon terminals. Two types of transport systems carry materials from the cell body to the axon terminals and back. – Slow axonal transport conveys axoplasm in one direction only – from the cell body toward t ...
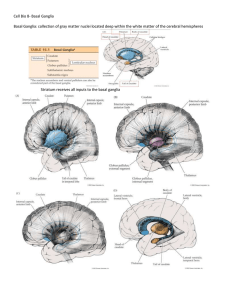
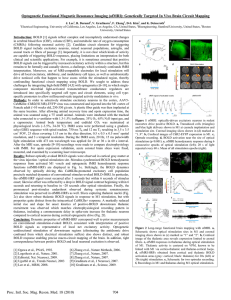
Cell Bio 8- Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia: collection of gray matter
... from a decreased input from the ventrolateral (VL) nucleus of the thalamus to the motor cortex of the brain. This input, which is modulated by the basal ganglia, normally modifies descending cortical motor output to allow the individual to initiate voluntary movements at an appropriate pace. o Thala ...
... from a decreased input from the ventrolateral (VL) nucleus of the thalamus to the motor cortex of the brain. This input, which is modulated by the basal ganglia, normally modifies descending cortical motor output to allow the individual to initiate voluntary movements at an appropriate pace. o Thala ...
The Cells of the Nervous System Lab
... viewing the animation, which rotates the cell in 3-D. Alternatively, the cell can be viewed using the 3D neuron viewer, and rotated manually by holding right click and dragging the mouse to rotate. The purkinje cell axons, not shown here, are inhibitory, and provide the entire output of the cerebell ...
... viewing the animation, which rotates the cell in 3-D. Alternatively, the cell can be viewed using the 3D neuron viewer, and rotated manually by holding right click and dragging the mouse to rotate. The purkinje cell axons, not shown here, are inhibitory, and provide the entire output of the cerebell ...
An Examination of the cell densities in Fmr1Ko mice
... Neural circuits of the PPC mediate complex functions related to integrating odor cues with behavior, affective states, and multisensory processing. Relatively simple three cortical layers, convenient segregation of afferent and associative inputs, and that the understanding of the PPC microcircu ...
... Neural circuits of the PPC mediate complex functions related to integrating odor cues with behavior, affective states, and multisensory processing. Relatively simple three cortical layers, convenient segregation of afferent and associative inputs, and that the understanding of the PPC microcircu ...
Acoustic Information Flow-ICCS'06-RIOFRIO
... It is reasonable to think that through evolution the neurons are becoming those cellular entities that explore the potentialities of electromagnetic field management. In this respect, we support our studies in the results and proposals which, precisely, claim that those things known as mental phenom ...
... It is reasonable to think that through evolution the neurons are becoming those cellular entities that explore the potentialities of electromagnetic field management. In this respect, we support our studies in the results and proposals which, precisely, claim that those things known as mental phenom ...
Nonlinear Behavior of Neocortical Networks
... would cause hyperactivity that would not be informative (which was mimicked in vitro with the administration of picrotoxin, a GABA-receptor antagonist, causing epileptic behavior). These findings could have interesting ramifications for studies of abnormalities in the cortex, such as epilepsy. Any e ...
... would cause hyperactivity that would not be informative (which was mimicked in vitro with the administration of picrotoxin, a GABA-receptor antagonist, causing epileptic behavior). These findings could have interesting ramifications for studies of abnormalities in the cortex, such as epilepsy. Any e ...
Nervous Tissue
... Repolarizing Phase of Action Potential • When threshold potential of -55mV is reached, voltage-gated K+ channels open • K+ channel opening is much slower than Na+ channel opening which caused depolarization • When K+ channels finally do open, the Na+ channels have already closed (Na+ inflow stops) ...
... Repolarizing Phase of Action Potential • When threshold potential of -55mV is reached, voltage-gated K+ channels open • K+ channel opening is much slower than Na+ channel opening which caused depolarization • When K+ channels finally do open, the Na+ channels have already closed (Na+ inflow stops) ...
A"computational"approach"towards"the"ontogeny"of" mirror"neurons
... Currently, this threshold is imposed as a fixed constant. An extension of this work would be to model homeostatic plasticity by dynamically determining the threshold value based on the overall network activity. Second, mirror neuron behavior can only be imposed if the bounds for the excitatory neuro ...
... Currently, this threshold is imposed as a fixed constant. An extension of this work would be to model homeostatic plasticity by dynamically determining the threshold value based on the overall network activity. Second, mirror neuron behavior can only be imposed if the bounds for the excitatory neuro ...
Optogenetic Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ofMRI
... clinical and scientific applications. For example, it is sometimes assumed that positive BOLD signals can be triggered by increased excitatory activity within a structure, but this remains to be formally and causally shown, a challenge, which seriously confounds fMRI interpretation. Moreover, use of ...
... clinical and scientific applications. For example, it is sometimes assumed that positive BOLD signals can be triggered by increased excitatory activity within a structure, but this remains to be formally and causally shown, a challenge, which seriously confounds fMRI interpretation. Moreover, use of ...
3cf1482f14bbaf7
... musculature to maintaining posture and balance - Synapse in some intermediate nucleus rather than directly with lower motor neurons ...
... musculature to maintaining posture and balance - Synapse in some intermediate nucleus rather than directly with lower motor neurons ...
Document
... Modulates activity in muscles that rotate the head and upper torso and modulate adjustments pertinent to limb and body orientation in the gravitational field. ...
... Modulates activity in muscles that rotate the head and upper torso and modulate adjustments pertinent to limb and body orientation in the gravitational field. ...
Module_3vs9_Final - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • GABA neurons – GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA • GABA keys – Alcohol molecules so closely resemble those of the GABA neurotransmitter that alcohol can function like GABA keys and open GABA receptors – When GABA neurons a ...
... • GABA neurons – GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA • GABA keys – Alcohol molecules so closely resemble those of the GABA neurotransmitter that alcohol can function like GABA keys and open GABA receptors – When GABA neurons a ...
chapter32_part2
... • A reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus, a movement or other action that does not require thought • Examples: Stretch reflex, knee-jerk reflex, withdrawal reflex • Spinal reflexes do not involve the brain • Sensory signals flow to the spinal cord, which commands a response by way of motor ...
... • A reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus, a movement or other action that does not require thought • Examples: Stretch reflex, knee-jerk reflex, withdrawal reflex • Spinal reflexes do not involve the brain • Sensory signals flow to the spinal cord, which commands a response by way of motor ...
Brain PowerPoint
... That is, people get “smarter,” or “learn,” by growing more synaptic connections and increasing dendritic branching - INCREMENTAL NOT FIXED! ...
... That is, people get “smarter,” or “learn,” by growing more synaptic connections and increasing dendritic branching - INCREMENTAL NOT FIXED! ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Cranial nerves – 12 pairs of nerves originate from the brain to innervate the head and neck. Most cranial nerves are mixed, but some are sensory. Only the vagus nerve extends to thoracic and abdominal cavities. (Cranial nerves are listed in table 7.1.) Spinal nerves – 31 pairs of mixed nerves are fo ...
... Cranial nerves – 12 pairs of nerves originate from the brain to innervate the head and neck. Most cranial nerves are mixed, but some are sensory. Only the vagus nerve extends to thoracic and abdominal cavities. (Cranial nerves are listed in table 7.1.) Spinal nerves – 31 pairs of mixed nerves are fo ...
What is C. elegans? What are its navigational strategies?
... Thermotactic behavior depends on the previous cultivation temperature (Ts) and on the ambient temperature (T) ...
... Thermotactic behavior depends on the previous cultivation temperature (Ts) and on the ambient temperature (T) ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.