Synaptic Democracy and Vesicular Transport in Axons
... body (soma) of a neuron can play an effective role in neuronal function. For example, stimulated synapses far from the soma are unlikely to influence the firing of a neuron unless some sort of active dendritic processing occurs. Analogously, the motor-driven transport of newly synthesized proteins f ...
... body (soma) of a neuron can play an effective role in neuronal function. For example, stimulated synapses far from the soma are unlikely to influence the firing of a neuron unless some sort of active dendritic processing occurs. Analogously, the motor-driven transport of newly synthesized proteins f ...
48nervous
... – More common than electrical synapses. – Postsynaptic chemically-gated channels exist for ions such as Na+, K+, and Cl-. • Depending on which gates open the postsynaptic neuron can depolarize or hyperpolarize. ...
... – More common than electrical synapses. – Postsynaptic chemically-gated channels exist for ions such as Na+, K+, and Cl-. • Depending on which gates open the postsynaptic neuron can depolarize or hyperpolarize. ...
A1990CP63600001
... at the labeled cells in the paraventricular nucleus, I knew that this was a major finding. The paraventricular nucleus had previously been considered mainly a neuroendocrine structure, secreting oxytocin and vasopressin from its axon terminals in the posterior pituitary gland. The possibility now wa ...
... at the labeled cells in the paraventricular nucleus, I knew that this was a major finding. The paraventricular nucleus had previously been considered mainly a neuroendocrine structure, secreting oxytocin and vasopressin from its axon terminals in the posterior pituitary gland. The possibility now wa ...
Chapter 04: The Action Potential
... • At peak of action potential the membrane potential reverses polarity • Becomes positive inside as predicted by the Ena Called OVERSHOOT • Return to membrane potential to a more negative potential than at rest ...
... • At peak of action potential the membrane potential reverses polarity • Becomes positive inside as predicted by the Ena Called OVERSHOOT • Return to membrane potential to a more negative potential than at rest ...
File
... The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. The synaptic cleft separates the axon terminal from the dendrites of the adjacent cell. Terminals contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit ...
... The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. The synaptic cleft separates the axon terminal from the dendrites of the adjacent cell. Terminals contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit ...
Section 35-2: The Nervous System The nervous system controls and
... The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. The synaptic cleft separates the axon terminal from the dendrites of the adjacent cell. Terminals contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit ...
... The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. The synaptic cleft separates the axon terminal from the dendrites of the adjacent cell. Terminals contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit ...
nervous system
... whereas the intercellular fluid contains high concentration of potassium ions and negatively charged nondiffusible organic molecules, particularly proteins and phosphates. This unequal distribution of ions and charges around the membrane results in a net negative charge inside and a positive charge ...
... whereas the intercellular fluid contains high concentration of potassium ions and negatively charged nondiffusible organic molecules, particularly proteins and phosphates. This unequal distribution of ions and charges around the membrane results in a net negative charge inside and a positive charge ...
the autonomic nervous system
... Typical Responses Produced By the Sympathetic Division During Exercise: 1. Increased heart rate and force of contraction increase blood pressure and the movement of blood. 2. As skeletal or cardiac muscle contracts, oxygen and nutrients are used and waste products are produced. During exercise, a de ...
... Typical Responses Produced By the Sympathetic Division During Exercise: 1. Increased heart rate and force of contraction increase blood pressure and the movement of blood. 2. As skeletal or cardiac muscle contracts, oxygen and nutrients are used and waste products are produced. During exercise, a de ...
Inferring spike-timing-dependent plasticity from spike train data
... neural activity [1, 2]. A number of experimental results, using intracellular recordings in vitro, have shown that synaptic plasticity depends on the precise pairing of pre- and post-synaptic spiking [3]. While such spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) is thought to serve as a powerful regulator ...
... neural activity [1, 2]. A number of experimental results, using intracellular recordings in vitro, have shown that synaptic plasticity depends on the precise pairing of pre- and post-synaptic spiking [3]. While such spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) is thought to serve as a powerful regulator ...
High-performance genetically targetable optical neural
... point). d, Trypan-blue staining of neurons lentivirally infected with Arch versus wild-type (WT) neurons, measured at 18 days in vitro (n 5 669 Archexpressing, 512 wild-type neurons). e–g, Membrane capacitance (e), membrane resistance (f), and resting potential (g) in neurons lentivirally infected w ...
... point). d, Trypan-blue staining of neurons lentivirally infected with Arch versus wild-type (WT) neurons, measured at 18 days in vitro (n 5 669 Archexpressing, 512 wild-type neurons). e–g, Membrane capacitance (e), membrane resistance (f), and resting potential (g) in neurons lentivirally infected w ...
nerve
... neuron. Myelin is not part of the structure of the neuron but consists of a thick layer mostly made up of lipids, present at regular intervals along the length of the axon. • Such fibers are called myelinated fibers. • The water-soluble ions carrying the current across the membrane cannot permeate t ...
... neuron. Myelin is not part of the structure of the neuron but consists of a thick layer mostly made up of lipids, present at regular intervals along the length of the axon. • Such fibers are called myelinated fibers. • The water-soluble ions carrying the current across the membrane cannot permeate t ...
Schizophrenia and Other Disorders
... • There is normally a negative feedback between PFC and NAc. (May inhibit impulses, thoughts) – Less PFC activity decreases that (-) feedback. ...
... • There is normally a negative feedback between PFC and NAc. (May inhibit impulses, thoughts) – Less PFC activity decreases that (-) feedback. ...
A1982NC82200001
... or in experimental animals. Such activity should, in principle, be detectable by signal averaging methods if the brain activity related to movement could be adequately synchronized. “We initially observed movement-related p0tentials from scalp recordings overlying the motor cortex when brisk respons ...
... or in experimental animals. Such activity should, in principle, be detectable by signal averaging methods if the brain activity related to movement could be adequately synchronized. “We initially observed movement-related p0tentials from scalp recordings overlying the motor cortex when brisk respons ...
Physiology 59 [5-12
... o Bipolar disorder or manic-depressive psychosis = alternate between depression and mania (treat with lithium compounds) Schizophrenia = voices, delusions, fear, paranoia (sense of persecution); from blockage of signals to prefrontal lobes (loss of response to glutamate), excessive excitement of dop ...
... o Bipolar disorder or manic-depressive psychosis = alternate between depression and mania (treat with lithium compounds) Schizophrenia = voices, delusions, fear, paranoia (sense of persecution); from blockage of signals to prefrontal lobes (loss of response to glutamate), excessive excitement of dop ...
Two dimensional synaptically generated traveling waves in a theta
... Traveling waves have received much attention lately due to recent experimental and theoretical work [1,5,7,8]. Previous work explored the one-dimensional aspect of the problem as the "rst step toward a better understanding of the underlying neural circuitry. Traveling activity waves are encountered ...
... Traveling waves have received much attention lately due to recent experimental and theoretical work [1,5,7,8]. Previous work explored the one-dimensional aspect of the problem as the "rst step toward a better understanding of the underlying neural circuitry. Traveling activity waves are encountered ...
Your Amazing Brain:
... When Things Go Wrong: Stroke • Cause: blood clot (embolus) or ruptured blood vessel (aneurysm) • Symptoms: weakness, trouble speaking, paralysis, severe headache, vision problems • Treatment: TPA to bust clot (must be within 3 hrs), surgery if aneurysm, therapy to minimize deficits • Prevention: co ...
... When Things Go Wrong: Stroke • Cause: blood clot (embolus) or ruptured blood vessel (aneurysm) • Symptoms: weakness, trouble speaking, paralysis, severe headache, vision problems • Treatment: TPA to bust clot (must be within 3 hrs), surgery if aneurysm, therapy to minimize deficits • Prevention: co ...
Synaptic plasticity: taming the beast
... depends on the relative timing of the pre- and postsynaptic spikes, but not on their order ( Fig. 2d and e). In the cerebellum-like structure of electric fish, LTP and LTD are reversed relative to other systems (Fig. 2c ), perhaps because the postsynaptic neuron is inhibitory rather than excitatory. ...
... depends on the relative timing of the pre- and postsynaptic spikes, but not on their order ( Fig. 2d and e). In the cerebellum-like structure of electric fish, LTP and LTD are reversed relative to other systems (Fig. 2c ), perhaps because the postsynaptic neuron is inhibitory rather than excitatory. ...
Detecting Action Potentials in Neuronal Populations with Calcium
... ideal indicator should translate membrane potential ...
... ideal indicator should translate membrane potential ...
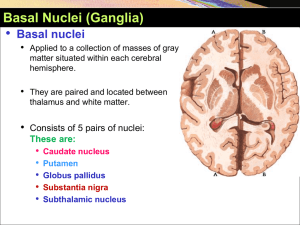
Basal Ganglia YAYDAR 2012-2013
... Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow back to motor areas of cere ...
... Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow back to motor areas of cere ...
ACQ_and_the_Basal_Ganglia
... – The lateral hypothalamus does project to the SNc, VTA, and the ventral striatum (Saper et al., 1979; Fadel & Deutch, 2002; Brog et al., 1993) – The accumbens shell of the ventral striatum is reciprocally connected with the lateral hypothalamus and has been called a “sensory sentinel” or “visceral ...
... – The lateral hypothalamus does project to the SNc, VTA, and the ventral striatum (Saper et al., 1979; Fadel & Deutch, 2002; Brog et al., 1993) – The accumbens shell of the ventral striatum is reciprocally connected with the lateral hypothalamus and has been called a “sensory sentinel” or “visceral ...
Chapter 7
... The current theory of pitch perception uses a combination of the previous theories: • From 20 Hz to 400 Hz, frequency theory accounts for pitch perception (the firing rate of individual neurons in the auditory nerve directly matches the frequency of the sound). • From 400 Hz to 4 kHz, volley princip ...
... The current theory of pitch perception uses a combination of the previous theories: • From 20 Hz to 400 Hz, frequency theory accounts for pitch perception (the firing rate of individual neurons in the auditory nerve directly matches the frequency of the sound). • From 400 Hz to 4 kHz, volley princip ...
Abstract
... al., 1983), and putamen (Crutcher and DeLong, 1981, In the rat, antidromic stimulation studies indicate that 1983), which have revealed specific relations between cell low discharge rate “type I” cells in the SNpc project to discharge and both movement of individual body parts the striatum, whereas ...
... al., 1983), and putamen (Crutcher and DeLong, 1981, In the rat, antidromic stimulation studies indicate that 1983), which have revealed specific relations between cell low discharge rate “type I” cells in the SNpc project to discharge and both movement of individual body parts the striatum, whereas ...
Voltage-Sensitive Dye Imaging: Technique review and Models
... (VSDI). This optical imaging technique offers the possibility to visualize, in real time, the cortical activity of large neuronal populations with high spatial resolution (down to 20-50 µm) and high temporal resolution (down to the millisecond). With such resolutions, VSDI appears to be the best tec ...
... (VSDI). This optical imaging technique offers the possibility to visualize, in real time, the cortical activity of large neuronal populations with high spatial resolution (down to 20-50 µm) and high temporal resolution (down to the millisecond). With such resolutions, VSDI appears to be the best tec ...
Object Detectors Emerge in Deep Scene CNNs
... Experiment 5: Receptive Fields for Localization and Segmentation ▪ Use neurons in inner layers to perform localization ▪ Use tags provided by AMT workers ...
... Experiment 5: Receptive Fields for Localization and Segmentation ▪ Use neurons in inner layers to perform localization ▪ Use tags provided by AMT workers ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.