S.ID Interpreting Categorical and Quantitative Data
... skew right. Therefore, the mean for Checker A would be less than the mean for Checker B. Part 2: The standard deviation for checker A is 2.8. The standard deviation for checker B is 2.4. The spread of the points for both checkers is very similar, just in different directions. Checker A’s p ...
... skew right. Therefore, the mean for Checker A would be less than the mean for Checker B. Part 2: The standard deviation for checker A is 2.8. The standard deviation for checker B is 2.4. The spread of the points for both checkers is very similar, just in different directions. Checker A’s p ...
Chapter 1 Descriptive Statistics
... Statistics is the area of science that deals with collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. ...
... Statistics is the area of science that deals with collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. ...
Section 4 powerpoint
... used measure of spread for a data set is the standard deviation. The key concept for understanding the standard deviation is the concept of deviation from the mean. If A is the average of the data set and x is an arbitrary data value, the difference x – A is x’s deviation from the mean. The deviatio ...
... used measure of spread for a data set is the standard deviation. The key concept for understanding the standard deviation is the concept of deviation from the mean. If A is the average of the data set and x is an arbitrary data value, the difference x – A is x’s deviation from the mean. The deviatio ...
02Data - UCLA Computer Science
... doing classification)—not effective when the % of missing values per attribute varies considerably • Fill in the missing value manually: tedious + infeasible? • Fill in it automatically with • a global constant : e.g., “unknown”, a new class?! • the attribute mean • the attribute mean for all sample ...
... doing classification)—not effective when the % of missing values per attribute varies considerably • Fill in the missing value manually: tedious + infeasible? • Fill in it automatically with • a global constant : e.g., “unknown”, a new class?! • the attribute mean • the attribute mean for all sample ...
02data - UCLA Computer Science
... doing classification)—not effective when the % of missing values per attribute varies considerably • Fill in the missing value manually: tedious + infeasible? ...
... doing classification)—not effective when the % of missing values per attribute varies considerably • Fill in the missing value manually: tedious + infeasible? ...
Exploring Data With Base SAS® Software
... other data values. SET4 has data values which are almost uniformly distrbuted over the interval [44.5, 53.0]. We notice that there are two irregular values, 49.79 and 72.71. The outliers cause the mean to be greater than the median. The positive skewness measure indicates that data values located to ...
... other data values. SET4 has data values which are almost uniformly distrbuted over the interval [44.5, 53.0]. We notice that there are two irregular values, 49.79 and 72.71. The outliers cause the mean to be greater than the median. The positive skewness measure indicates that data values located to ...
f - Hinchingbrooke
... estimate the area” so the more people you have guessing the more accurate they will be? 3) “I predict that the boys will be better at estimating as there are fewer, meaning that there is less chance for anomalous results” so you get the best results by having a small sample size? Mode – generally us ...
... estimate the area” so the more people you have guessing the more accurate they will be? 3) “I predict that the boys will be better at estimating as there are fewer, meaning that there is less chance for anomalous results” so you get the best results by having a small sample size? Mode – generally us ...
Lect 2
... Partitioning of the attribute value ranges into classes. The important attributes should be used on the outer levels. Adequate for data with ordinal attributes of low cardinality But, difficult to display more than nine dimensions Important to map dimensions appropriately ...
... Partitioning of the attribute value ranges into classes. The important attributes should be used on the outer levels. Adequate for data with ordinal attributes of low cardinality But, difficult to display more than nine dimensions Important to map dimensions appropriately ...
Measures of Position
... Example: The Nielsen data. We suspect that the largest value, 66 could be an outlying observation. We calculate Q3 + 1.5IQR = 36.5 + (1.5)(36.5 – 23) = 56.75. Since 66 > 56.75, then the largest data value is actually an outlier, and should be investigated individually. Defn: A boxplot is a graphical ...
... Example: The Nielsen data. We suspect that the largest value, 66 could be an outlying observation. We calculate Q3 + 1.5IQR = 36.5 + (1.5)(36.5 – 23) = 56.75. Since 66 > 56.75, then the largest data value is actually an outlier, and should be investigated individually. Defn: A boxplot is a graphical ...
Document
... The pattern of the data when a large sample is used will be more likely to look like chart A. This is considered a “normal distribution.” It is sometimes called a Bell Curve. ...
... The pattern of the data when a large sample is used will be more likely to look like chart A. This is considered a “normal distribution.” It is sometimes called a Bell Curve. ...
Data Analysis and Assessment Katie Jean Curtis
... Use scatterplots to analyze patterns and describe relationships between two variables. Using technology, determine regression lines (line of best ...
... Use scatterplots to analyze patterns and describe relationships between two variables. Using technology, determine regression lines (line of best ...
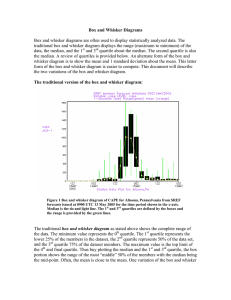
Box and Whisker Diagrams
... diagram is to show the mean and the median. This provides a first approximation of the skewness of the data. The whiskers of the box and whisker diagram provide the full extent of the range of the data. The length of the whiskers from the end of the box and from the median provides a measure of how ...
... diagram is to show the mean and the median. This provides a first approximation of the skewness of the data. The whiskers of the box and whisker diagram provide the full extent of the range of the data. The length of the whiskers from the end of the box and from the median provides a measure of how ...
A Macro for Calculating Percentiles on Left Censored Environmental Data using the Kaplan-Meier Method
... often qualified with a laboratory or validation qualifier of “<” or “U.” Unlike detected data that are reported as measured concentrations and are uncensored, for chemicals, the estimated concentration for non-detects is known only to be within the interval from 0 to the reporting limit provided by ...
... often qualified with a laboratory or validation qualifier of “<” or “U.” Unlike detected data that are reported as measured concentrations and are uncensored, for chemicals, the estimated concentration for non-detects is known only to be within the interval from 0 to the reporting limit provided by ...