STATISTICS IS THE STUDY OF DATA
... The median is 14.5 (When there are an even number of data values, the median is the average of the two middle values: 14 and 15.) Using the table to find the 50th percentile, we see 0.50 exactly in the table; the procedure tells us to average the x value, 14, and the next x value, 15. This correctly ...
... The median is 14.5 (When there are an even number of data values, the median is the average of the two middle values: 14 and 15.) Using the table to find the 50th percentile, we see 0.50 exactly in the table; the procedure tells us to average the x value, 14, and the next x value, 15. This correctly ...
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques
... Faulty data collection instruments Human or computer error at data entry Errors in data transmission ...
... Faulty data collection instruments Human or computer error at data entry Errors in data transmission ...
Chapter 4 - Institut Montefiore
... Food for thought using a “basic model” for outlier detection • Data is usually multivariate, i.e., multi-dimensional o basic model is univariate, i.e., 1-dimensional (see previous plot!!!) • There is usually more than one generating mechanism/statistical process underlying the “normal” data o basic ...
... Food for thought using a “basic model” for outlier detection • Data is usually multivariate, i.e., multi-dimensional o basic model is univariate, i.e., 1-dimensional (see previous plot!!!) • There is usually more than one generating mechanism/statistical process underlying the “normal” data o basic ...
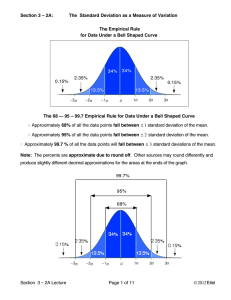
Section 3 – 2A
... points close to the mean are very common. Data Points farther from the mean are less common. Values at the far ends of a data set occur at such a low frequency that their occurrence is considered unusual. For the purposes of this book we define all data points that are outside of 2 standard deviatio ...
... points close to the mean are very common. Data Points farther from the mean are less common. Values at the far ends of a data set occur at such a low frequency that their occurrence is considered unusual. For the purposes of this book we define all data points that are outside of 2 standard deviatio ...
Chapt4II
... All three measures describe a typical entry of a data set. Advantage of using the mean: The mean is a reliable measure because it takes into account every entry of a data set. Disadvantage of using the mean: Greatly affected by outliers (a data entry that is far removed from the other entries in ...
... All three measures describe a typical entry of a data set. Advantage of using the mean: The mean is a reliable measure because it takes into account every entry of a data set. Disadvantage of using the mean: Greatly affected by outliers (a data entry that is far removed from the other entries in ...
Describing Data and Descriptive Statistics
... Likert Scale: This is one of the most common ordinal scales in biomedical studies. These are the 5-‐point scales that ask someone if they like something, or dislike something. Other medical examp ...
... Likert Scale: This is one of the most common ordinal scales in biomedical studies. These are the 5-‐point scales that ask someone if they like something, or dislike something. Other medical examp ...
3.1 Measures of central tendency: mode, median, mean, midrange
... had no siblings. One student had 13 brothers and sisters. The complete data set is as follows: ...
... had no siblings. One student had 13 brothers and sisters. The complete data set is as follows: ...
CHAPTER 1
... 80th percentile: adding “5” to all the data points has the same effect as in the calculation of the first or third quartile. The value will be increased by “5” Range: adding “5” to the all the data points will have no effect on the calculation of the range. Since both the highest value and the lowe ...
... 80th percentile: adding “5” to all the data points has the same effect as in the calculation of the first or third quartile. The value will be increased by “5” Range: adding “5” to the all the data points will have no effect on the calculation of the range. Since both the highest value and the lowe ...
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques — Chapter 2
... Why data reduction? A database/data warehouse may store terabytes of data Complex data analysis/mining may take a very long time to run on the complete data set Data reduction Obtain a reduced representation of the data set that is much smaller in volume but yet produce the same (or almost the ...
... Why data reduction? A database/data warehouse may store terabytes of data Complex data analysis/mining may take a very long time to run on the complete data set Data reduction Obtain a reduced representation of the data set that is much smaller in volume but yet produce the same (or almost the ...
International Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and
... There are several algorithms that discover the frequent periodic patterns having (user specified) minimum number of repetitions or with minimum confidence (ratio between number of occurrences found and maximum possible occurrences), e.g., [4]–[5], [6], and [7]. However, not much work has been done f ...
... There are several algorithms that discover the frequent periodic patterns having (user specified) minimum number of repetitions or with minimum confidence (ratio between number of occurrences found and maximum possible occurrences), e.g., [4]–[5], [6], and [7]. However, not much work has been done f ...
ppt - DIT
... and store average for each bucket Can be constructed optimally in one dimension using dynamic programming Related to quantization problems ...
... and store average for each bucket Can be constructed optimally in one dimension using dynamic programming Related to quantization problems ...
Statistical Technique for Analyzing Quantitative Data
... Nominal data are those for which numbers are used only to identify different categories of people, objects, or other entities; they do not reflect a particular quantity or degree of something Ordinal data are those for which the assigned numbers reflect a particular order or sequence. They tell us t ...
... Nominal data are those for which numbers are used only to identify different categories of people, objects, or other entities; they do not reflect a particular quantity or degree of something Ordinal data are those for which the assigned numbers reflect a particular order or sequence. They tell us t ...
Chapter 5: Checking Resampling Results 5.1 How many trials to use
... actual confidence level compares to the confidence level that was requested for different sizes of data sets. The actual confidence level is defined to be the fraction of times that the computed confidence interval contains the true mean of the distribution from which the data sets were drawn. Three ...
... actual confidence level compares to the confidence level that was requested for different sizes of data sets. The actual confidence level is defined to be the fraction of times that the computed confidence interval contains the true mean of the distribution from which the data sets were drawn. Three ...
3 國立聯合大學資訊管理學系資料探勘課程(陳士杰)
... “Not applicable (不合用)” data value when collected Different considerations between the time when the data was collected and when it is analyzed. Human/hardware/software problems ...
... “Not applicable (不合用)” data value when collected Different considerations between the time when the data was collected and when it is analyzed. Human/hardware/software problems ...
Describing Data - Descriptive Statistics
... score was 65 and the highest was 95. The range would then be 30. Note that a good approximation of the standard deviation can be obtained by dividing the range by 4. — Percentiles measure the percentage of data points which lie below a certain value when the values are ordered. For example, a studen ...
... score was 65 and the highest was 95. The range would then be 30. Note that a good approximation of the standard deviation can be obtained by dividing the range by 4. — Percentiles measure the percentage of data points which lie below a certain value when the values are ordered. For example, a studen ...
chapter 1 - UniMAP Portal
... the methods of statistics allow scientists and engineers to design valid experiments and to draw reliable conclusions from the data they produce ...
... the methods of statistics allow scientists and engineers to design valid experiments and to draw reliable conclusions from the data they produce ...
Part A
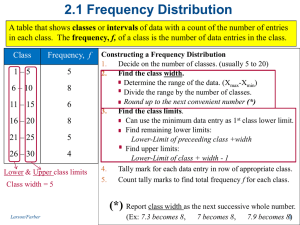
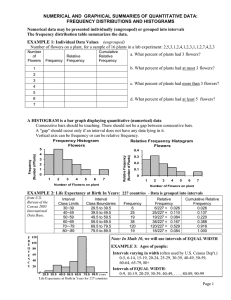
... Ø A bar style display showing frequency of data over _________________, rather than displaying each individual data value. Ø Each interval length must be the same. Ø Histograms are often used for larger sets of data. Ø Always title the graph and label ...
... Ø A bar style display showing frequency of data over _________________, rather than displaying each individual data value. Ø Each interval length must be the same. Ø Histograms are often used for larger sets of data. Ø Always title the graph and label ...