Chapter 17 Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and Heredity
... bodies located in the cells but outside the nuclei, contain rRNA ◦ Consists of about 35% protein and 65% ribosomal RNA Small Nuclear RNA (snRNA): found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. ◦ 100-200 nucleotides long, neither subunit tRNA or rRNA ◦ To help with the processing of the initial mRNA trans ...
... bodies located in the cells but outside the nuclei, contain rRNA ◦ Consists of about 35% protein and 65% ribosomal RNA Small Nuclear RNA (snRNA): found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. ◦ 100-200 nucleotides long, neither subunit tRNA or rRNA ◦ To help with the processing of the initial mRNA trans ...
DNA & RNA
... Consists of a long chain of nucleotides 3 main differences between RNA & DNA The 5 carbon sugar is ribose, not deoxyribose RNA is generally single stranded RNA contains uracil instead of thymine ...
... Consists of a long chain of nucleotides 3 main differences between RNA & DNA The 5 carbon sugar is ribose, not deoxyribose RNA is generally single stranded RNA contains uracil instead of thymine ...
DISTINCTION BETWEEN AOX PLANT
... But DNA can also be transcribed into non-coding RNA … tRNA (transfer): transfer of amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. rRNA (ribosomal): essential component of the ribosomes (complex with rProteins). ...
... But DNA can also be transcribed into non-coding RNA … tRNA (transfer): transfer of amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. rRNA (ribosomal): essential component of the ribosomes (complex with rProteins). ...
Regulation of gene expression
... recognized by a gene regulatory proteins • regulatory gene – is localized outside the operon, codes for regulatory protein, its expression is usually constitutive and controlled by its own promoter • regulatory proteins – bind to the promoter/operator, (encoded by regulatory gene) – Repressor protei ...
... recognized by a gene regulatory proteins • regulatory gene – is localized outside the operon, codes for regulatory protein, its expression is usually constitutive and controlled by its own promoter • regulatory proteins – bind to the promoter/operator, (encoded by regulatory gene) – Repressor protei ...
Genetics 3 - MaxSkyFan
... Before the gene can be transcribed, the doublestranded DNA molecule must be unwound a bit so the two strands can be separated. Then the RNA bases are matched to the DNA strand to complete transcription. Now let’s try translation, where we translate from nucleic acid language to amino acid language. ...
... Before the gene can be transcribed, the doublestranded DNA molecule must be unwound a bit so the two strands can be separated. Then the RNA bases are matched to the DNA strand to complete transcription. Now let’s try translation, where we translate from nucleic acid language to amino acid language. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Control
... conformational change in histone proteins transcription factors have easier access to genes ...
... conformational change in histone proteins transcription factors have easier access to genes ...
student worksheet
... Introduction: Origami is an art form based on paper folded into elaborate designs that often look like a real object. To make the designs, detailed instructions must be provided. For example, “fold the paper in half twice”. Is this a good description? Why or why not? In living things, the detailed d ...
... Introduction: Origami is an art form based on paper folded into elaborate designs that often look like a real object. To make the designs, detailed instructions must be provided. For example, “fold the paper in half twice”. Is this a good description? Why or why not? In living things, the detailed d ...
Section 6: Information Flow
... changes in the DNA. To introduce the central dogma, we can ask why changes in DNA result in observable changes (perhaps providing a student plate as an example—why do the different isolates look different?) We focus on nucleic acid structure and the central dogma at its most basic level—the mechanis ...
... changes in the DNA. To introduce the central dogma, we can ask why changes in DNA result in observable changes (perhaps providing a student plate as an example—why do the different isolates look different?) We focus on nucleic acid structure and the central dogma at its most basic level—the mechanis ...
Simulating Protein Synthesis and RNA Interference in the
... The students represent the active portions of the protein synthesis pathway, whether it be proteins or RNA. The paper represents information carried either in the DNA or the mRNA and contains the instructions for the creation of specific proteins. The teacher represents the RNA silencing protein com ...
... The students represent the active portions of the protein synthesis pathway, whether it be proteins or RNA. The paper represents information carried either in the DNA or the mRNA and contains the instructions for the creation of specific proteins. The teacher represents the RNA silencing protein com ...
How Genes Work
... Its complex unwinds DNA It copies bases using complimentary base pairing (U v.s. T) Moves down one strand Stops at terminator ...
... Its complex unwinds DNA It copies bases using complimentary base pairing (U v.s. T) Moves down one strand Stops at terminator ...
3-Session 5-Lec 9 What is a gene and transcription
... Transcription factors TFII A and B bind to TBP, then RNA polymerase II binds to these factors and to DNA, and is aligned at the startpoint for transcription. Then TFII E, F, and H bind, TFII H acts as ATP-dependent DNA helicase which is unwinding DNA for transcription. This intiation complex can tra ...
... Transcription factors TFII A and B bind to TBP, then RNA polymerase II binds to these factors and to DNA, and is aligned at the startpoint for transcription. Then TFII E, F, and H bind, TFII H acts as ATP-dependent DNA helicase which is unwinding DNA for transcription. This intiation complex can tra ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
doc
... 1. Ask students about their answers. In discussing their answers make sure that students know that the most abundant molecule in the body is water; second is protein. The relative amounts of DNA, sugar, and fats vary depending on the person, but you could discuss which one they suspect would be most ...
... 1. Ask students about their answers. In discussing their answers make sure that students know that the most abundant molecule in the body is water; second is protein. The relative amounts of DNA, sugar, and fats vary depending on the person, but you could discuss which one they suspect would be most ...
notes pdf - Auburn University
... H. for an average-sized polypeptide chain (~300-400 amino acids long) translation takes less than a minute I. ...
... H. for an average-sized polypeptide chain (~300-400 amino acids long) translation takes less than a minute I. ...
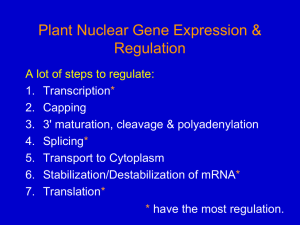
Nuclear gene expression 1
... 1. 2 large subunits have regions of homology with ß and ß’ subunits of E. coli RNAP. 2. Largest subunit is phosphorylated on its ...
... 1. 2 large subunits have regions of homology with ß and ß’ subunits of E. coli RNAP. 2. Largest subunit is phosphorylated on its ...
Station A
... influenced by environmental factors. 2. Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells. The hemoglobin molecules produced by some people have one specific amino acid that is different from the amino acid at that position in normal hemoglobin. Which is the most likely cause? ...
... influenced by environmental factors. 2. Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells. The hemoglobin molecules produced by some people have one specific amino acid that is different from the amino acid at that position in normal hemoglobin. Which is the most likely cause? ...
Lecture#7 - Eukaryote gene structure and regulation.
... The biochemistry of intron splicing is well understood and involves the lariat model. For some genes (most) the processed mature mRNA is the same product each time. ...
... The biochemistry of intron splicing is well understood and involves the lariat model. For some genes (most) the processed mature mRNA is the same product each time. ...
PartFourSumm_ThemesInRegulation.doc
... transription. Note that the same regulatory protein (cAMP-CAP) can make different contacts with RNA polymerase at different operons and activate transcription by different mechanisms, affecting the affinity of the polymerase for the promoter in one case and the rate of closed to open complex in the ...
... transription. Note that the same regulatory protein (cAMP-CAP) can make different contacts with RNA polymerase at different operons and activate transcription by different mechanisms, affecting the affinity of the polymerase for the promoter in one case and the rate of closed to open complex in the ...
Poster
... to create a model of the T7 RNA Polymerase (T7 RNAP) using data from the Protein Data Bank and a visualization program called RasMol. T7 is virus that infects bacteria, but its RNA Polymerase is a very important molecule to scientists. Scientists can use T7 RNAP to create large amounts of a specific ...
... to create a model of the T7 RNA Polymerase (T7 RNAP) using data from the Protein Data Bank and a visualization program called RasMol. T7 is virus that infects bacteria, but its RNA Polymerase is a very important molecule to scientists. Scientists can use T7 RNAP to create large amounts of a specific ...
Slide 1
... Sequences of 3 bases in RNA code for a single amino acid There are 64 possible ‘triplets’ that can be formed from the 4 different bases, but there are only 20 amino acids (AA) In most cases, more than one type of triplet codes for a given AA For example, CAA and CAG both code for the same AA, glutam ...
... Sequences of 3 bases in RNA code for a single amino acid There are 64 possible ‘triplets’ that can be formed from the 4 different bases, but there are only 20 amino acids (AA) In most cases, more than one type of triplet codes for a given AA For example, CAA and CAG both code for the same AA, glutam ...