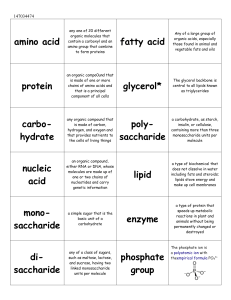
NAME
... out of the m-RNA molecule before it is read by the ribosomes EXON – Expressed sequence of DNA that codes for a protein REPRESSOR – molecule that binds to the operator region of an operon and “turns the gene off” OPERATOR – region in an operon to which the repressor protein binds when the operon is “ ...
... out of the m-RNA molecule before it is read by the ribosomes EXON – Expressed sequence of DNA that codes for a protein REPRESSOR – molecule that binds to the operator region of an operon and “turns the gene off” OPERATOR – region in an operon to which the repressor protein binds when the operon is “ ...
Control of Gene Expression Control of Gene Expression Regulatory
... • Methylation (the addition of –CH3 to DNA or histone proteins) is associated with the control of gene expression. • Clusters of methylated cytosine nucleotides bind to a protein that prevents activators from binding to DNA. • Methylated histone proteins are associated with inactive regions of chrom ...
... • Methylation (the addition of –CH3 to DNA or histone proteins) is associated with the control of gene expression. • Clusters of methylated cytosine nucleotides bind to a protein that prevents activators from binding to DNA. • Methylated histone proteins are associated with inactive regions of chrom ...
chapter9_Sections 4-6 - (per 3) and wed 4/24 (per 2,6)
... rRNA and tRNA: The Translators • Ribosomes (containing rRNA and structural proteins) and tRNAs interact to translate an mRNA into a polypeptide • One large and one small ribosomal subunit join with mRNA, and rRNA enzymatically catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between amino acids • Transfer ...
... rRNA and tRNA: The Translators • Ribosomes (containing rRNA and structural proteins) and tRNAs interact to translate an mRNA into a polypeptide • One large and one small ribosomal subunit join with mRNA, and rRNA enzymatically catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between amino acids • Transfer ...
TNA: Transcription and Triplet Code
... • The termination of transcription is brought about by polyadenylation (poly-A). This is a sequence of A's about 200 bp's long. • While there is no DNA template for poly A, there is a signal sequence in mRNA that "triggers" poly A addition. An RNA endonuclease cleaves the poly-A recognition site and ...
... • The termination of transcription is brought about by polyadenylation (poly-A). This is a sequence of A's about 200 bp's long. • While there is no DNA template for poly A, there is a signal sequence in mRNA that "triggers" poly A addition. An RNA endonuclease cleaves the poly-A recognition site and ...
1) Where does glycolysis occur in the cell
... 24) Without any oxygen, a cell can only yield a NET production of _______ ATP per molecule of glucose. a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 ...
... 24) Without any oxygen, a cell can only yield a NET production of _______ ATP per molecule of glucose. a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 ...
chapter 12 practice test - open to see diagrams
... a. adenine. c. phosphate groups. b. uracil. d. thymine. 4. Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis? a. transfer RNA only b. messenger RNA only c. ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA only d. messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA 5. How many codons are needed to specify three am ...
... a. adenine. c. phosphate groups. b. uracil. d. thymine. 4. Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis? a. transfer RNA only b. messenger RNA only c. ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA only d. messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA 5. How many codons are needed to specify three am ...
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein 1. Overview of Gene Expression 2. Transcription
... contains intervening sequences called introns that need to be removed or “spliced out”. The regions that are retained are called exons which after splicing form a continuous coding region. ...
... contains intervening sequences called introns that need to be removed or “spliced out”. The regions that are retained are called exons which after splicing form a continuous coding region. ...
Steps in gene expression: comparison of
... Six steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. In prokaryotic cells, genes do not have introns (no step 2) and transcription and translation are not separated in space and time (no step 3). ...
... Six steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. In prokaryotic cells, genes do not have introns (no step 2) and transcription and translation are not separated in space and time (no step 3). ...
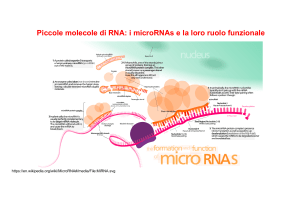
Types of RNA
... can cleave complementary mRNA, block the mRNA from being translated, or accelerate its degradation. While small interfering RNAs (siRNA; 20-25 nt) are often produced by breakdown of viral RNA, there are also endogenous sources of siRNAs. siRNAs act through RNA interference in a fashion similar to mi ...
... can cleave complementary mRNA, block the mRNA from being translated, or accelerate its degradation. While small interfering RNAs (siRNA; 20-25 nt) are often produced by breakdown of viral RNA, there are also endogenous sources of siRNAs. siRNAs act through RNA interference in a fashion similar to mi ...
Gene Regulation
... mRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm. • Following transcription, at the 5’ end of the mRNA molecule, a modified form of guanine is added, the 5’ cap and a poly-A tail. – These helps protect mRNA from hydrolytic ...
... mRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm. • Following transcription, at the 5’ end of the mRNA molecule, a modified form of guanine is added, the 5’ cap and a poly-A tail. – These helps protect mRNA from hydrolytic ...
Chapter 13 Lecture Notes: DNA Function I. Transcription (General
... a) Can bind to specific DNA sequences and help RNA polymerase initiate transcription via protein-protein interactions or by altering the structure of the DNA. b) Transcription of some promoters requires an accessory transcriptional activator; at other promoters, the activators just increase the rate ...
... a) Can bind to specific DNA sequences and help RNA polymerase initiate transcription via protein-protein interactions or by altering the structure of the DNA. b) Transcription of some promoters requires an accessory transcriptional activator; at other promoters, the activators just increase the rate ...
1 BIOL 213 Second Exam All atoms, chemical bonding and
... 8. After translation proteins can be processed in several ways. Identify five (5) co-translational or post-translational protein modifications that would qualify as “protein processing” in eucaryotic cells. ...
... 8. After translation proteins can be processed in several ways. Identify five (5) co-translational or post-translational protein modifications that would qualify as “protein processing” in eucaryotic cells. ...
EOC Review Part 4
... What does diploid mean? What does haploid mean? Diploid = Having two copies of every gene/chromosome; haploid = having one copy During meiosis, when does crossing over take place? Prophase I ...
... What does diploid mean? What does haploid mean? Diploid = Having two copies of every gene/chromosome; haploid = having one copy During meiosis, when does crossing over take place? Prophase I ...
Central Dogma Activity Worksheet
... Every cell in your body has the same "blueprint" or the same DNA. Like the blueprints of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? ...
... Every cell in your body has the same "blueprint" or the same DNA. Like the blueprints of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? ...
Molecular Biology
... • The disease results from a single base change in the gene for b-globin – Altered base causes insertion an incorrect amino acid into one position of the b-globin protein – Altered protein results in distortion of red ...
... • The disease results from a single base change in the gene for b-globin – Altered base causes insertion an incorrect amino acid into one position of the b-globin protein – Altered protein results in distortion of red ...
Gene Expression (Epigenetics)
... • Transcription initiation complexes also regulate gene expression • Enhancer region upstream from the gene is joined to the transcription initiation complex by activators (proteins) = start transcription • http://www.dnai.org/a/index.html ...
... • Transcription initiation complexes also regulate gene expression • Enhancer region upstream from the gene is joined to the transcription initiation complex by activators (proteins) = start transcription • http://www.dnai.org/a/index.html ...
PowerPoint Notes
... the amino acids, such as Ser for serine.) The codon AUG not only stands for methionine (Met), but also functions as a signal to "start" translating an RNA transcript. There are also three "stop" codons that do not code for amino acids, but signal the end of each genetic message. ...
... the amino acids, such as Ser for serine.) The codon AUG not only stands for methionine (Met), but also functions as a signal to "start" translating an RNA transcript. There are also three "stop" codons that do not code for amino acids, but signal the end of each genetic message. ...
Daily Learning Targets
... 12. I can describe the processes of replication, transcription, and translation. (C.1.a) ...
... 12. I can describe the processes of replication, transcription, and translation. (C.1.a) ...
Name: Date: Quiz name: Unit 4 Quiz (Replication/ transcription and tr
... DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase If a DNA molecule is found to be composed of 40% thymine, what percentage of guanine would be ...
... DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase If a DNA molecule is found to be composed of 40% thymine, what percentage of guanine would be ...
Bioinformatics
... • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is made up of purine bases (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidine bases (cytosine and thymine). Bases are part of nucleotides which are formed using the sugar deoxyribose. Nucleotides are connected by condensation reaction from the 5’OH to the 3’OH. ...
... • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is made up of purine bases (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidine bases (cytosine and thymine). Bases are part of nucleotides which are formed using the sugar deoxyribose. Nucleotides are connected by condensation reaction from the 5’OH to the 3’OH. ...
genes
... Promoter gene – site where RNA polymerase binds to the DNA 4. In primitive prokaryotes life bacteria, the promoter and their associated structural genes are called an operon ...
... Promoter gene – site where RNA polymerase binds to the DNA 4. In primitive prokaryotes life bacteria, the promoter and their associated structural genes are called an operon ...
10 gene expression: transcription
... mRNA. So let’s first try to figure out the coding region of the laf+ gene. The initiation codon will have to be an AUG. There are two codons early on: at positions 83–85 and 118–120. The latter is almost immediately followed by a termination signal, UAA. Therefore, the initiation codon is located at ...
... mRNA. So let’s first try to figure out the coding region of the laf+ gene. The initiation codon will have to be an AUG. There are two codons early on: at positions 83–85 and 118–120. The latter is almost immediately followed by a termination signal, UAA. Therefore, the initiation codon is located at ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... between Isw1 and Ioc3 in the Isw1a complex. We show that, although defective in nucleosome remodeling, Isw1 lacking the SANT domain is able to repress transcription initiation at the MET16 promoter. Thus, chromatin remodeling and transcriptional repression are distinct activities of Isw1. ...
... between Isw1 and Ioc3 in the Isw1a complex. We show that, although defective in nucleosome remodeling, Isw1 lacking the SANT domain is able to repress transcription initiation at the MET16 promoter. Thus, chromatin remodeling and transcriptional repression are distinct activities of Isw1. ...