Ch 3 Cells - Review Cell theory The cell is the smallest unit of life
... Here's what is really significant to our understanding of genetics in physiology Genes can be turned on and turned off. Chemicals that turn genes on/off are called transcription factors. Transcription factors affect the binding of RNA polymerase to the promotor. This allows the "copying" of DNA (gen ...
... Here's what is really significant to our understanding of genetics in physiology Genes can be turned on and turned off. Chemicals that turn genes on/off are called transcription factors. Transcription factors affect the binding of RNA polymerase to the promotor. This allows the "copying" of DNA (gen ...
File
... After transcription occurs the transcribed mRNA moves out from the nucleus through the nuclear pore into the cytoplasm and binds to the ribosome unit either in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER Translation is the process where amino acids are combined to form proteins (polypeptides). Three c ...
... After transcription occurs the transcribed mRNA moves out from the nucleus through the nuclear pore into the cytoplasm and binds to the ribosome unit either in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER Translation is the process where amino acids are combined to form proteins (polypeptides). Three c ...
RNA Secondary Structure Based Prediction of Simian
... 5’-leader sequence showed that there are highly conserved regions among SIV subtypes. From these regions, the secondary structures were predicted to find several stem-loops. Gel shift assay showed that some SIV candidate stem-loops had relatively high binding affinity with NCp8. Although further experi ...
... 5’-leader sequence showed that there are highly conserved regions among SIV subtypes. From these regions, the secondary structures were predicted to find several stem-loops. Gel shift assay showed that some SIV candidate stem-loops had relatively high binding affinity with NCp8. Although further experi ...
Powerpoint Slides
... It uses a complex of EF-Tu•GDP•AA-tRNA•mRNA•Ribosome to test the codonanticodon interaction via a conformational change that stresses this interaction. • EF-Tu•GTP•AA-tRNA binds the A-site with a strained anitcodon stem-loop • Anticodon-codon interactions in the A-site induce EF-Tu’s hydrolysis of G ...
... It uses a complex of EF-Tu•GDP•AA-tRNA•mRNA•Ribosome to test the codonanticodon interaction via a conformational change that stresses this interaction. • EF-Tu•GTP•AA-tRNA binds the A-site with a strained anitcodon stem-loop • Anticodon-codon interactions in the A-site induce EF-Tu’s hydrolysis of G ...
Proteins
... Alternative splicing • There are more than 1,000,000 different human antibodies. How is this possible with only ~30,000 genes? • Alternative splicing refers to the different ways of combining a gene’s exons. This can produce different forms of a protein for the same gene. • Alternative pre-mRNA spl ...
... Alternative splicing • There are more than 1,000,000 different human antibodies. How is this possible with only ~30,000 genes? • Alternative splicing refers to the different ways of combining a gene’s exons. This can produce different forms of a protein for the same gene. • Alternative pre-mRNA spl ...
Biology 12 DNA Functions Functions of DNA: 1. To replicate or make
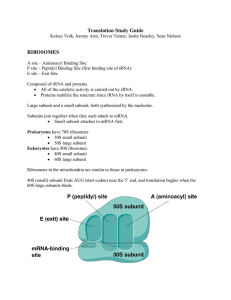
... (3 bases on mRNA called a codon) 4. tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome. (3 bases on tRNA called an anticodon). Anticodons match with codons. Amino Acids link through peptide bonds. 5. ribosome travels down mRNA, tRNA’s continue to bring amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. ...
... (3 bases on mRNA called a codon) 4. tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome. (3 bases on tRNA called an anticodon). Anticodons match with codons. Amino Acids link through peptide bonds. 5. ribosome travels down mRNA, tRNA’s continue to bring amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. ...
PBS Unit 3 Key Terms
... The building block of a nucleic acid, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids. The creation of a protein from a DNA template. A type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers ...
... The building block of a nucleic acid, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids. The creation of a protein from a DNA template. A type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers ...
Biochemists Break the Code
... Binding of the ribosome 30S subunit with IFs 1) IF3 promotes the dissociation of the ribosome into its two component subunits. The presence of IF3 permits the assembly of the initiation complex and prevents binding of the 50S subunit prematurely. 2) IF1 assists IF3 in some way. Binding of the mRNA a ...
... Binding of the ribosome 30S subunit with IFs 1) IF3 promotes the dissociation of the ribosome into its two component subunits. The presence of IF3 permits the assembly of the initiation complex and prevents binding of the 50S subunit prematurely. 2) IF1 assists IF3 in some way. Binding of the mRNA a ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... The Structure of RNA List the three main differences between RNA and DNA. 1. RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose. 2. RNA is generally single-stranded, instead of double-stranded. 3.RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. ...
... The Structure of RNA List the three main differences between RNA and DNA. 1. RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose. 2. RNA is generally single-stranded, instead of double-stranded. 3.RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. ...
DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid
... • Problem: there are only 4 N-bases, and 20 amino acids to make a protein! • We need a TRANSLATION! • What’s the code? ...
... • Problem: there are only 4 N-bases, and 20 amino acids to make a protein! • We need a TRANSLATION! • What’s the code? ...
2 - Blue Valley Schools
... the experiments they conducted in order to make their specific conclusions. 5. You should be able to name those scientists who contributed to our knowledge of DNA’s structure, as well as describe the general methods they used in order to make their specific conclusions. 6. You should know the monome ...
... the experiments they conducted in order to make their specific conclusions. 5. You should be able to name those scientists who contributed to our knowledge of DNA’s structure, as well as describe the general methods they used in order to make their specific conclusions. 6. You should know the monome ...
Matt Reuter
... Some introns form microRNAs that create RNA interference, inhibiting other genes. ...
... Some introns form microRNAs that create RNA interference, inhibiting other genes. ...
Study Guide- DNA, Protein Synthesis, Mitosis and Meiosis
... 3) Be able to describe in detail the structure of DNA, including where each molecule is located, how it connects, and it’s larger shape. 4) Explain DNA replication. Include Okazaki fragments, helicases, DNA polymerase, ligase, 5’ and 3’ and semiconservative in your explanation. 5) Discuss the three ...
... 3) Be able to describe in detail the structure of DNA, including where each molecule is located, how it connects, and it’s larger shape. 4) Explain DNA replication. Include Okazaki fragments, helicases, DNA polymerase, ligase, 5’ and 3’ and semiconservative in your explanation. 5) Discuss the three ...
Outline Wprowadzenie do genetyki i zastosowa statystyki w
... • determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, • store this information in databases, • improve tools for data analysis, • transfer related technologies to the private sector, and • address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise from the p ...
... • determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, • store this information in databases, • improve tools for data analysis, • transfer related technologies to the private sector, and • address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise from the p ...
Principles of Life
... translated into an amino acid sequence in a protein. Francis Crick proposed that the intermediary between DNA and protein was RNA and genetic evidence pointed to triplets of nucleotides on RNA specifying each amino acid. The race was on to identify which triplet coded for which amino acid. Cellfree ...
... translated into an amino acid sequence in a protein. Francis Crick proposed that the intermediary between DNA and protein was RNA and genetic evidence pointed to triplets of nucleotides on RNA specifying each amino acid. The race was on to identify which triplet coded for which amino acid. Cellfree ...
Prokaryotic Gene Expression Mechanisms RNA Types of RNA Other
... repressor for lacO to 2 x 1010, but the affinity for random DNA sequences remains the same. So the specificity of repressor for lacO drops 3 orders of magnitude (or 1000-fold). Under these conditions, you can calculate that less than 3% of the lacO sites should have repressor bound to them (when IPT ...
... repressor for lacO to 2 x 1010, but the affinity for random DNA sequences remains the same. So the specificity of repressor for lacO drops 3 orders of magnitude (or 1000-fold). Under these conditions, you can calculate that less than 3% of the lacO sites should have repressor bound to them (when IPT ...
Review - Qc.edu
... bioarchaeology, paleopathology, human biology, ergonomics, forensics. 2. Theory of evolution as a scientific theory. Scientific method, testing a hypothesis. Charles Darwin & Alfred Russel Wallace. Natural selection. 3. Cell and its structure. Eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes; endosymbiotic theory; nucleu ...
... bioarchaeology, paleopathology, human biology, ergonomics, forensics. 2. Theory of evolution as a scientific theory. Scientific method, testing a hypothesis. Charles Darwin & Alfred Russel Wallace. Natural selection. 3. Cell and its structure. Eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes; endosymbiotic theory; nucleu ...
handout
... 2. The bond attaching the amino acid chain to the tRNA in the P site is broken and a peptide bond is formed to the new tRNA amino acid in the A site moving the growing chain from the P site to the A site. 3. The large subunit of the ribosome shifts one codon, moving the tRNA with the growing amino ...
... 2. The bond attaching the amino acid chain to the tRNA in the P site is broken and a peptide bond is formed to the new tRNA amino acid in the A site moving the growing chain from the P site to the A site. 3. The large subunit of the ribosome shifts one codon, moving the tRNA with the growing amino ...
Assessment Schedule – 2007 Biology: Describe the role of DNA in
... because both types of haemoglobin / red blood cell are present. ...
... because both types of haemoglobin / red blood cell are present. ...
Oct26 - Staff Web Pages
... [Transcription Diagram #1] [Transcription Diagram #2] Codon: sequence of 3 nucleotides on m-RNA that codes for one amino acid. Each amino acid has one to several different codons. A Site with a good beginning Animation of Transcription (Needs Shockwave) ...
... [Transcription Diagram #1] [Transcription Diagram #2] Codon: sequence of 3 nucleotides on m-RNA that codes for one amino acid. Each amino acid has one to several different codons. A Site with a good beginning Animation of Transcription (Needs Shockwave) ...
Origins of Sugars in the Prebiotic World
... • This reaction is specific: – Pb2+ binds to U59/C60 (if these are mutated no binding) – Cleavage is specific requires 2’-OH at B17 – One of few systems where x-ray structure is available revealing potential mechanism ...
... • This reaction is specific: – Pb2+ binds to U59/C60 (if these are mutated no binding) – Cleavage is specific requires 2’-OH at B17 – One of few systems where x-ray structure is available revealing potential mechanism ...
Origin of Life (IB)
... such as protein and nucleic acids. a. How would this occur without enzymes? b. In experiments, polymerization does occur when solutions of monomers are dropped onto hot sand, clay or rock. ...
... such as protein and nucleic acids. a. How would this occur without enzymes? b. In experiments, polymerization does occur when solutions of monomers are dropped onto hot sand, clay or rock. ...