Operantmine
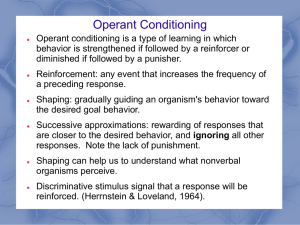
... strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
... strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
Chapter 2 An Introduction to ABA Concepts: Terminology, Principles
... 2. Define the term learning and give an example. (p.21) 3. In relation to the definition of learning, how would you define teaching? (p. 21) 4. Change the following examples into response or operant class descriptions: (p. 22) a. Paul’s socks are stinky b. John’s is disruptive in class c. Glenda’s e ...
... 2. Define the term learning and give an example. (p.21) 3. In relation to the definition of learning, how would you define teaching? (p. 21) 4. Change the following examples into response or operant class descriptions: (p. 22) a. Paul’s socks are stinky b. John’s is disruptive in class c. Glenda’s e ...
Behavior - Catawba County Schools
... to any words that describe innate, or unlearned, behaviors. Write the letter “L” next to any words that describe learned behaviors. Student answers may include the following: Blinking eyes (I), Tapping pencil (L), Rubbing your eyes (I), Crying (I), Building a spider web (I), Migration (I and L), Hib ...
... to any words that describe innate, or unlearned, behaviors. Write the letter “L” next to any words that describe learned behaviors. Student answers may include the following: Blinking eyes (I), Tapping pencil (L), Rubbing your eyes (I), Crying (I), Building a spider web (I), Migration (I and L), Hib ...
to the PDF file.
... B.F. Skinner (1938) coined the term operant conditioning; it means roughly changing of behavior by the use of reinforcement which is given after the desired response. Skinner identified three types of responses or operant that can follow behavior. • Neutral operants: responses from the environment t ...
... B.F. Skinner (1938) coined the term operant conditioning; it means roughly changing of behavior by the use of reinforcement which is given after the desired response. Skinner identified three types of responses or operant that can follow behavior. • Neutral operants: responses from the environment t ...
Behaviorism
... Effects of Punishment Suppress behavior in general Conditioning of negative feelings by associating a strong aversive stimulus with the behavior being punished Spreading of its effects because any stimulus associated with the punishment may be suppressed or avoided ...
... Effects of Punishment Suppress behavior in general Conditioning of negative feelings by associating a strong aversive stimulus with the behavior being punished Spreading of its effects because any stimulus associated with the punishment may be suppressed or avoided ...
Explaining Behavior with Learning Theory – The Behaviorists What
... Explaining Behavior with Learning Theory – The Behaviorists ...
... Explaining Behavior with Learning Theory – The Behaviorists ...
Developmental Psychology
... stimuli or active explorers in their surroundings? Children are active in shaping, controlling, and directing the course of their own development. ...
... stimuli or active explorers in their surroundings? Children are active in shaping, controlling, and directing the course of their own development. ...
B.F. Skinner: The Behavioral Approach
... will affect the rate at which the response occurs Most of human behavior learned this way Behaviors that work are frequently displayed; ineffective behaviors are not repeated Personality ...
... will affect the rate at which the response occurs Most of human behavior learned this way Behaviors that work are frequently displayed; ineffective behaviors are not repeated Personality ...
document
... Figure 6.13 Intermittent reinforcement schedules Skinner’s laboratory pigeons produced these response patterns to each of four reinforcement schedules. (Reinforcers are indicated by diagonal marks.) For people, as for pigeons, reinforcement linked to number of responses (a ratio schedule) produces ...
... Figure 6.13 Intermittent reinforcement schedules Skinner’s laboratory pigeons produced these response patterns to each of four reinforcement schedules. (Reinforcers are indicated by diagonal marks.) For people, as for pigeons, reinforcement linked to number of responses (a ratio schedule) produces ...
Operant Conditioning
... People and animals learn to do things (and not to do others) because of the results of what they do. Learning from the consequences. In operant conditioning, behaviors that people and animals have control over are conditioned. ...
... People and animals learn to do things (and not to do others) because of the results of what they do. Learning from the consequences. In operant conditioning, behaviors that people and animals have control over are conditioned. ...
Notes_7 Learning - Biloxi Public Schools
... -ex: awaiting mail on Friday but the delivery time is different each week, you would check more often to see if it has arrived since you do not know exactly when it will get there -ex: being paid by an employer for every 7 toys assembled ...
... -ex: awaiting mail on Friday but the delivery time is different each week, you would check more often to see if it has arrived since you do not know exactly when it will get there -ex: being paid by an employer for every 7 toys assembled ...
Convert - public.coe.edu
... Treatment of phobias Peter fearful of white rabbit Counterconditioning Pairing favorite food & rabbit Exposure therapy Gradually moved rabbit closer Peter watched another child play with rabbit ~ ...
... Treatment of phobias Peter fearful of white rabbit Counterconditioning Pairing favorite food & rabbit Exposure therapy Gradually moved rabbit closer Peter watched another child play with rabbit ~ ...
Module 21 Operant Conditioning
... Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment. Primary reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. Eg: food & sex. Conditionered (or secondary) reinforcer: a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. ...
... Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment. Primary reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. Eg: food & sex. Conditionered (or secondary) reinforcer: a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. ...
Convert - public.coe.edu
... Treatment of phobias Peter fearful of white rabbit Counterconditioning Pairing favorite food & rabbit Exposure therapy Gradually moved rabbit closer Peter watched another child play with rabbit ~ ...
... Treatment of phobias Peter fearful of white rabbit Counterconditioning Pairing favorite food & rabbit Exposure therapy Gradually moved rabbit closer Peter watched another child play with rabbit ~ ...
Ivan Pavlov
... Makes Causes Has no the aeffect behavior avoidance organism sifhabituation thethe of reward ofto less the avoid punishment, is previously greater punisher, likely, getting or ... the caught, or... than noted effects or... punishment is aversive, or... ...
... Makes Causes Has no the aeffect behavior avoidance organism sifhabituation thethe of reward ofto less the avoid punishment, is previously greater punisher, likely, getting or ... the caught, or... than noted effects or... punishment is aversive, or... ...
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Learning
... Pavlov's dogs learned to salivate upon hearing the tone. ) o Conditioned Stimulus (CS): a neutral stimulus that triggers a learned response. (The tone is a CS because the dogs learned to salivate upon hearing the tone as opposed to food.) This kind of association is possible because Pavlov presented ...
... Pavlov's dogs learned to salivate upon hearing the tone. ) o Conditioned Stimulus (CS): a neutral stimulus that triggers a learned response. (The tone is a CS because the dogs learned to salivate upon hearing the tone as opposed to food.) This kind of association is possible because Pavlov presented ...
Negative Reinforcement
... learning that occurs (like cognitive map) that is not apparent (hidden) until there is an incentive to justify it. Ex: rats that were not reinforced while in a maze could navigate it just as fast when there was a reward put at the end. If there was no food at the end, they just roamed through the ma ...
... learning that occurs (like cognitive map) that is not apparent (hidden) until there is an incentive to justify it. Ex: rats that were not reinforced while in a maze could navigate it just as fast when there was a reward put at the end. If there was no food at the end, they just roamed through the ma ...
skinner theory of operent conditioning and shaping
... Shaping is a conditioning paradigm used primarily in the experimental analysis of behaviour. Skinner proved this using a Bird in a Cage. Skinner says,” it is constructed by a continual process of differential reinforcement from undifferentiated behavior, just as the sculptor shapes his figure ...
... Shaping is a conditioning paradigm used primarily in the experimental analysis of behaviour. Skinner proved this using a Bird in a Cage. Skinner says,” it is constructed by a continual process of differential reinforcement from undifferentiated behavior, just as the sculptor shapes his figure ...
Chapter 1: The Science of Psychology Module 1: Psychology`s
... people power over their own lives and behavior; the importance of environment. ...
... people power over their own lives and behavior; the importance of environment. ...