an introduction to lifespan development
... What the heck is a cohort? Cohort (biology) a taxonomic term in biology Cohort (educational group) students working through the same academic curriculum Cohort (military unit) the basic tactical unit of a Roman legion Cohort (statistics) subjects with a common defining characteristic — typically ag ...
... What the heck is a cohort? Cohort (biology) a taxonomic term in biology Cohort (educational group) students working through the same academic curriculum Cohort (military unit) the basic tactical unit of a Roman legion Cohort (statistics) subjects with a common defining characteristic — typically ag ...
Instrumental Conditioning: Theoretical Issues
... Mild punishment produces temporary suppression ...
... Mild punishment produces temporary suppression ...
Punishment and Learning
... • “Of several responses made to the same situation, those which are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction…will be more likely to recur” Situation ...
... • “Of several responses made to the same situation, those which are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction…will be more likely to recur” Situation ...
The Basics - Fall Creek High School
... -Broader variation: social-cognitive theory “If I do X , Y will happen” -Environment and cognitive factors -Values, goals, and expectations important -Behavior therapy – applying learning principles to treat psychological problems ...
... -Broader variation: social-cognitive theory “If I do X , Y will happen” -Environment and cognitive factors -Values, goals, and expectations important -Behavior therapy – applying learning principles to treat psychological problems ...
Chapter 13
... After lower level needs satisfied, person seeks higher needs. When unable to satisfy higher needs, lower needs motivation is raised. ...
... After lower level needs satisfied, person seeks higher needs. When unable to satisfy higher needs, lower needs motivation is raised. ...
Observational Learning
... • Based on principle that punishment tells you what not to do, reinforcement tells you what to do – A swat is used only as backup to milder disciplinary tactics, like a time-out, removing them from reinforcing surroundings – Swatting with a generous dose of reasoning ...
... • Based on principle that punishment tells you what not to do, reinforcement tells you what to do – A swat is used only as backup to milder disciplinary tactics, like a time-out, removing them from reinforcing surroundings – Swatting with a generous dose of reasoning ...
PSYCHOLOGY (9th Edition) David Myers
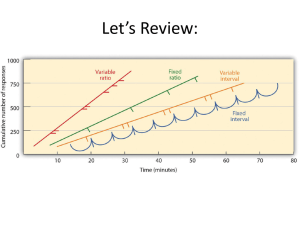
... 1. Fixed-interval schedule: Reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed. (e.g., preparing for an exam only when the exam draws close.) 2. Variable-interval schedule: Reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals, which produces slow, steady responses. (e.g., pop quiz.) ...
... 1. Fixed-interval schedule: Reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed. (e.g., preparing for an exam only when the exam draws close.) 2. Variable-interval schedule: Reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals, which produces slow, steady responses. (e.g., pop quiz.) ...
Famous Experiments
... The girls in the aggressive model conditions also showed more physical aggressive responses if the model was male but more verbal aggressive responses if the model was female; (However, the exception to this general pattern was the observation of how often they punched Bobo, and in this case the eff ...
... The girls in the aggressive model conditions also showed more physical aggressive responses if the model was male but more verbal aggressive responses if the model was female; (However, the exception to this general pattern was the observation of how often they punched Bobo, and in this case the eff ...
History of Behavior Analysis: An introduction
... This article represented a sharp break with previous psychological trends. However, students of psychology and young scientists of this field welcomed behaviorism and quickly started to apply its principles in research. In 1919, Watson published a book where he presented a more complete statement of ...
... This article represented a sharp break with previous psychological trends. However, students of psychology and young scientists of this field welcomed behaviorism and quickly started to apply its principles in research. In 1919, Watson published a book where he presented a more complete statement of ...
A.P. Psychology 6 (C) - Operant Conditioning
... Which one do you think is least effective? Which one do you think is most effective? Which one do you think is most addictive? ...
... Which one do you think is least effective? Which one do you think is most effective? Which one do you think is most addictive? ...
LECTURE 26 INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR
... – Few differences between men and women that affect job performance (like physical ability) – Should operate on assumption that there is no significant difference in performance based on gender (consider profession as well) – Women have higher absenteeism rate ...
... – Few differences between men and women that affect job performance (like physical ability) – Should operate on assumption that there is no significant difference in performance based on gender (consider profession as well) – Women have higher absenteeism rate ...
0538478462_392237
... Associated with “doing the job,” include interesting and challenging work, self-direction and responsibility, variety, opportunities to use one’s skills and abilities, and sufficient feedback regarding one’s efforts ...
... Associated with “doing the job,” include interesting and challenging work, self-direction and responsibility, variety, opportunities to use one’s skills and abilities, and sufficient feedback regarding one’s efforts ...
Study Guide for Learning Evaluation #4
... type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment operates (acts) on environment produces consequences Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors ...
... type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment operates (acts) on environment produces consequences Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors ...
Psychology Review Part 1 – Chapters 1-8
... information neuron to neuron, chemically and electrically through neurotransmitters and therefore can localize the information. The endocrine system transmits chemicals from glands to the entire body through the blood stream. 6. Who was Phineas Gage? Why was he important to psychology? Phineas Gage ...
... information neuron to neuron, chemically and electrically through neurotransmitters and therefore can localize the information. The endocrine system transmits chemicals from glands to the entire body through the blood stream. 6. Who was Phineas Gage? Why was he important to psychology? Phineas Gage ...
Ability - Assignment Point
... A type of conditioning in which an individual responds to some stimulus that would not ordinarily produce such a response. Key Concepts ...
... A type of conditioning in which an individual responds to some stimulus that would not ordinarily produce such a response. Key Concepts ...
Operant Conditioning
... Which one do you think is least effective? Which one do you think is most effective? Which one do you think is most addictive? ...
... Which one do you think is least effective? Which one do you think is most effective? Which one do you think is most addictive? ...
classical conditioning
... Acquisition – “Initial Learning” The initial stage where the associating of a neutral stimulus with an UCS occurs so that a CR is elicited Extinction – The diminishing of CR, when a UCS does not follow a CS Spontaneous Recovery – The reappearance (after a period of time) of an extinguished CR. Gener ...
... Acquisition – “Initial Learning” The initial stage where the associating of a neutral stimulus with an UCS occurs so that a CR is elicited Extinction – The diminishing of CR, when a UCS does not follow a CS Spontaneous Recovery – The reappearance (after a period of time) of an extinguished CR. Gener ...
Behaviorism Behaviorism was a movement in psychology and
... solution increased gradually as a result of previous puzzle exposure. Such results, he maintained, support the hypothesis that learning is a result of habits formed through trial and error, and Thorndike formulated "laws of behavior," describing habit formation processes, based on these results. Mos ...
... solution increased gradually as a result of previous puzzle exposure. Such results, he maintained, support the hypothesis that learning is a result of habits formed through trial and error, and Thorndike formulated "laws of behavior," describing habit formation processes, based on these results. Mos ...
Conditioning: classical and operant
... for raising his hand in class, he will repeat that behavior. However, if a child is ignored or punished for raising her hand, she will be less likely to repeat that behavior. Second, exhibition of the behavioral response prior to conditioning is not required in each conditioning procedure. In classi ...
... for raising his hand in class, he will repeat that behavior. However, if a child is ignored or punished for raising her hand, she will be less likely to repeat that behavior. Second, exhibition of the behavioral response prior to conditioning is not required in each conditioning procedure. In classi ...
Learning PPT
... fixed number of behaviors occur • Variable-ratio – reinforcement after different numbers of behaviors ...
... fixed number of behaviors occur • Variable-ratio – reinforcement after different numbers of behaviors ...
Memory
... We may be inclined to engage in small immediate reinforcers (watching TV) rather than large delayed reinforcers (getting an A in a course) which require ...
... We may be inclined to engage in small immediate reinforcers (watching TV) rather than large delayed reinforcers (getting an A in a course) which require ...
1 4.0 learning - eduNEPAL.info
... invariably produce such a response. Classical conditioning grew out of experience to teach dogs to salivate in response to ringing of the bell, conducted by Russian psychologist, Wan Pavlov. A simple surgical procedure allowed Pavlov to measure accurately the amount of saliva secreted by a dog. When ...
... invariably produce such a response. Classical conditioning grew out of experience to teach dogs to salivate in response to ringing of the bell, conducted by Russian psychologist, Wan Pavlov. A simple surgical procedure allowed Pavlov to measure accurately the amount of saliva secreted by a dog. When ...
Ch.08 - Learning
... • Rewarding someone for doing something they already enjoy may cause them to lose their intrinsic interest in the task. Rewarding an already justifiable activity becomes “overjustified” because of the additional reward. ...
... • Rewarding someone for doing something they already enjoy may cause them to lose their intrinsic interest in the task. Rewarding an already justifiable activity becomes “overjustified” because of the additional reward. ...